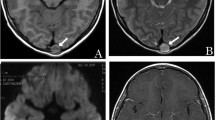
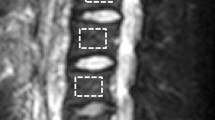
Abstract
Diffusion-weighted imaging allows for measurement of tissue microstructure and reflects the random motion of water protons. It provides a new method to study bone marrow and bone marrow alterations on the basis of altered water-proton mobility in various diseases. Different diffusion-weighted methods have proved to be capable of differentiating between benign edema and tumorous involvement of bone marrow. It is especially useful for the distinction of acute benign osteoporotic and malignant vertebral compression fractures. Diagnosis is based on the contrast to normal bone marrow. Hypo- or isointensity reflects acute benign collapse, whereas hyperintensity is indicative of the tumorous nature of a fracture. Apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) are significantly lower in metastatic disease than in bone marrow edema. Furthermore, bone marrow cellularity can be estimated by ADC measurements. Diffusion-weighted imaging might be helpful for monitoring response to therapy in metastatic disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161:401–407
Lee LJ, Kidwell CS, Alger J, Starkman S, Saver JL (2000) Impact on stroke subtype diagnosis of early diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography. Stroke 31:1081–1089
Chien D, Kwong KK, Gress DR, Buonanno FS, Buxton RB, Rosen BR (1992) MR diffusion imaging of cerebral infarction in humans. Am J Neuroradiol 13:1097–1102
Kim YJ, Chang KH, Song IC (1998) Brain abscess and necrotic or cystic brain tumor: discrimination with signal intensity on diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol 171:1487–1490
Tievsky AL, Ptak T, Farkas J (1999) Investigation of apparent diffusion coefficient and diffusion tensor anisotropy in acute and chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491–1499
Tsuruda JS, Chew WM, Moseley ME, Norman D (1990) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain: value of differentiating between extraaxial cysts and epidermoid tumors. Am J Neuroradiol 11:925–931
Namimoto T, Yamashita Y, Sumi S, Tang Y, Takahashi M (1997) Focal liver masses: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 204:739–744
Moteki T, Ishizaka H (1999) Evaluation of cystic ovarian lesions using apparent diffusion coefficient calculated from reordered turboFLASH MR images. Magn Reson Imaging 17:955–963
Ahvenjärvi L, Jauhiainen J, Oikarinen J, Tervonen O (2000) Exercise induced signal intensity and ADC changes in skeletal muscle. In: Book of abstracts. Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Colorado, p 756
Blanco R, Ahvenjärvi L, Jauhiainen J, Oikarinen J, Siniluoto T, Tervonen O (1999) Diffusion imaging in vivo in skeletal muscle tissue and correlation to the arteriosclerosis of the lower extremities. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med, p 1784
Knauss R, Schiller J, Fleischer J, Kärger J, Arnold K (1999) Self-diffusion of water in cartilage and cartilage components as studied by pulsed field gradient NMR. Magn Reson Med 41:285–292
Baur A, Huber A, Arbogast S, Dürr HR, Zysk SP, Wendtner C, Deimling M, Reiser M (2001) Diffusion-weighted imaging of tumor recurrencies and posttherapeutic soft-tissue changes in humans. Eur Radiol 11:828–833
Lang P, Wendland MF, Saeed M, Gindele A, Rosenau W, Mathur A, Gooding CA, Genant HK (1998) Osteogenic sarcoma: noninvasive in vivo assessment of tumor necrosis with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 206:227–235
Eustace S, Masi M di, Adams J, Ward R, Caruthers S, McAlindon T (2000) In vitro and in vivo spin echo diffusion imaging characteristics of synovial fluid: potential non-invasive differentiation of inflammatory and degenerative arthritis. Skeletal Radiol 29:320–323
Baur A, Stäbler A, Brüning R, Bartl R, Krödel A, Deimling M, Reiser M (1998) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of bone marrow: differentiation of benign versus pathologic vertebral compression fractures. Radiology 207:349–356
Baur A, Huber A, Ertl-Wagner B, Dürr HR, Zysk S, Arbogast S, Deimling M, Reiser M (2001) Diagnostic value of increased diffusion-weighting of a steady-state free precession sequence for the differentiation of acute benign osteoporotic versus pathologic vertebral compression fractures. Am J Neuroradiol 22:366–372
Baur A, Huber A, Dürr HR, Nikolaou K, Stäbler A, Deimling M, Reiser M (2002) Differentiation of benign osteoporotic and neoplastic vertebral compression fractures with a diffusion-weighted, steady-state free precession sequence. Fortschr Röntgenstr 174:70–75
Zhou XJ, Leeds NE, McKinnon GC, Kumar AJ (2002) Characterization of benign and metastatic vertebral compression fractures with quantitative diffusion MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 23:165–170
Chan JH, Peh WC, Tsui EY, Chau LF, Cheung KK, Chan KB, Yuen MK, Wong ET, Wong KP (2002) Acute vertbral body compression fractures: discrimination between benign and malignant causes using apparent diffusion coefficients. Br J Radiol 75:207–214
Herneth AM, Philipp MO, Naude J, Funovics M, Beichel RR, Bammer R, Imhof H (2002) Verterbral metastases: assessment with apparent diffusion coefficient. Radiology 225:889–894
Spüntrup E, Buecker A, Adam G, van Vaals J, Günther RW (2001) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging for differentiation of benign fracture edema and tumor infiltration of the vertebral body. Am J Roentgenol 176:351–358
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 42:288–292
Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, Barnett A, Chiro G di (1996) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201:637–648
