Abstract
Whole-body MRI (W-B MRI) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) are two novel techniques that greatly facilitate the evaluation of many disorders of childhood. In the musculoskeletal system, these techniques primarily aid in the evaluation of the marrow, although there is increasing interest in the study of soft-tissue abnormalities with W-B MRI and of cartilage with DWI.
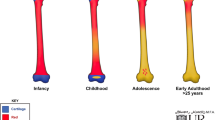
The normal pattern of marrow transformation affects both modalities throughout childhood. Haematopoietic marrow has a much higher signal intensity than fatty marrow on W-B MRI short tau inversion recovery (STIR) images (Darge et al. Eur J Radiol 68:289–298, 2008). Diffusion is greater in haematopoietic marrow than in fatty marrow and decreases in the skeleton with age (Jaramillo et al. Pediatr Radiol 34:S48, 2004). It is important therefore to remember that the entire skeleton is haematopoietic at birth and that there is a process of marrow transformation to fatty marrow. Marrow conversion proceeds from the fingers to the shoulders and from the toes to the hips. Within each bone, fatty marrow transformation begins in the epiphyses, and within the shaft of the long bones fatty marrow transformation begins at the diaphysis and proceeds towards the metaphyses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darge K, Jaramillo D, Siegel MJ (2008) Whole-body MRI in children: current status and future applications. Eur J Radiol 68:289–298
Jaramillo D, Menezes NM, Olear EA et al (2004) Line scan diffusion shows epiphyseal and metaphyseal abnormalities in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Pediatr Radiol 34:S48
Schmidt GP, Reiser MF, Baur-Melnyk A (2009) Whole-body MRI for the staging and follow-up of patients with metastasis. Eur J Radiol 70:393–400
Jaramillo D, Laor T (2007) Pediatric musculoskeletal MRI: basic principles to optimize success. Pediatr Radiol 38:379–391
Baur-Melnyk A (2009) Whole body imaging. Eur J Radiol 70:381
Kuhl CK, Traber F, Gieseke J et al (2008) Whole-body high-field-strength (3.0-T) MR imaging in clinical practice. Part II. Technical considerations and clinical applications. Radiology 247:16–35
Goo HW (2009) Whole-body MRI of neuroblastoma. Eur J Radiol Sep 23 [Epub ahead of print]
Fritz J, Tzaribatchev N, Claussen CD et al (2009) Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis: comparison of whole-body MR imaging with radiography and correlation with clinical and laboratory data. Radiology 252:842–851
Goo HW, Yang DH, Ra YS et al (2006) Whole-body MRI of Langerhans cell histiocytosis: comparison with radiography and bone scintigraphy. Pediatr Radiol 36:1019–1031
Cai W, Kassarjian A, Bredella MA et al (2009) Tumor burden in patients with neurofibromatosis types 1 and 2 and schwannomatosis: determination on whole-body MR images. Radiology 250:665–673
Connor A, Stebbings S, Anne Hung N et al (2007) STIR MRI to direct muscle biopsy in suspected idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. J Clin Rheumatol 13:341–345
Baur-Melnyk A (2009) Malignant versus benign vertebral collapse: are new imaging techniques useful? Cancer Imaging 9 Spec No A:S49–51
Daldrup-Link HE, Franzius C, Link TM et al (2001) Whole-body MR imaging for detection of bone metastases in children and young adults: comparison with skeletal scintigraphy and FDG PET. AJR 177:229–236
Yi CA, Shin KM, Lee KS et al (2008) Non-small cell lung cancer staging: efficacy comparison of integrated PET/CT versus 3.0-T whole-body MR imaging. Radiology 248:632–642
Krohmer S, Sorge I, Krausse A et al (2009) Whole-body MRI for primary evaluation of malignant disease in children. Eur J Radiol Mar 9 [Epub ahead of print]
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C et al (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:534–546
Bley TA, Wieben O, Uhl M (2009) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in musculoskeletal radiology: applications in trauma, tumors, and inflammation. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 17:263–275
Baur A, Dietrich O, Reiser M (2003) Diffusion-weighted imaging of bone marrow: current status. Eur Radiol 13:1699–1708
MacKenzie JD, Gonzalez L, Hernandez A et al (2007) Diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor imaging for pediatric musculoskeletal disorders. Pediatr Radiol 37:781–788
Mahmoud OM, Tominaga A, Amatya VJ et al (2009) Role of PROPELLER diffusion weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient in the diagnosis of sellar and parasellar lesions. Eur J Radiol Apr 24 [Epub ahead of print]
