Abstract
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is one of the most lethal congenital heart defects, and remains clinically challenging. While surgical palliation allows most HLHS patients to survive their critical heart disease with a single-ventricle physiology, many will suffer heart failure, requiring heart transplantation as the only therapeutic course. Current paradigm suggests HLHS is largely of hemodynamic origin, but recent findings from analysis of the first mouse model of HLHS showed intrinsic cardiomyocyte proliferation and differentiation defects underlying the left ventricular (LV) hypoplasia. The findings of similar defects of lesser severity in the right ventricle suggest this could contribute to the heart failure risks in surgically palliated HLHS patients. Analysis of 8 independent HLHS mouse lines showed HLHS is genetically heterogeneous and multigenic in etiology. Detailed analysis of the Ohia mouse line accompanied by validation studies in CRISPR gene-targeted mice revealed a digenic etiology for HLHS. Mutation in Sap130, a component of the HDAC repressor complex, was demonstrated to drive the LV hypoplasia, while mutation in Pcdha9, a protocadherin cell adhesion molecule played a pivotal role in the valvular defects associated with HLHS. Based on these findings, we propose a new paradigm in which complex CHD such as HLHS may arise in a modular fashion, mediated by multiple mutations. The finding of intrinsic cardiomyocyte defects would suggest hemodynamic intervention may not rescue LV growth. The profound genetic heterogeneity and oligogenic etiology indicated for HLHS would suggest that the genetic landscape of HLHS may be complex and more accessible in clinical studies built on a familial study design.

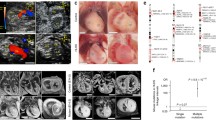
Adapted with permission from Liu et al. [34]

Adapted with permission from Liu et al. [34]

Adapted with permission from Liu et al. [34]

Adapted with permission from Liu et al. [34]

Adapted with permission from Liu et al. [34]

Adapted with permission from Liu et al. [34]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moodie D (2011) Adult congenital heart disease: past, present, and future. Tex Heart Inst J 38:705
Delmo Walter EM, Hubler M, Alexi-Meskishvili V, Miera O, Weng Y, Loforte A, Berger F, Hetzer R (2009) Staged surgical palliation in hypoplastic left heart syndrome and its variants. J Card Surg 24:383–391
Gordon BM, Rodriguez S, Lee M, Chang RK (2008) Decreasing number of deaths of infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J Pediatr 153:354–358
Feinstein JA, Benson DW, Dubin AM, Cohen MS, Maxey DM, Mahle WT, Pahl E, Villafane J, Bhatt AB, Peng LF, Johnson BA, Marsden AL, Daniels CJ, Rudd NA, Caldarone CA, Mussatto KA, Morales DL, Ivy DD, Gaynor JW, Tweddell JS, Deal BJ, Furck AK, Rosenthal GL, Ohye RG, Ghanayem NS, Cheatham JP, Tworetzky W, Martin GR (2012) Hypoplastic left heart syndrome: current considerations and expectations. J Am Coll Cardiol 59:S1-42
Kern JH, Hayes CJ, Michler RE, Gersony WM, Quaegebeur JM (1997) Survival and risk factor analysis for the Norwood procedure for hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Am J Cardiol 80:170–174
Donofrio MT, Moon-Grady AJ, Hornberger LK, Copel JA, Sklansky MS, Abuhamad A, Cuneo BF, Huhta JC, Jonas RA, Krishnan A, Lacey S, Lee W, Michelfelder EC Sr, Rempel GR, Silverman NH, Spray TL, Strasburger JF, Tworetzky W, Rychik J, American Heart Association Adults with Congenital Heart Disease Joint Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, Council on Clinical Cardiology CoCS, Anesthesia, Council on Cardiovascular, Stroke Nursing (2014) Diagnosis and treatment of fetal cardiac disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 129:2183–2242
Verheijen PM, Lisowski LA, Plantinga RF, Hitchcock JF, Bennink GB, Stoutenbeek P, Meijboom EJ (2003) Prenatal diagnosis of the fetus with hypoplastic left heart syndrome management and outcome. Herz 28:250–256
Rychik J (2014) Hypoplastic left heart syndrome: can we change the rules of the game? Circulation 130:629–631
