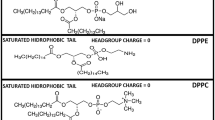
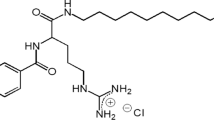
Abstract
Gentamicin possesses strong adverse actions like oto and nephrotoxicity. The latter is a result of strong gentamicin–acid phospholipid interactions, resulting in cell fusion, fission, etc., ions as calcium interact with gentamicin and effectively deter its toxicity. In this work, the interactions of gentamicin and Ca2+ with phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine (PS/PC) mixtures of different ratio are experimentally characterized. Special attention is paid to bridge thermodynamic and morphological properties of adsorption monolayers and thin liquid films (TLFs) composed of these lipid mixtures. Our results show that gentamicin decreases the stability of common black TLFs formed of pure PS coupled with suppression of lipid surface adsorption to the monolayers at the air–water interface; also, gentamicin reveals effects of lowering of lipid spreading on the interface and significant loss of material during monolayer cycling, increase of condensed phase, and organization of dense net-like domain monolayer texture. Gentamicin addition results in opposite effects for films formed of DPPC/PS (95:5) mixture. It increases the stability of Newton black TLFs formed by DPPC/PS correlated with faster and stronger surface adsorption and better surface spreading; also, gentamicin lowers the amount of condensed phase and organization of domains of smaller size. We also showed that Ca2+ itself decreases the stability of common black TLFs formed of PS accompanied with weaker surface adsorption, formation of higher amounts of condensed phase and organization of domains. In our experiments, Ca2+ softens, even deters, the effects of gentamicin on both PS and DPPC/PS films.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Bilayers containing a water core between the film monolayers.
Bilayers without water core between the film monolayers.
See error bars of the curves DPPC/PS/Ca2+ and DPPC/PS/Ca2+/gentamicin at 10−6 M of Fig. 5.
References
Adamson A, Gast A (1997) Physical chemistry of surfaces. Wiley, New York
Alexander AM, Gonda I, Harpur ES, Kayes JB (1979) Interaction of aminoglycoside antibiotics with phospholipid liposomes studies by microelectrophoresis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 32:504–510
Antoine DJ, Srivastava A, Pirmohamed M, Park BK (2009) Statins inhibit aminoglycoside accumulation and cytotoxicity to renal proximal tubule cells. Biochem Pharmacol. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.09.021, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.09.021
Aramaki Y, Tsuchiya S (1989) Interactions between aminoglycosides and phospholipids using liposomes: a possible mechanism of nephrotoxicity. Pharm Res 6:362–366
Baggio CL, Silveira AF, Hyppolito MA (2009) Experimental morphological and functional study of gentamicin cochleotoxicity using the regular dose given to neonates. Pro Fono 21:137–142
Bambeke FV, Tulkens P, Brasseur R, Mingeot-Leclercq M (1995) Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce aggregation but not fusion of negatively-charged liposomes. Eur J Pharmacol 289:321–333
Baronas ET, Lee JW, Alden C, Hsieh FY (2007) Biomarkers to monitor drug-induced phospholipidosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 218:72–78 doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.10.015 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2006.10.015
Bates DE, Beaumont SJ, Baylis BW (2002) Ototoxicity induced by gentamicin and furosemide. Ann Pharmacother 36:446–451
Behnoud F, Davoudpur K, Goodarzi MT (2009) Can aspirin protect or at least attenuate gentamicin ototoxicity in humans? Saudi Med J 30:1165–1169
Bennett WM, Elliott WC, Houghton DC, Gilbert DN, DeFehr J, McCarron DA (1982) Reduction of experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats by dietary calcium loading. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 22:508–512
Brasseur R, Laurent G, Ruysschaert JM, Tulkens P (1984) Interactions of aminoglycoside antibiotics with negatively charged lipid layers. Biochemical and conformational studies. Biochem Pharmacol 33:629–637
Bryan LE, Elzen HMVD (1977) Effects of membrane-energy mutations and cations on streptomycin and gentamicin accumulation by bacteria: a model for entry of streptomycin and gentamicin in susceptible and resistant bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 12:163–177
Carlier MB, Laurent G, Claes PJ, Vanderhaeghe HJ, Tulkens PM (1983) Inhibition of lysosomal phospholipases by aminoglycoside antibiotics: in vitro comparative studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 23:440–449
Christova Y, Enchev E, Lalchev Z (1999) Effects of pulmonary surfactant proteins sp-b and sp-c and calcium ions on the surface properties of hydrophobic fractions of lung surfactant. Eur Biophys J 28:59–66
Chung L, Kaloyanides G, McDaniel R, McLaughlin A, McLaughlin S (1985) Interaction of gentamicin and spermine with bilayer membranes containing negatively charged phospholipids. Biochemistry 24:442–452
