Abstract
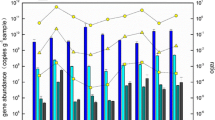
Under the increasing pressure of human activities, Hangzhou Bay has become one of the most seriously polluted waters along China’s coast. Considering the excessive inorganic nitrogen detected in the bay, in this study, the impact of an effluent from a coastal industrial park on ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms (AOMs) of the receiving area was interpreted for the first time by molecular technologies. Revealed by real-time PCR, the ratio of archaeal amoA/bacterial amoA ranged from 5.68 × 10−6 to 4.79 × 10−5 in the activated sludge from two wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) and 0.54–3.44 in the sediments from the effluent receiving coastal area. Analyzed by clone and pyrosequencing libraries, genus Nitrosomonas was the predominant ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), but no ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) was abundant enough for sequencing in the activated sludge from the WWTPs; genus Nitrosomonas and Nitrosopumilus were the dominant AOB and AOA, respectively, in the coastal sediments. The different abundance of AOA but similar structure of AOB between the WWTPs and nearby coastal area probably indicated an anthropogenic impact on the microbial ecology in Hangzhou Bay.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando Y, Nakagawa T, Takahashi R, Yoshihara K, Tokuyama T (2009) Seasonal changes in abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and their nitrification in sand of an eelgrass zone. Microbes Environ 24(1):21–27
Bai Y, Shi Q, Wen D, Li Z, Jefferson WA, Feng C, Tang X (2012a) Bacterial communities in the sediments of Dianchi Lake, a partitioned eutrophic waterbody in China. PLoS ONE 7(5):e37796
Bai Y, Sun Q, Wen D, Tang X (2012b) Abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in industrial and domestic wastewater treatment systems. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 80(2):323–330
Bates ST, Berg-Lyons D, Caporaso JG, Walters WA, Knight R, Fierer N (2011) Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME J 5(5):908–917
Bayer K, Schmitt S, Hentschel U (2008) Physiology, phylogeny and in situ evidence for bacterial and archaeal nitrifiers in the marine sponge Aplysina aerophoba. Environ Microbiol 10(11):2942–2955
Beman JM, Popp BN, Francis CA (2008) Molecular and biogeochemical evidence for ammonia oxidation by marine Crenarchaeota in the Gulf of California. ISME J 2(4):429–441
Beman JM, Sachdeva R, Fuhrman JA (2010) Population ecology of nitrifying archaea and bacteria in the Southern California Bight. Environ Microbiol 12(5):1282–1292
Bouskill NJ, Eveillard D, Chien D, Jayakumar A, Ward BB (2012) Environmental factors determining ammonia-oxidizing organism distribution and diversity in marine environments. Environ Microbiol 14(3):714–729
Brown MN, Briones A, Diana J, Raskin L (2013) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea and nitrite-oxidizing nitrospiras in the biofilter of a shrimp recirculating aquaculture system. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 83(1):17–25
Caffrey JM, Bano N, Kalanetra K, Hollibaugh JT (2007) Ammonia oxidation and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea from estuaries with differing histories of hypoxia. ISME J 1(7):660–662
Cao H, Auguet J-C, Gu J-D (2013) Global ecological pattern of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. PLoS ONE 8(2):e52853
Cao H, Hong Y, Li M, Gu J-D (2012) Community shift of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria along an anthropogenic pollution gradient from the pearl river delta to the South China Sea. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(1):247–259
Cao H, Li M, Hong Y, Gu J-D (2011) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in polluted mangrove sediment. Syst Appl Microbiol 34(7):513–523
Chen X-P, Zhu Y-G, Xia Y, Shen J-P, He J-Z (2008) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea: important players in paddy rhizosphere soil? Environ Microbiol 10(8):1978–1987
Christman GD, Cottrell MT, Popp BN, Gier E, Kirchman DL (2011) Abundance, diversity, and activity of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in the coastal Arctic Ocean in summer and winter. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(6):2026–2034
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(41):14683–14688
Gao J-F, Luo X, Wu G-X, Li T, Peng Y-Z (2013) Quantitative analyses of the composition and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in eight full-scale biological wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour Technol 138:285–296