Freud LR, McElhinney DB, Marshall AC, Marx GR, Friedman KG, Pedro J, Emani SM, Lafranchi T, Silva V, Wilkins-Haug LE (2014) Fetal aortic valvuloplasty for evolving hypoplastic left heart syndrome: postnatal outcomes of the first 100 patients. Circulation 130:638–645
Nawaytou HM, Peyvandi S, Brook MM, Silverman N, Moon-Grady AJ (2016) Right ventricular systolic-to-diastolic time index: hypoplastic left heart fetuses differ significantly from normal fetuses. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 29:143–149
Arnold RR, Loukanov T, Gorenflo M (2014) Hypoplastic left heart syndrome—unresolved issues. Front Pediatr 2:125
Oechslin EN, Harrison DA, Connelly MS, Webb GD, Siu SC (2000) Mode of death in adults with congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol 86:1111–1116
Khairy P, Fernandes SM, Mayer JE Jr, Triedman JK, Walsh EP, Lock JE, Landzberg MJ (2008) Long-term survival, modes of death, and predictors of mortality in patients with Fontan surgery. Circulation 117:85–92
Nora JJ, Nora AH (1988) Update on counseling the family with a first-degree relative with a congenital heart defect. Am J Med Genet 29:137–142
Maestri NE, Beaty TH, Liang KY, Boughman JA, Ferencz C (1988) Assessing familial aggregation of congenital cardiovascular malformations in case-control studies. Genet Epidemiol 5:343–354
Briard ML, Chauvet ML, Le Merrer M, Frezal J (1984) Epidemiological and genetic study of 3 congenital cardiopathies with neonatal disclosure. Archives francaises de pediatrie 41:313–321
Dennis NR, Warren J (1981) Risks to the offspring of patients with some common congenital heart defects. Am J Med Genet 18:8–16
Loffredo CA, Chokkalingam A, Sill AM, Boughman JA, Clark EB, Scheel J, Brenner JI (2004) Prevalence of congenital cardiovascular malformations among relatives of infants with hypoplastic left heart, coarctation of the aorta, and d-transposition of the great arteries. Am J Med Genet Part A 124A:225–230
Hinton RB Jr, Martin LJ, Tabangin ME, Mazwi ML, Cripe LH, Benson DW (2007) Hypoplastic left heart syndrome is heritable. J Am Coll Cardiol 50:1590–1595
Laursen HB (1980) Some epidemiological aspects of congenital heart disease in Denmark. Acta Paediatr Scand 69:619–624
McBride KL, Marengo L, Canfield M, Langlois P, Fixler D, Belmont JW (2005) Epidemiology of noncomplex left ventricular outflow tract obstruction malformations (aortic valve stenosis, coarctation of the aorta, hypoplastic left heart syndrome) in Texas, 1999–2001. Birth Defects Res A 73:555–561
Natowicz M, Kelley RI (1987) Association of Turner syndrome with hypoplastic left-heart syndrome. Am J Dis Child 141:218–220
Grossfeld PD, Mattina T, Lai Z, Favier R, Jones KL, Cotter F, Jones C (2004) The 11q terminal deletion disorder: a prospective study of 110 cases. Am J Med Genet Part A 129A:51–61
Feinstein JA, Benson DW, Dubin AM, Cohen MS, Maxey DM, Mahle WT, Pahl E, Villafañe J, Bhatt AB, Peng LF (2012) Hypoplastic left heart syndrome: current considerations and expectations. J Am Coll Cardiol 59:S1–S42
Elliott DA, Kirk EP, Yeoh T, Chandar S, McKenzie F, Taylor P, Grossfeld P, Fatkin D, Jones O, Hayes P, Feneley M, Harvey RP (2003) Cardiac homeobox gene NKX2-5 mutations and congenital heart disease: associations with atrial septal defect and hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 41:2072–2076
Dasgupta C, Martinez AM, Zuppan CW, Shah MM, Bailey LL, Fletcher WH (2001) Identification of connexin43 (alpha1) gap junction gene mutations in patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). Mutat Res 479:173–186
Iascone M, Ciccone R, Galletti L, Marchetti D, Seddio F, Lincesso AR, Pezzoli L, Vetro A, Barachetti D, Boni L, Federici D, Soto AM, Comas JV, Ferrazzi P, Zuffardi O (2012) Identification of de novo mutations and rare variants in hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Clin Genet 81:542–554
Reamon-Buettner SM, Ciribilli Y, Inga A, Borlak J (2008) A loss-of-function mutation in the binding domain of HAND1 predicts hypoplasia of the human hearts. Hum Mol Genet 17:1397–1405
