Abstract
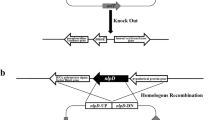
E. coli JM109∆envC∆nlpD deleted with genes envC and nlpD responsible for degrading peptidoglycan (PG) led to long filamentous cell shapes. When cell fission ring location genes minC and minD of Escherichia coli were deleted, E. coli JM109∆minCD changed the cell growth pattern from binary division to multiple fissions. Bacterial morphology can be further engineered by overexpressing sulA gene resulting in inhibition on FtsZ, thus generating very long cellular filaments. By overexpressing sulA in E. coli JM109∆envC∆nlpD and E. coli JM109∆minCD harboring poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) synthesis operon phbCAB encoded in plasmid pBHR68, respectively, both engineered cells became long filaments and accumulated more PHB compared with the wild-type. Under same shake flask growth conditions, E. coli JM109∆minCD (pBHR68) overexpressing sulA grown in multiple fission pattern accumulated approximately 70 % PHB in 9 g/L cell dry mass (CDM), which was significantly higher than E. coli JM109∆envC∆nlpD and the wild type, that produced 7.6 g/L and 8 g/L CDM containing 64 % and 51 % PHB, respectively. Results demonstrated that a combination of the new division pattern with elongated shape of E. coli improved PHB production. This provided a new vision on the enhanced production of inclusion bodies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson AJ, Dawes EA (1990) Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol Rev 54:450–472
Anderson DE, Gueiros-Filho FJ, Erickson HP (2004) Assembly dynamics of FtsZ rings in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli and effects of FtsZ-regulating proteins. J Bacteriol 186:5775–5781
Andreessen B, Taylor N, Steinbűchel A (2014) Poly(3-hydroxypropionate): a promising alternative to fossil fuel-based materials. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:6574–6582
Bernhardt TG, de Boer PA (2004) Screening for synthetic lethal mutants in Escherichia coli and identification of EnvC (YibP) as a periplasmic septal ring factor with murein hydrolase activity. Mol Microbiol 52:1255–1269
Bernhardt TG, de Boer PA (2005) SlmA, a nucleoid-associated, FtsZ binding protein required for blocking septal ring assembly over chromosomes in E. coli. Mol Cell 18:555–564
Bi E, Lutkenhaus J (1991) Ftsz ring structure associated with division in Escherichia-Coli. Nature 354:161–164
Bi E, Lutkenhaus J (1993) Cell division inhibitors SulA and MinCD prevent formation of the FtsZ ring. J Bacteriol 175:1118–1125
Brandl H, Gross RA, Lenz RW, Fuller RC (1988) Pseudomonas oleovorans as a source of poly(beta-Hydroxyalkanoates) for potential applications as biodegradable polyesters. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1977–1982
Chen GQ, Hajnal I, Wu H, Lv L, Ye J (2014) Engineering biosynthesis mechanisms for diversifying polyhydroxyalkanoates. Trends Biotechnol 33:565–574
Chen Y, Milam SL, Erickson HP (2012) SulA inhibits assembly of FtsZ by a simple sequestration mechanism. Biochemistry 51:3100–3109
Choi J, Lee SY (1999) Efficient and economical recovery of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) from recombinant Escherichia coli by simple digestion with chemicals. Biotechnol Bioeng 62:546–553
Chong L (2001) Molecular cloning—a laboratory manual, 3rd edition. Science 292:446–446
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:6640–6645
den Blaauwen T, de Pedro MA, Nguyen-Disteche M, Ayala JA (2008) Morphogenesis of rod-shaped sacculi. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:321–344
Eggers J, Steinbűchel A (2014) Impact of Ralstonia eutropha’s poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) depolymerases and phasins on PHB storage in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:7702–7709
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang RY, Venter JC, Hutchison CA, Smith HO (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6:343–U41
Horvat P, Koller M, Braunegg G (2015) Recent advances in elementary flux modes and yield space analysis as useful tools in metabolic network studies. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:1315–1328
Howard M (2004) A mechanism for polar protein localization in bacteria. J Mol Biol 335:655–663
Jiang XR, Wang H, Shen R, Chen GQ (2015) Engineering the bacterial shapes for enhanced inclusion bodies accumulation. Metab Eng 29:227–237
Kachrimanidou V, Kopsahelis N, Papanikolaou S, Kookos IK, De Bruyn M, Clark JH, Koutinas AA (2014) Sunflower-based biorefinery: poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) production from crude glycerol, sunflower meal and levulinic acid. Bioresour Technol 172:121–130
Kang Z, Wang Q, Zhang H, Qi Q (2008) Construction of a stress-induced system in Escherichia coli for efficient polyhydroxyalkanoates production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:203–208
Klockner A, Otten C, Derouaux A, Vollmer W, Buhl H, De Benedetti S, Munch D, Josten M, Molleken K, Sahl HG, Henrichfreise B (2014) AmiA is a penicillin target enzyme with dual activity in the intracellular pathogen chlamydia pneumoniae. Nat Commun 5:4201
Koutinas M, Menelaou M, Nicolaou EN (2014) Development of a hybrid fermentation-enzymatic bioprocess for the production of ethyl lactate from dairy waste. Bioresour Technol 165:343–349
Lock RL, Harry EJ (2008) Cell-division inhibitors: new insights for future antibiotics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:324–338