Merboldt KD, Hänicke W, Frahm J (1991) Diffusion imaging using stimulated echoes. Magn Reson Med 19:233–239
Ordidge RJ, Helpern JA, Qing ZX, Knight RA, Nagesh V (1994) Correction of motional artifacts in diffusion-weighted MR images using navigator echoes. Magn Reson Imaging 12:455–460
Anderson AW, Gore JC (1994) Analysis and correction of motion artifacts in diffusion weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med 32:379–387
Gmitro AF, Alexander AL (1993) Use of a projection reconstruction method to decrease motion sensitivity in diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn Reson Med 29:835–838
Dietrich O, Herlihy A, Dannels WR, Fiebach J, Heiland S, Hajnal JV, Sartor K (2001) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the spine using radial k-space trajectories. MAGMA 12:23–31
Chun T, Ulug AM, van Zijl PC (1998) Single-shot diffusion-weighted trace imaging on a clinical scanner. Magn Reson Med 40:622–628
Norris DG, Börnert P, Reese T, Leibfritz D (1992) On the application of ultra-fast RARE experiments. Magn Reson Med 27:142–164
Le Bihan D (1988) Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging using steady-state free precession. Magn Reson Med 7:346–351
Merboldt K, Hänicke W, Gyngell ML, Frahm J, Bruhn H (1989) Rapid NMR imaging of molecular self-diffusion using a modified CE-FAST sequence. J Magn Reson 82:115–121
Buxton RB (1993) The diffusion sensitivity of fast steady-state free precession imaging. Magn Reson Med 29:235–243
Vande Berg BC, Malghem J, Lecouvet FE, Maldague B (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging of normal bone marrow. Eur Radiol 8:1327–1334
Vanel D, Dromain C, Tardivon A (2000) MRI of bone marrow disorders. Eur Radiol 10:224–229
Feydy A, Drape JL, Argaud C (2001) Diffusion-weighted MRI and ADC measurement of tumoral bone marrow. In: Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 9:2117
Ward R, Caruthers S, Yablon C, Blake M, Masi M di, Eustace S (2000) Analysis of diffusion changes in posttraumatic bone marrow using navigator-corrected diffusion gradients. Am J Roentgenol 174:731–734
Baur A, Staebler A, Arbogast S, Duerr HR, Bartl R, Reiser M (2002) Acute osteoporotic and neoplastic vertebral compression fractures: fluid sign at MR imaging. Radiology 225:730–735
Yuh WTC, Zachar CK, Barloon TJ, Sato Y, Sickels WJ, Hawes DR (1989) Vertebral compression fractures: distinction between benign and malignant causes with MR imaging. Radiology 172:215–218
Baker LL, Goodman SB, Perkash I, Lane B, Enzmann DR (1990) Benign versus pathologic compression fractures of vertebral bodies: assessment with conventional spin-echo, chemical shift, and STIR MR imaging. Radiology 174:495–502
Matoba M, Tonami H, Yokota H, Kuginuki Y, Yamamoto (1999) Role of diffusion-weighted MRI and P31-MRS in differentiating between malignant and benign vertebral compression fractures. Proc Int Soc Mag Reson Med:1038
Tasaly N, Ünlü E, Cokal N, Tatoolu H, Karakap HM, Cakyr B (2000) Can we differentiate benign versus malignant vertebral fractures with Diffusion-weighted MR imaging? Radiology (Suppl) 217:68
Nakagawa K, Sakuma H, Ichikawa Y, Kitagwa K, Kawada N, Kadoya I, Hirnao T, Matsumura K, Takeda K, Matsusaka JP, Tsu JP (2000) Vertebral compression fractures: differentiation between benign and malignant lesions with diffusion-weighted single-shot echo planar MR imaging. Book of abstracts. Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Colorado, p 2144
Castillo M, Arbelaez A, Smith K, Fisher LL (2000) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging offers no advantage over routine noncontrast MR imaging in the detection of vertebral metastases. Am J Neuroradiol 21:948–953
Buyn WM, Shin SO, Chang Y, Lee SJ, Finsterbusch J, Frahm J (2002) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of metastatic disease of the spine: assessment of response to therapy. Am J Neuroradiol 23:906–912
Buyn WM (2001) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of vertebral bone marrow. Differentiation of degenerative spines and spondylitis involving bone marrow adjacent to end plates. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 9:1626
Stäbler A, Baur A, Krüger A, Weiss M, Helmberger T, Reiser M (1998) Differential diagnosis of erosive osteochondrosis and bacterial spondylitis in MRI. Fortschr Röntgenstr 168:421–428
Nonomura Y, Yasumoto M, Yoshimura R, Haraguchi K, Ito S, Akashi T, Ohashi I (2001) Relationship between bone marrow cellularity and apparent diffusion coefficient. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:757–760
Yasumoto M, Nonomura Y, Yoshimura R, Haraguchi K, Ito S, Ohashi I, Shibuya H (2002) MR detection of iliac bone marrow involvement by malignant lymphoma with various MR sequences including diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging. Skeletal Radiol 31:263–269
Ballon D, Dyke J, Schwartz LH, Lis E, Schneider E, Lauto A, Jakubowski AA (2001) Bone marrow segmentation in leukemia using diffusion and T2-weighted echo planar magnetic resonance imaging. NMR Biomed 13:321–328
Le Bihan DJ (1998) Differentiation of benign versus pathologic compression fractures with diffusion-weighted MR imaging: a closer step toward the "holy grail of tissue characterization"? (editorial) Radiology 207:305–307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baur, A., Dietrich, O. & Reiser, M. Diffusion-weighted imaging of bone marrow: current status. Eur Radiol 13, 1699–1708 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1873-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1873-0