Abstract
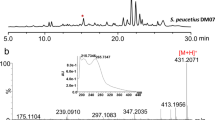
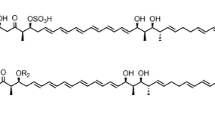
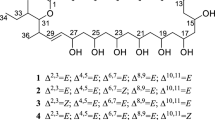
Streptomyces peucetius ATCC 27952 is a well-known producer of important anticancer compounds, daunorubicin and doxorubicin. In this study, we successfully identified a new macrolide, 25-hydroxy peucemycin, that exhibited an antibacterial effect on some pathogens. Based on the structure of a newly identified compound and through the inactivation of a polyketide synthase gene, we successfully identified its biosynthetic gene cluster which was considered to be the cryptic biosynthetic gene cluster. The biosynthetic gene cluster spans 51 kb with 16 open reading frames. Five type I polyketide synthase (PKS) genes encode eight modules that synthesize the polyketide chain of peucemycin before undergoing post-PKS tailoring steps. In addition to the regular starter and extender units, some modules have specificity towards ethylmalonyl-CoA and unusual butylmalonyl-CoA. A credible explanation for the specificity of the unusual extender unit has been searched for. Moreover, the enzyme responsible for the final tailoring pathway was also identified. Based on all findings, a plausible biosynthetic pathway is here proposed.
Key points
• Identification of a new macrolide, 25-hydroxy peucemycin.
• An FMN-dependent monooxygenase is responsible for the hydroxylation of peucemycin.
• The module encoded by peuC is unique to accept the butylmalonyl-CoA as an unusual extender unit.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Akagawa H, Okanishi M, Umezawa H (1975) A plasmid involved in chloramphenicol production in Streptomyces venezuelae: evidence from genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol 90:336–346. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-90-2-336
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Arcamone F, Cassinelli G (1998) Biosynthetic anthracyclines. Curr Med Chem 5:391–419
Arcamone F, Cassinelli G, Faktini G, Grein A, Orezzi P, Pol C, Spalla C (1969) Adriamycin, 14-hydroxydaunomycin, a new antitumor antibiotic from S. peucetius var. caesius. Biotechnol Bioeng 11:1101–1110. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260110607
Bachmann BO, Ravel J (2009) Chapter 8 Methods for in silico prediction of microbial polyketide and nonribosomal peptide biosynthetic pathways from DNA sequence data. Methods Enzymol. 458:181–217.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(09)04808-3
Bayly CL, Yadav VG (2017) Towards precision engineering of canonical polyketide synthase domains: recent advances and future prospects. Molecules 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020235
Benson DA, Cavanaugh M, Clark K, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Sayers EW (2013) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 41:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1195
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeño-Tárraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O’Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/417141a
Berkhan G, Hahn F (2014) A dehydratase domain in ambruticin biosynthesis displays additional activity as a pyran-forming cyclase. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 53:14240–14244. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201407979
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Nagaraja Rao R, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(92)90627-2
Blin K, Shaw S, Kloosterman AM, Charlop-Powers Z, Van Wezel GP, Medema MH, Weber T (2021) AntiSMASH 6.0: improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res 49:W29–W35. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab335
Chaudhary AK, Dhakal D, Sohng JK (2013) An insight into the “-Omics” based engineering of streptomycetes for secondary metabolite overproduction. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/968518
Choi SS, Hur YA, Sherman DH, Kim ES (2007) Isolation of the biosynthetic gene cluster for tautomycetin, a linear polyketide T cell-specific immunomodulator from Streptomyces sp. CK4412. Microbiology 153:1095–1102. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.2006/003194-0
Craney A, Ahmed S, Nodwell J (2013) Towards a new science of secondary metabolism. J Antibiot (tokyo) 66:387–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2013.25
Dhakal D, Lim SK, Kim DH, Kim BG, Yamaguchi T, Sohng JK (2018) Complete genome sequence of Streptomyces peucetius ATCC 27952, the producer of anticancer anthracyclines and diverse secondary metabolites. J Biotechnol 267:50–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.12.024