Matsumoto K, Taguchi S (2013) Enzyme and metabolic engineering for the production of novel biopolymers: crossover of biological and chemical processes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24:1054–1060
Meng DC, Shen R, Yao H, Chen JC, Wu Q, Chen GQ (2014) Engineering the diversity of polyesters. Curr Opin Biotechnol 29:24–33
Nishii W, Takahashi K (2003) Determination of the cleavage sites in SulA, a cell division inhibitor, by the ATP-dependent HslVU protease from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett 553:351–354
Novak M (2015) Mathematical modelling as a tool for optimized PHA production. Chem Biochem Eng Q 29:183–220
Peters NT, Dinh T, Bernhardt TG (2011) A fail-safe mechanism in the septal ring assembly pathway generated by the sequential recruitment of cell separation amidases and their activators. J Bacteriol 193:4973–4983
Pichoff S, Lutkenhaus J (2001) Escherichia coli division inhibitor MinCD blocks septation by preventing Z-ring formation. J Bacteriol 183:6630–6635
Priyadarshini R, Popham DL, Young KD (2006) Daughter cell separation by penicillin-binding proteins and peptidoglycan amidases in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 188:5345–5355
Reyes-Lamothe R, Nicolas E, Sherratt DJ (2012) Chromosome replication and segregation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet 46:121–143
Rocaboy M, Herman R, Sauvage E, Remaut H, Moonens K, Terrak M, Charlier P, Kerff F (2013) The crystal structure of the cell division amidase AmiC reveals the fold of the AMIN domain, a new peptidoglycan binding domain. Mol Microbiol 90:267–277
Rodriguez-Carmona E, Cano-Garrido O, Seras-Franzoso J, Villaverde A, Garcia-Fruitos E (2010) Isolation of cell-free bacterial inclusion bodies. Microb Cell Factories 9:71
Rodriguez-Contreras A, Koller M, Braunegg G, Marques-Calvo MS (2016) Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] production under different salinity conditions by a novel Bacillus megaterium strain. New Biotechnol 33:73–77
Rowlett VW, Margolin W (2013) The bacterial Min system. Curr Biol 23:R553–R556
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Shishatskaya EI, Voinova ON, Goreva AV, Mogilnaya OA, Volova TG (2008) Biocompatibility of polyhydroxybutyrate microspheres: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:2493–2502
Sim SJ, Snell KD, Hogan SA, Stubbe J, Rha C, Sinskey AJ (1997) PHA synthase activity controls the molecular weight and polydispersity of polyhydroxybutyrate in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 15:63–67
Spiekermann P, Rehm BH, Kalscheuer R, Baumeister D, Steinbűchel A (1999) A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Arch Microbiol 171:73–80
Steinbüchel A, Valentin HE (1995) Diversity of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoic acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett 128:219–228
Tsakona S, Kopsahelis N, Chatzifragkou A, Papanikolaou S, Kookos IK, Koutinas AA (2014) Formulation of fermentation media from flour-rich waste streams for microbial lipid production by Lipomyces starkeyi. J Biotechnol 189:36–45
Uehara T, Dinh T, Bernhardt TG (2009) LytM-domain factors are required for daughter cell separation and rapid ampicillin-induced lysis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 191:5094–5107
Uehara T, Parzych KR, Dinh T, Bernhardt TG (2010) Daughter cell separation is controlled by cytokinetic ring-activated cell wall hydrolysis. EMBO J 29:1412–1422
Wang Y, Wu H, Jiang XR, Chen GQ (2014a) Engineering Escherichia coli for enhanced production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) in larger cellular space. Metab Eng 25:183–193
Wang Y, Yin J, Chen GQ (2014b) Polyhydroxyalkanoates, challenges and opportunities. Curr Opin Biotechnol 30:59–65
Wang Y, Zhao F, Fan X, Wang S, Song C (2016) Enhancement of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates biosynthesis from glucose by metabolic engineering in Pseudomonas mendocina. Biotechnol Lett 38:313–320
Wu H, Wang H, Chen J, Chen GQ (2014) Effects of cascaded vgb promoters on poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) synthesis by recombinant Escherichia coli grown micro-aerobically. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:10013–10021
Yakhnina AA, McManus HR, Bernhardt TG (2015) The cell wall amidase AmiB is essential for Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell division, drug resistance and viability. Mol Microbiol 97:957–973
Yang DC, Tan K, Joachimiak A, Bernhardt TG (2012) A conformational switch controls cell wall-remodelling enzymes required for bacterial cell division. Mol Microbiol 85:768–781
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Center of Biomedical Analysis, Tsinghua University for the SEM and TEM studies. Plasmid pBHR68 was kindly donated by Professor Alexander Steinbűchel of Műnster University in Germany. This research was financially supported by the State Basic Science Foundation 973 (Grant no. 2012CB725201) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31430003 and 31270146).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 326 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Chen, J. & Chen, GQ. Engineering the growth pattern and cell morphology for enhanced PHB production by Escherichia coli . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 9907–9916 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7715-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7715-1