Gomez-Silvan C, Molina-Munoz M, Poyatos JM, Ramos A, Hontoria E, Rodelas B, Gonzalez-Lopez J (2010) Structure of archaeal communities in membrane-bioreactor and submerged-biofilter wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour Technol 101(7):2096–2105
Hatzenpichler R, Lebedeva EV, Spieck E, Stoecker K, Richter A, Daims H, Wagner M (2008) A moderately thermophilic ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeote from a hot spring. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(6):2134–2139
He S, Gall DL, McMahon KD (2007) “Candidatus Accumulibacter” population structure in enhanced biological phosphorus removal Sludges as revealed by polyphosphate kinase genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(18):5865–5874
Hu A, Yao T, Jiao N, Liu Y, Yang Z, Liu X (2010) Community structures of ammonia-oxidising archaea and bacteria in high-altitude lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Freshw Biol 55(11):2375–2390
Jin T, Zhang T, Yan Q (2010) Characterization and quantification of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and bacteria (AOB) in a nitrogen-removing reactor using T-RFLP and qPCR. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87(3):1167–1176
Jin T, Zhang T, Ye L, Lee OO, Wong YH, Qian PY (2011) Diversity and quantity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90(3):1137–1145
Kayee P, Sonthiphand P, Rongsayamanont C, Limpiyakorn T (2011) Archaeal amoA Genes outnumber bacterial amoA genes in municipal wastewater treatment plants in Bangkok. Microb Ecol 62(4):776–788
Konneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437(7058):543–546
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9(4):299–306
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schuster SC, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442(7104):806–809
Li Z, Jin W, Liang Z, Yue Y, Lv J (2013) Abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in response to various habitats in Pearl River Delta of China, a subtropical maritime zone. J Environ Sci (China) 25(6):1195–1205
Limpiyakorn T, Sonthiphand P, Rongsayamanont C, Polprasert C (2011) Abundance of amoA genes of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in activated sludge of full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour Technol 102(4):3694–3701
Liu S, Shen L, Lou L, Tian G, Zheng P, Hu B (2013) Spatial distribution and factors shaping the niche segregation of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in the Qiantang River, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(13):4065–4071
Magalhaes CM, Machado A, Bordalo AA (2009) Temporal variability in the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria vs. archaea in sandy sediments of the Douro River estuary, Portugal. Aquat Microb Ecol 56(1):13–23
Martens-Habbena W, Berube PM, Urakawa H, de la Torre JR, Stahl DA (2009) Ammonia oxidation kinetics determine niche separation of nitrifying archaea and bacteria. Nature 461(7266):976–981
Mincer TJ, Church MJ, Taylor LT, Preston C, Kar DM, DeLong EF (2007) Quantitative distribution of presumptive archaeal and bacterial nitrifiers in Monterey Bay and the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Environ Microbiol 9(5):1162–1175
Molina V, Belmar L, Ulloa O (2010) High diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in permanent and seasonal oxygen-deficient waters of the eastern South Pacific. Environ Microbiol 12(9):2450–2465
Mosier AC, Francis CA (2008) Relative abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the San Francisco Bay estuary. Environ Microbiol 10(11):3002–3016
Mussmann M, Brito I, Pitcher A, Damste JSS, Hatzenpichler R, Richter A, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH, Mueller A, Daims H, Wagner M, Head IM (2011) Thaumarchaeotes abundant in refinery nitrifying sludges express amoA but are not obligate autotrophic ammonia oxidizers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(40):16771–16776
Newell SE, Babbin AR, Jayakumar A, Ward BB (2011) Ammonia oxidation rates and nitrification in the Arabian Sea. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 25(4):Gb4016. doi:10.1029/2010gb003940
Nold SC, Zhou JZ, Devol AH, Tiedje JM (2000) Pacific northwest marine sediments contain ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in the β subdivision of the Proteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(10):4532–4535
Ozdemir B, Mertoglu B, Yapsakli K, Aliyazicioglu C, Saatci A, Yenigun O (2011) Investigation of nitrogen converters in membrane bioreactor. J Environ Sci Health A 46(5):500–508
Park H-D, Wells GF, Bae H, Criddle CS, Francis CA (2006) Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in wastewater treatment plant bioreactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(8):5643–5647