Distler J, Ebert A, Mansouri K, Pissowotzki K, Stockmann M, Piepersberg W (1987) Gene cluster for streptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces griseus: nucleotide sequence of three genes and analysis of transcriptional activity. Nucleic Acids Res 15:8041–8056. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/15.19.8041
Du D, Katsuyama Y, Onaka H, Fujie M, Satoh N, Shin-ya K, Ohnishi Y (2016) Production of a novel amide-containing polyene by activating a cryptic biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces sp. MSC090213JE08. ChemBioChem 1464–1471. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201600167
Eustáquio AS, McGlinchey RP, Liu Y, Hazzard C, Beer LL, Florova G, Alhamadsheh MM, Lechner A, Kale AJ, Kobayashi Y, Reynolds KA, Moore BS (2009) Biosynthesis of the salinosporamide A polyketide synthase substrate chloroethylmalonyl-coenzyme A from S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(30):12295–12300. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0901237106
Fjærvik E, Zotchev SB (2005) Biosynthesis of the polyene macrolide antibiotic nystatin in Streptomyces noursei. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:436–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1802-4
Frandsen RJN, Schütt C, Lund BW, Staerk D, Nielsen J, Olsson S, Giese H (2011) Two novel classes of enzymes are required for the biosynthesis of aurofusarin in Fusarium graminearum. J Biol Chem 286:10419–10428. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.179853
Ghimire GP, Oh TJ, Liou K, Sohng JK (2008) Identification of a cryptic type III polyketide synthase (1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene synthase) from Streptomyces peucetius ATCC 27952. Mol Cells 26:362–367
Ghimire GP, Koirala N, Sohng JK (2015) Activation of cryptic hop genes from Streptomyces peucetius ATCC 27952 involved in hopanoid biosynthesis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:658–661. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1408.08058
Greule A, Intra B, Flemming S, Rommel MGE, Panbangred W, Bechthold A (2016) The draft genome sequence of Actinokineospora bangkokensis 44EHWT reveals the biosynthetic pathway of the antifungal thailandin compounds with unusual butylmalonyl-CoA extender units. Molecules 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111607
Hickey RJ, Tresner HD (1952) A cobalt-containing medium for sporulation of Streptomyces species. J Bacteriol 64:891–892. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.64.6.891-892.1952
Hou XF, Song YJ, Zhang M, Lan W, Meng S, Wang C, Pan HX, Cao C, Tang GL (2018) Enzymology of anthraquinone-γ-pyrone ring formation in complex aromatic polyketide biosynthesis. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 57:13475–13479. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201806729
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M, Omura S (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol. 21:526–531. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt820
Jiang C, Wang H, Kang Q, Liu J, Bai L (2012) Cloning and characterization of the polyether salinomycin biosynthesis gene cluster of Streptomyces albus XM211. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:994–1003. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06701-11
Kautsar SA, Blin K, Shaw S, Navarro-Muñoz JC, Terlouw BR, Van Der Hooft JJJ, Van Santen JA, Tracanna V, Suarez Duran HG, Pascal Andreu V, Selem-Mojica N, Alanjary M, Robinson SL, Lund G, Epstein SC, Sisto AC, Charkoudian LK, Collemare J, Linington RG, Weber T, Medema MH (2020) MIBiG 2.0: a repository for biosynthetic gene clusters of known function. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D454–D458. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz882
Keatinge-Clay A (2008) Crystal structure of the erythromycin polyketide synthase dehydratase. J Mol Biol 384:941–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.084
Keatinge-Clay AT (2012) The structures of type I polyketide synthases. Nat Prod Rep 29:1050–1073. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2np20019h
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kim BS, Cropp TA, Beck BJ, Sherman DH, Reynolds KA (2002) Biochemical evidence for an editing role of thioesterase II in the biosynthesis of the polyketide pikromycin. J Biol Chem 277:48028–48034. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M207770200