Homsy J, Zaidi S, Shen Y, Ware JS, Samocha KE, Karczewski KJ, DePalma SR, McKean D, Wakimoto H, Gorham J, Jin SC, Deanfield J, Giardini A, Porter GA Jr, Kim R, Bilguvar K, Lopez-Giraldez F, Tikhonova I, Mane S, Romano-Adesman A, Qi H, Vardarajan B, Ma L, Daly M, Roberts AE, Russell MW, Mital S, Newburger JW, Gaynor JW, Breitbart RE, Iossifov I, Ronemus M, Sanders SJ, Kaltman JR, Seidman JG, Brueckner M, Gelb BD, Goldmuntz E, Lifton RP, Seidman CE, Chung WK (2015) De novo mutations in congenital heart disease with neurodevelopmental and other congenital anomalies. Science 350:1262–1266
Theis JL, Hrstka SC, Evans JM, O’Byrne MM, de Andrade M, O’Leary PW, Nelson TJ, Olson TM (2015) Compound heterozygous NOTCH1 mutations underlie impaired cardiogenesis in a patient with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Hum Genet 134:1003–1011
Theis JL, Zimmermann MT, Evans JM, Eckloff BW, Wieben ED, Qureshi MY, O’Leary PW, Olson TM (2015) Recessive MYH6 mutations in hypoplastic left heart with reduced ejection fraction. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 8:564–571
McBride KL, Pignatelli R, Lewin M, Ho T, Fernbach S, Menesses A, Lam W, Leal SM, Kaplan N, Schliekelman P, Towbin JA, Belmont JW (2005) Inheritance analysis of congenital left ventricular outflow tract obstruction malformations: segregation, multiplex relative risk, and heritability. Am J Med Genet Part A 134A:180–186
Liu X, Francis R, Kim AJ, Ramirez R, Chen G, Subramanian R, Anderton S, Kim Y, Wong L, Morgan J (2014) Interrogating congenital heart defects with noninvasive fetal echocardiography in a mouse forward genetic screen. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 7:31–42
Liu X, Yagi H, Saeed S, Bais AS, Gabriel GC, Chen Z, Peterson KA, Li Y, Schwartz MC, Reynolds WT, Saydmohammed M, Gibbs B, Wu Y, Devine W, Chatterjee B, Klena NT, Kostka D, de Mesy Bentley KL, Ganapathiraju MK, Dexheimer P, Leatherbury L, Khalifa O, Bhagat A, Zahid M, Pu W, Watkins S, Grossfeld P, Murray SA, Porter GA Jr, Tsang M, Martin LJ, Benson DW, Aronow BJ, Lo CW (2017) The complex genetics of hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Nat Genet 49:1152–1159
Hinton RB, Martin LJ, Rame-Gowda S, Tabangin ME, Cripe LH, Benson DW (2009) Hypoplastic left heart syndrome links to chromosomes 10q and 6q and is genetically related to bicuspid aortic valve. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:1065–1071
Taketazu M, Barrea C, Smallhorn JF, Wilson GJ, Hornberger LK (2004) Intrauterine pulmonary venous flow and restrictive foramen ovale in fetal hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:1902–1907
Martin LJ, Pilipenko V, Kaufman KM, Cripe L, Kottyan LC, Keddache M, Dexheimer P, Weirauch MT, Benson DW (2014) Whole exome sequencing for familial bicuspid aortic valve identifies putative variants. Circ Cardiovasc Gene 7:677–683
Martin LJ, Ramachandran V, Cripe LH, Hinton RB, Andelfinger G, Tabangin M, Shooner K, Keddache M, Benson DW (2007) Evidence in favor of linkage to human chromosomal regions 18q, 5q and 13q for bicuspid aortic valve and associated cardiovascular malformations. Hum Genet 121:275–284
Chen WV, Maniatis T (2013) Clustered protocadherins. Development 140:3297–3302
Esumi S, Kakazu N, Taguchi Y, Hirayama T, Sasaki A, Hirabayashi T, Koide T, Kitsukawa T, Hamada S, Yagi T (2005) Monoallelic yet combinatorial expression of variable exons of the protocadherin-alpha gene cluster in single neurons. Nat Genet 37:171–176
Thu CA, Chen WV, Rubinstein R, Chevee M, Wolcott HN, Felsovalyi KO, Tapia JC, Shapiro L, Honig B, Maniatis T (2014) Single-cell identity generated by combinatorial homophilic interactions between alpha, beta, and gamma protocadherins. Cell 158:1045–1059
Lewin MB, McBride KL, Pignatelli R, Fernbach S, Combes A, Menesses A, Lam W, Bezold LI, Kaplan N, Towbin JA, Belmont JW (2004) Echocardiographic evaluation of asymptomatic parental and sibling cardiovascular anomalies associated with congenital left ventricular outflow tract lesions. Pediatrics 114:691–696
Martin PS, Kloesel B, Norris RA, Lindsay M, Milan D, Body SC (2015) Embryonic development of the bicuspid aortic valve. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis 2:248–272
Noonan JP, Li J, Nguyen L, Caoile C, Dickson M, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Feldman MW, Myers RM (2003) Extensive linkage disequilibrium, a common 16.7-kilobase deletion, and evidence of balancing selection in the human protocadherin alpha cluster. Am J Hum Genet 72:621–635