de Aquino TJM, de Oliveira JAA, Rossato M (2008) Ototoxicity and otoprotection in the inner ear of guinea pigs using gentamicin and amikacin: ultrastructural and functional aspects. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 74:843–852
Döbereiner HG, Käs J, Noppl D, Sprenger I, Sackmann E (1993) Budding and fission of vesicles. Biophys J 65:1396–1403. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81203-7, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81203-7
Dominguez JH, Hale CC, Qulali M (1996) Studies of renal injury. i. gentamicin toxicity and expression of basolateral transporters. Am J Physiol 270:F245–F253
Dornbusch K (1980) Influence of medium composition on bacterial susceptibility testing to gentamicin and netilmicin. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl 23:46–53
East JE, Foweraker JE, Murgatroyd FD (2005) Gentamicin induced ototoxicity during treatment of enterococcal endocarditis: resolution with substitution by netilmicin. Heart 91:e32. doi:10.1136/hrt.2003.028308, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2003.028308
Eksperova D, Lalchev Z, Marinov B, Ognianov K (1984) [prenatal diagnosis of the idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome by using thin liquid films (foam films) at the solution/air phase interface.] Akush Ginekol (Sofiia) 23:457–462
Exerowa D, Krugliakov P (1998) Foam and foam films—theory, experiment, application. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Forge A, Zajic G, Davies S, Weiner N, Schacht J (1989) Gentamicin alters membrane structure as shown by freeze-fracture of liposomes. Hear Res 37:129–139
Fujii K, Nagai J, Sawada T, Yumoto R, Takano M (2009) Effect of pegylation of n-wasp181-200 on the inhibitory potency for renal aminoglycoside accumulation. Bioconjug Chem. doi:10.1021/bc900094g, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1021/bc900094g
Georgiev G, Lalchev Z (2004) Model study of interactions of high-molecular dextran sulfate with lipid monolayers and foam films. Eur Biophys J 33:742–748. doi:10.1007/s00249-004-0421-4, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00249-004-0421-4
Georgiev GD, Georgiev GA, Lalchev Z (2007) Influence of steroid hormone progesterone on the properties of phosphatidyl serine monolayers and thin liquid films. Biophys Chem 130:48–54. doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2007.07.002, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2007.07.002
Goodman FR (1978) Distribution of “4c-gentamicin in vascular smooth muscle. Pharmacology 16:17–25
Gurnani K, Khouri H, Couture M, Bergeron MG, Beauchamp D, Carrier D (1995) Molecular basis of the inhibition of gentamicin nephrotoxicity by daptomycin; an infrared spectroscopic investigation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1237:86–94
Hénon S, Meunier J (1993) Phase transitions in gibbs films: star textural defects in tilted mesophases. J Chem Phys 98:9148
Hirode M, Ono A, Miyagishima T, Nagao T, Ohno Y, Urushidani T (2008) Gene expression profiling in rat liver treated with compounds inducing phospholipidosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 229:290–299. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2008.01.036, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2008.01.036
Huy PTB, Deffrennes D (1988) Aminoglycoside binding sites in the inner ears of guinea pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 32:467–472
Huy PTB, Deffrennes D (1990) Influence of membrane surface potential and of net charge on aminoglycoside binding to the organ of corti of guinea pigs. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 52:121–126
Jutila A (2001) Lateral heterogenity in model membranes: inducement and effects. PhD thesis, University of Helsinki
Kahlmeter G, Dahlager JI (1984) Aminoglycoside toxicity—a review of clinical studies published between 1975 and 1982. J Antimicrob Chemother 13(Suppl A):9–22
Kim J, Mosior M, Chung LA, Wu H, McLaughli S (1991) Binding of peptides with basic residues to membranes containing acidic phospholipids. Biophys J 60:135–148
Kohlhepp SJ, Hou L, Gilbert DN (1994) Pig kidney (llc-pk1) cell membrane fluidity during exposure to gentamicin or tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:2169–2171
Kornguth ML, Bayer WH, Kunin CM (1980) Binding of gentamicin to subcellular fractions of rabbit kidney: inhibition by spermine and other polyamines. J Antimicrob Chemother 6:121–131
Kubo M, Gardner MF, Hostetler KY (1986) Binding of propranolol and gentamicin to small unilamellar phospholipid vesicles. Contribution of ionic and hydrophobic forces. Biochem Pharmacol 35:3761–3765
Lalchev Z (1984) PhD thesis Sofia University
Lalchev Z (1997) Surface properties of lipids and proteins at bio-interfaces. CRC, Boca Raton
Lalchev Z (2007) Colloid stability—the role of surface forces. In: Tadros TF (ed) Phospholipid foam films—types, properties and applications, vol 1. Wiley, New York, pp 383–408