Kino T, Hatanaka H, Hashimito M, Nishiyama M, Goto T, Okuhara M, Kohasaka M, Aoki H, Imanaka H (1987) FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces. I. Fermentation, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological characteristics. J Antibiot (tokyo) 40:1249–1255. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.40.1249
Kodani S, Komaki H, Suzuki M, Kobayakawa F, Hemmi H (2015) Structure determination of a siderophore peucechelin from Streptomyces peucetius. BioMetals 28:791–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-015-9866-4
Kotowska M, Pawlik K (2014) Roles of type II thioesterases and their application for secondary metabolite yield improvement. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:7735–7746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5952-8
Kotowska M, Pawlik K, Smulczyk-Krawczyszyn A, Bartosz-Bechowski H, Kuczek K (2009) Type II thioesterase ScoT, associated with Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) modular polyketide synthase Cpk, hydrolyzes acyl residues and has a preference for propionate. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:887–896. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01371-08
Leeper FJ, Staunton J (1984) The biosynthesis of rubrofusarin, a polyketide naphthopyrone from Fusarium culmorum: 13C N.M.R. assignments and incorporation of 13C- and 2H-labelled acetates. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1:2919–2925. https://doi.org/10.1039/P19840002919
Li C, Roege KE, Kelly WL (2009) Analysis of the indanomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces antibioticus NRRL 8167. ChemBioChem. 10:1064–1072. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200800822
Lomovskaya N, Otten SL, Doi-Katayama Y, Fonstein L, Liu XC, Takatsu T, Inventi-Solari A, Filippini S, Torti F, Colombo AL, Hutchinson CR (1999) Doxorubicin overproduction in Streptomyces peucetius: cloning and characterization of the dnrU ketoreductase and dnrV genes and the doxA cytochrome P-450 hydroxylase gene. J Bacteriol 181:305–318. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.181.1.305-318.1999
Long PF, Wilkinson CJ, Bisang CP, Cortés J, Dunster N, Oliynyk M, McCormick E, McArthur H, Mendez C, Salas JA, Staunton J, Leadlay PF (2002) Engineering specificity of starter unit selection by the erythromycin-producing polyketide synthase. Mol Microbiol 43:1215–1225. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02815.x
Luhavaya H, Dias MVB, Williams SR, Hong H, De Oliveira LG, Leadlay PF (2015) Enzymology of pyran ring A formation in salinomycin biosynthesis. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 54:13622–13625. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201507090
Marchler-Bauer A, Derbyshire MK, Gonzales NR, Lu S, Chitsaz F, Geer LY, Geer RC, He J, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Lanczycki CJ, Lu F, Marchler GH, Song JS, Thanki N, Wang Z, Yamashita RA, Zhang D, Zheng C, Bryant SH (2015) CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D222–D226. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1221
Malla S, Niraula NP, Liou K, Sohng JK (2009) Enhancement of doxorubicin production by expression of structural sugar biosynthesis and glycosyltransferase genes in Streptomyces peucetius. J Biosci Bioeng 108:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.03.002
Mo S, Kim DH, Lee JH, Park JW, Basnet DB, Ban YH, Yoo YJ, Chen SW, Park SR, Choi EA, Kim E, Jin YY, Lee SK, Park JY, Liu Y, Lee MO, Lee KS, Kim SJ, Kim D, Park BC, Lee SG, Kwon HJ, Suh JW, Moore BS, Lim SK, Yoon YJ (2011) Biosynthesis of the allylmalonyl-CoA extender unit for the FK506 polyketide synthase proceeds through a dedicated polyketide synthase and facilitates the mutasynthesis of analogues. J Am Chem Soc 133:976–985. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja108399b
Musiol-Kroll EM, Wohlleben W (2018) Acyltransferases as tools for polyketide synthase engineering. Antibiotics 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030062
Narva KE, Feitelson JS (1990) Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of the redD locus of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 172:326–333. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.1.326-333.1990
Nguyen CT, Dhakal D, Pham VTT, Nguyen HT, Sohng JK (2020) Recent advances in strategies for activation and discovery/characterization of cryptic biosynthetic gene clusters in Streptomyces. Microorganisms 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040616