Pester M, Rattei T, Flechl S, Grongroft A, Richter A, Overmann J, Reinhold-Hurek B, Loy A, Wagner M (2012) amoA-based consensus phylogeny of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and deep sequencing of amoA genes from soils of four different geographic regions. Environ Microbiol 14(2):525–539
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(12):4704–4712
Santoro AE, Casciotti KL, Francis CA (2010) Activity, abundance and diversity of nitrifying archaea and bacteria in the central California current. Environ Microbiol 12(7):1989–2006
Santoro AE, Francis CA, de Sieyes NR, Boehm AB (2008) Shifts in the relative abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea across physicochemical gradients in a subterranean estuary. Environ Microbiol 10(4):1068–1079
Schleper C, Nicol GW (2010) Ammonia-oxidising archaea—physiology, ecology and evolution. In: Poole RK (ed). Adv Microb Physiol 57:1–41
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(23):7537–7541
Sims A, Horton J, Gajaraj S, McIntosh S, Miles RJ, Mueller R, Reed R, Hu Z (2012) Temporal and spatial distributions of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria and their ratio as an indicator of oligotrophic conditions in natural wetlands. Water Res 46(13):4121–4129
Sonthiphand P, Limpiyakorn T (2011) Change in ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in enriched nitrifying activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 89(3):843–853
Wang X, Wen X, Xia Y, Hu M, Zhao F, Ding K (2012) Ammonia oxidizing bacteria community dynamics in a pilot-scale wastewater treatment plant. PLoS ONE 7(4) doi:e36272
Wells GF, Park H-D, Yeung C-H, Eggleston B, Francis CA, Criddle CS (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing communities in a highly aerated full-scale activated sludge bioreactor: betaproteobacterial dynamics and low relative abundance of Crenarchaea. Environ Microbiol 11(9):2310–2328
Wu Y-J, Whang L-M, Fukushima T, Chang S-H (2013) Responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaeal and betaproteobacterial populations to wastewater salinity in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant. J Biosci Bioeng 115(4):424–432
Wuchter C, Abbas B, Coolen MJL, Herfort L, van Bleijswijk J, Timmers P, Strous M, Teira E, Herndl GJ, Middelburg JJ, Schouten S, Damste JSS (2006) Archaeal nitrification in the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(33):12317–12322
Xia W, Zhang C, Zeng X, Feng Y, Weng J, Lin X, Zhu J, Xiong Z, Xu J, Cai Z, Jia Z (2011) Autotrophic growth of nitrifying community in an agricultural soil. ISME J 5(7):1226–1236
Yapsakli K (2010) Co-occurrence of nitrogen-converting organisms in full-scale treatment plants. J Environ Sci Health A 45(9):1060–1070
Zhang T, Jin T, Yan Q, Shao M, Wells G, Criddle C, Fang HHP (2009) Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in activated sludges of a laboratory scale reactor and two wastewater treatment plants. J Appl Microbiol 107(3):970–977
Zhang T, Ye L, Tong AHY, Shao M-F, Lok S (2011) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in six full-scale wastewater treatment bioreactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(4):1215–1225
Zhang Y, Chen L, Sun R, Dai T, Tian J, Liu R, Wen D (2014) Effect of wastewater disposal on the bacterial and archaeal community of sea sediment in an industrial area in China. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 88(2):320–332
Zheng Y, Hou L, Liu M, Lu M, Zhao H, Yin G, Zhou J (2013) Diversity, abundance, and activity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in Chongming eastern intertidal sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(18):8351–8363
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a General Project (No. 51178002) granted by the Natural Science Foundation of China. We are sincerely grateful to the Zhoushan Environmental Protection Bureau and the Zhoushan Marine Ecological Envionmental Monitoring Station, Zhejiang Province, for providing the background data of Hangzhou Bay. We also thank Zhongyuan Zheng, Jing Zhang, Zhichao Li, Chengfeng Zhang from Peking University, Cong Liu from Tsinghua University, and Yin Zhang from Shanghai Normal University for helping in the sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Sun, R. et al. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in wastewater treatment plant sludge and nearby coastal sediment in an industrial area in China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 4495–4507 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6352-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6352-9