Li J, Li QX, Xie XF, Ao Y, Tie CR, Song RJ (2009) Differential roles of dihydropyridine calcium antagonist nifedipine, nitrendipine and amlodipine on gentamicin-induced renal tubular toxicity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 620:97–104. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.08.021, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.08.021
Lipowsky R (1995) The morphology of lipid membranes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 5:531–540
Mingeot-Leclercq MP, Tulkens PM (1999) Aminoglycosides: nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:1003–1012
Mingeot-Leclercq MP, Laurent G, Tulkens PM (1988) Biochemical mechanism of aminoglycoside-induced inhibition of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by lysosomal phospholipases. Biochem Pharmacol 37:591–599
Mingeot-Leclercq MP, Schanck A, Ronveaux-Dupal MF, Deleers M, Brasseur R, Ruysschaert JM, Laurent G, Tulkens PM (1989) Ultrastructural, physico-chemical and conformational study of the interactions of gentamicin and bis(beta-diethylaminoethylether) hexestrol with negatively-charged phospholipid layers. Biochem Pharmacol 38:729–741
Myers DR, DeFehr J, Bennet WM, Porter GA, Olsen GD (1978) Gentamicin binding to serum and plasma proteins. Clin Pharmacol Ther 23:356–360
Naydenova S, Lalchev Z, Petrov AG, Exerowa D (1990) Pure and mixed lipid black foam films as models of membrane fusion. Eur Biophys J 17:343–347
Ozbek E, Ilbey Y, Simsek A, Cekmen M, Mete F, Somay A (2009) Rosiglitazone, peroxisome proliferator receptor-gamma agonist, ameliorates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int Urol Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s11255-009-9645-7, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11255-009-9645-7
Papahadjopoulos D, Vail WJ, Newton C, Nir S, Jacobson K, Poste G, Lazo R (1977) Studies on membrane fusion. iii. The role of calcium-induced phase changes. Biochim Biophys Acta 465:579–598
Portis A, Newton C, Pangborn W, Papahadjopoulos D (1979) Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: evidence for an intermembrane ca2+-phospholipid complex, synergism with mg2+, and inhibition by spectrin. Biochemistry 18:780–790
Reasor MJ, Kacew S (2001) Drug-induced phospholipidosis: are there functional consequences? Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 226:825–830
Reasor MJ, Hastings KL, Ulrich RG (2006) Drug-induced phospholipidosis: issues and future directions. Expert Opin Drug Saf 5:567–583. doi:10.1517/14740338.5.4.567, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1517/14740338.5.4.567
Rougier F, Claude D, Maurin M, Maire P (2004) Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord 4:153–162
Selimoglu E (2007) Aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity. Curr Pharm Des 13:119–126
Servais H, Ortiz A, Devuyst O, Denamur S, Tulkens PM, Mingeot-Leclercq MP (2008) Renal cell apoptosis induced by nephrotoxic drugs: cellular and molecular mechanisms and potential approaches to modulation. Apoptosis 13:11–32. doi:10.1007/s10495-007-0151-z, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0151-z
Soejima A, Ishizuka S, Miyake N, Fukuoka K, Suzuki M, Kamiya Y, Nagasawa T (2000) Simultaneous inhibition of renal phospholipase a(2) and glutathione synthesis by manoalide and dl-buthionine sulfoximine induces acute tubular dysfunction in rats. Exp Nephrol 8:84–90
Vitovic P, Alakoskela JM, Kinnunen PKJ (2008) Assessment of drug-lipid complex formation by a high-throughput langmuir-balance and correlation to phospholipidosis. J Med Chem 51:1842–1848. doi:10.1021/jm7013953, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm7013953
Vollhardt D, Melzer V (1997) Phase transition in adsorption layers at the air-water interface: bridging to Langmuir monolayers. J Phys Chem B 101:3370
Watanabe A, Nagai J, Adachi Y, Katsube T, Kitahara Y, Murakami T, Takano M (2004) Targeted prevention of renal accumulation and toxicity of gentamicin by aminoglycoside binding receptor antagonists. J Control Release 95:423–433. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2003.12.005, http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2003.12.005
Wilschut J, Papahadjopoulos D (1979) Ca2+-induced fusion of phospholipid vesicles monitored by mixing of aqueous content. Nature 281:690–692
Xia Z, Ying G, Hansson AL, Karlsson H, Xie Y, Bergstrand A, DePierre JW, Nässberger L (2000) Antidepressant-induced lipidosis with special reference to tricyclic compounds. Prog Neurobiol 60:501–512
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by NSFB—Bulgarian Ministry of Education and Science (grant N DO02-107/2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georgiev, G.D., Georgiev, G.A. & Lalchev, Z. Interaction of gentamicin with phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine mixtures in adsorption monolayers and thin liquid films: morphology and thermodynamic properties. Eur Biophys J 39, 1301–1312 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-010-0583-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-010-0583-1