Nicholas KB (1997) GeneDoc: analysis and visualization of genetic variation. Embnew News 4:14
Niraula NP, Kim SH, Sohng JK, Kim ES (2010) Biotechnological doxorubicin production: pathway and regulation engineering of strains for enhanced production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2675-3
Ohnishi Y, Ishikawa J, Hara H, Suzuki H, Ikenoya M, Ikeda H, Yamashita A, Hattori M, Horinouchi S (2008) Genome sequence of the streptomycin-producing microorganism Streptomyces griseus IFO 13350. J Bacteriol 190:4050–4060. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00204-08
Olano C, Méndez C, Salas JA (2009) Antitumor compounds from actinomycetes: from gene clusters to new derivatives by combinatorial biosynthesis. Nat Prod Rep 26:628–660. https://doi.org/10.1039/b822528a
Omura S, Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Takahashi C, Shinose M, Takahashi Y, Horikawa H, Nakazawa H, Osonoe T, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M (2001) Genome sequence of an industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis: deducing the ability of producing secondary metabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12215–12220. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.211433198
Park HM, Kim BG, Chang D, Malla S, Joo HS, Kim EJ, Park SJ, Sohng JK, Kim PI (2013) Genome-based cryptic gene discovery and functional identification of NRPS siderophore peptide in Streptomyces peucetius. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1213–1222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4268-9
Pham VTT, Nguyen HT, Nguyen CT, Choi YS, Dhakal D, Kim TS, Jung HJ, Yamaguchi T, Sohng JK (2021) Identification and enhancing production of a novel macrolide compound in engineered Streptomyces peucetius. RSC Adv 11:3168–3173. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra06099b
Pöplau P, Frank S, Morinaka BI, Piel J (2013) An enzymatic domain for the formation of cyclic ethers in complex polyketides. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 52:13215–13218. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201307406
Poudel PB, Dhakal D, Magar RT, Sohng JK (2022) Microbial biosynthesis of chrysazin derivatives in recombinant Escherichia coli and their biological activities. Molecules 27:5554. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175554
Rachid S, Huo L, Herrmann J, Stadler M, Köpcke B, Bitzer J, Müller R (2011) Mining the cinnabaramide biosynthetic pathway to generate novel proteasome inhibitors. ChemBioChem 12:922–931. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201100024
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Schulze CS, Donia MS, Siqueira-Neto JL, Ray D, Raskatov JA, Green RE, McKerrow JH, Fischbach MA, Linington RG (2015) Genome-directed lead discovery: biosynthesis, structure elucidation, and biological evaluation of two families of polyene macrolactams against Trypanosoma brucei. ACS Chem Biol 10:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00308
Shao L, Zi J, Zeng J, Zhan J (2012) Identification of the herboxidiene biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces chromofuscus ATCC 49982. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:2034–2038. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06904-11
Sheldon PJ, Busarow SB, Hutchinson CR (2002) Mapping the DNA-binding domain and target sequences of the Streptomyces peucetius daunorubicin biosynthesis regulatory protein, DnrI. Mol Microbiol 44:449–460. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02886.x
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Söding J, Thompson JD, Higgins DG (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2011.75
Singh B, Oh TJ, Sohng JK (2009) Exploration of geosmin synthase from Streptomyces peucetius ATCC 27952 by deletion of doxorubicin biosynthetic gene cluster. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1257–1265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-009-0605-0
Song L, Laureti L, Corre C, Leblond P, Aigle B, Challis GL (2014) Cytochrome P450-mediated hydroxylation is required for polyketide macrolactonization in stambomycin biosynthesis. J Antibiot (tokyo) 67:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2013.119
Sthapit B, Oh TJ, Lamichhane R, Liou K, Lee HC, Kim CG, Sohng JK (2004) Neocarzinostatin naphthoate synthase: an unique iterative type I PKS from neocarzinostatin producer Streptomyces carzinostaticus. FEBS Lett 566:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2004.04.033