Skare S, Newbould RD, Clayton DB et al (2007) Clinical multishot DW-EPI through parallel imaging with considerations of susceptibility, motion, and noise. Magn Reson Med 57:881–890
Raya JG, Dietrich O, Reiser MF et al (2005) Techniques for diffusion-weighted imaging of bone marrow. Eur J Radiol 55:64–73
Azuma T, Nakai R, Takizawa O et al (2009) In vivo structural analysis of articular cartilage using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 27:1242–1248
Baur A, Stabler A, Bruning R et al (1998) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of bone marrow: differentiation of benign versus pathologic compression fractures. Radiology 207:349–356
Gudbjartsson H, Maier SE, Mulkern RV et al (1996) Line scan diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 36:509–519
Menezes NM, Connolly SA, Shapiro F et al (2007) Early ischemia in growing piglet skeleton: MR diffusion and perfusion imaging. Radiology 242:129–136
Momot KI, Pope JM, Wellard RM (2009) Anisotropy of spin relaxation of water protons in cartilage and tendon. NMR Biomed [Epub ahead of print]
Low RN (2009) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging for whole body metastatic disease and lymphadenopathy. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 17:245–261
Uhl M, Altehoefer C, Kontny U et al (2002) MRI-diffusion imaging of neuroblastomas: first results and correlation to histology. Eur Radiol 12:2335–2338
Hayashida Y, Yakushiji T, Awai K et al (2006) Monitoring therapeutic responses of primary bone tumors by diffusion-weighted image: initial results. Eur Radiol 16:2637–2643
Reichardt W, Juettner E, Uhl M et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging as predictor of therapy response in an animal model of Ewing sarcoma. Invest Radiol 44:298–303
Uhl M, Saueressig U, Koehler G et al (2006) Evaluation of tumour necrosis during chemotherapy with diffusion-weighted MR imaging: preliminary results in osteosarcomas. Pediatr Radiol 36:1306–1311
Uhl M, Saueressig U, van Buiren M et al (2006) Osteosarcoma: preliminary results of in vivo assessment of tumor necrosis after chemotherapy with diffusion- and perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 41:618–623
Jaramillo D, Connolly SA, Vajapeyam S et al (2003) Normal and ischemic epiphysis of the femur: diffusion MR imaging study in piglets. Radiology 227:825–832
Merlini L, Combescure C, De Rosa V et al (2010) Diffusion-weighted imaging findings in Perthes disease with dynamic gadolinium-enhanced subtracted (DGS) MR correlation: a preliminary study. Pediatr Radiol Jan 6 [Epub ahead of print]
Hong N, Du X, Nie Z et al (2005) Diffusion-weighted MR study of femoral head avascular necrosis in severe acute respiratory syndrome patients. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:661–664
Herneth AM, Friedrich K, Weidekamm C et al (2005) Diffusion weighted imaging of bone marrow pathologies. Eur J Radiol 55:74–83
Stabler A, Baur A, Kruger A et al (1998) Differential diagnosis of erosive osteochondrosis and bacterial spondylitis: magnetic resonance tomography (MRT). Rofo 168:421–428
Chan JH, Peh WC, Tsui EY et al (2002) Acute vertebral body compression fractures: discrimination between benign and malignant causes using apparent diffusion coefficients. Br J Radiol 75:207–214
Pui MH, Mitha A, Rae WI et al (2005) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of spinal infection and malignancy. J Neuroimaging 15:164–170
Byun WM, Jang HW, Kim SW et al (2007) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of sacral insufficiency fractures: comparison with metastases of the sacrum. Spine 32:E820–824
Dietrich O, Biffar A, Reiser MF et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging of bone marrow. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 13:134–144
Balliu E, Vilanova JC, Pelaez I et al (2009) Diagnostic value of apparent diffusion coefficients to differentiate benign from malignant vertebral bone marrow lesions. Eur J Radiol 69:560–566
Xu X, Ma L, Zhang JS et al (2008) Feasibility of whole body diffusion weighted imaging in detecting bone metastasis on 3.0 T MR scanner. Chin Med Sci J 23:151–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaramillo, D. Whole-body MR imaging, bone diffusion imaging: how and why?. Pediatr Radiol 40, 978–984 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-010-1608-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-010-1608-8