Takahashi S, Toyoda A, Sekiyama Y, Takagi H, Nogawa T, Uramoto M, Suzuki R, Koshino H, Kumano T, Panthee S, Dairi T, Ishikawa J, Ikeda H, Sakaki Y, Osada H (2011) Reveromycin A biosynthesis uses RevG and RevJ for stereospecific spiroacetal formation. Nat Chem Biol 7:461–468. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.583
Takaishi M, Kudo F, Eguchi T (2013) Identification of the incednine biosynthetic gene cluster: characterization of novel β -glutamate-β -decarboxylase idnl3. J Antibiot (tokyo) 66:691–699. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2013.76
Thuan NH, Dhakal D, Pokhrel AR, Chu LL, Van Pham TT, Shrestha A, Sohng JK (2018) Genome-guided exploration of metabolic features of Streptomyces peucetius ATCC 27952: past current, and prospect. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:4355–4370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8957-x
Weinstein MP, Patel JB, Campeau S, Eliopoulos GM, Galas MF, Humphries RM, Jenkins SG, Lewis II JS, Limbago B, Mathers AJ, Mazzulli T, Patel R, Richter SS, Satlin M, Swenson JM, Zimmer BL (2018) Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests, 28th edn. Clinical and laboratory standards institute, Wayne, PA
Xue Y, Zhao L, Liu HW, Sherman DH (1998) A gene cluster for macrolide antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces venezuelae: architecture of metabolic diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12111–12116. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.21.12111
Yadav G, Gokhale RS, Mohanty D (2003) Computational approach for prediction of domain organization and substrate specificity of modular polyketide synthases. J Mol Biol 328:335–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00232-8
Yao T, Liu Z, Li T, Zhang H, Liu J, Li H, Che Q, Zhu T, Li D, Li W (2018) Characterization of the biosynthetic gene cluster of the polyene macrolide antibiotic reedsmycins from a marine-derived Streptomyces strain. Microb Cell Fact 17:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0943-6
Yasutake Y, Imoto N, Fujii Y, Fujii T, Arisawa A, Tamura T (2007) Crystal structure of cytochrome P450 MoxA from Nonomuraea recticatena (CYP105). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 361:876–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.07.062
Zerbe K, Pylypenko O, Vitali F, Zhang W, Rouset S, Heck M, Vrijbloed JW, Bischoff D, Bister B, Süssmuth RD, Pelzer S, Wohlleben W, Robinson JA, Schlichting I (2002) Crystal structure of OxyB, a cytochrome P450 implicated in an oxidative phenol coupling reaction during vancomycin biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 277:47476–47485. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M206342200
Zhang B, Wang KB, Wang W, Bi SF, Mei YN, Deng XZ, Jiao RH, Tan RX, Ge HM (2018) Discovery, biosynthesis, and heterologous production of streptoseomycin, an anti-microaerophilic bacteria macrodilactone. Org Lett 20:2967–2971. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01006
Zhang B, Wang KB, Wang W, Wang X, Liu F, Zhu J, Shi J, Li LY, Han H, Xu K, Qiao HY, Zhang X, Jiao RH, Houk KN, Liang Y, Tan RX, Ge HM (2019) Enzyme-catalysed [6+4] cycloadditions in the biosynthesis of natural products. Nature 568:122–126. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1021-x
Zhou Y, Meng Q, You D, Li J, Chen S, Ding D, Zhou X, Zhou H, Bai L, Deng Z (2008) Selective removal of aberrant extender units by a type II thioesterase for efficient FR-008/candicidin biosynthesis in Streptomyces sp. strain FR-008. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7235–7242. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01012-08
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (NRF-2021R1A2C2004775).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RTM performed the research and wrote the manuscript. RTM and VTTP conceived and designed the research. PBP helped in performing the antibacterial assay. HTN helped in analyzing the data. AFB helped in preparing some reagents and media. JKS supervised the research, helped in writing the manuscript, and edited the manuscript to final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Magar, R.T., Pham, V.T.T., Poudel, P.B. et al. Biosynthetic pathway of peucemycin and identification of its derivative from Streptomyces peucetius. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 1217–1231 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12385-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12385-8