Chandra S, Lang RM, Nicolarsen J, Gayat E, Spencer KT, Mor-Avi V, Hofmann Bowman MA (2012) Bicuspid aortic valve: inter-racial difference in frequency and aortic dimensions. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 5:981–989
Hasegawa S, Hamada S, Kumode Y, Esumi S, Katori S, Fukuda E, Uchiyama Y, Hirabayashi T, Mombaerts P, Yagi T (2008) The protocadherin-alpha family is involved in axonal coalescence of olfactory sensory neurons into glomeruli of the olfactory bulb in mouse. Mol Cell Neurosci 38:66–79
Suo L, Lu H, Ying G, Capecchi MR, Wu Q (2012) Protocadherin clusters and cell adhesion kinase regulate dendrite complexity through Rho GTPase. J Mol Cell Biol 4:362–376
Gaber N, Gagliardi M, Patel P, Kinnear C, Zhang C, Chitayat D, Shannon P, Jaeggi E, Tabori U, Keller G, Mital S (2013) Fetal reprogramming and senescence in hypoplastic left heart syndrome and in human pluripotent stem cells during cardiac differentiation. Am J Pathol 183:720–734
Tomoeda M, Yuki M, Kubo C, Yoshizawa H, Kitamura M, Nagata S, Nishizawa Y, Tomita Y (2011) Role of Meis1 in mitochondrial gene transcription of pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 410:798–802
Mahmoud AI, Kocabas F, Muralidhar SA, Kimura W, Koura AS, Thet S, Porrello ER, Sadek HA (2013) Meis1 regulates postnatal cardiomyocyte cell cycle arrest. Nature 497:249–253
Verma SK, Deshmukh V, Nutter CA, Jaworski E, Jin W, Wadhwa L, Abata J, Ricci M, Lincoln J, Martin JF, Yeo GW, Kuyumcu-Martinez MN (2016) Rbfox2 function in RNA metabolism is impaired in hypoplastic left heart syndrome patient hearts. Sci Rep 6:30896
Ricci M, Xu Y, Hammond HL, Willoughby DA, Nathanson L, Rodriguez MM, Vatta M, Lipshultz SE, Lincoln J (2012) Myocardial alternative RNA splicing and gene expression profiling in early stage hypoplastic left heart syndrome. PLoS ONE 7:e29784
Chen J, Bardes EE, Aronow BJ, Jegga AG (2009) ToppGene Suite for gene list enrichment analysis and candidate gene prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W305-311
Kasahara A, Cipolat S, Chen Y, Dorn GW 2nd, Scorrano L (2013) Mitochondrial fusion directs cardiomyocyte differentiation via calcineurin and Notch signaling. Science 342:734–737
Boskovski MT, Yuan S, Pedersen NB, Goth CK, Makova S, Clausen H, Brueckner M, Khokha MK (2013) The heterotaxy gene GALNT11 glycosylates Notch to orchestrate cilia type and laterality. Nature 504:456–459
Takeuchi JK, Lickert H, Bisgrove BW, Sun X, Yamamoto M, Chawengsaksophak K, Hamada H, Yost HJ, Rossant J, Bruneau BG (2007) Baf60c is a nuclear Notch signaling component required for the establishment of left-right asymmetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:846–851
Lee MP, Yutzey KE (2011) Twist1 directly regulates genes that promote cell proliferation and migration in developing heart valves. PLoS ONE 6:e29758
Rivera-Feliciano J, Lee KH, Kong SW, Rajagopal S, Ma Q, Springer Z, Izumo S, Tabin CJ, Pu WT (2006) Development of heart valves requires Gata4 expression in endothelial-derived cells. Development 133:3607–3618
Nakano H, Liu X, Arshi A, Nakashima Y, van Handel B, Sasidharan R, Harmon AW, Shin JH, Schwartz RJ, Conway SJ, Harvey RP, Pashmforoush M, Mikkola HK, Nakano A (2013) Haemogenic endocardium contributes to transient definitive haematopoiesis. Nat Commun 4:1564
van Loo PF, Mahtab EA, Wisse LJ, Hou J, Grosveld F, Suske G, Philipsen S, Gittenberger-de Groot AC (2007) Transcription factor Sp3 knockout mice display serious cardiac malformations. Mol Cell Biol 27:8571–8582
Manuylov NL, Tevosian SG (2009) Cardiac expression of Tnnt1 requires the GATA4-FOG2 transcription complex. Sci World J 9:575–587
Vijaya M, Manikandan J, Parakalan R, Dheen ST, Kumar SD, Tay SS (2013) Differential gene expression profiles during embryonic heart development in diabetic mice pregnancy. Gene 516:218–227
Martinez-Fernandez A, Li X, Hartjes KA, Terzic A, Nelson TJ (2013) Natural cardiogenesis-based template predicts cardiogenic potential of induced pluripotent stem cell lines. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 6:462–471
Magarin M, Schulz H, Thierfelder L, Drenckhahn JD (2016) Transcriptional profiling of regenerating embryonic mouse hearts. Genom Data 9:145–147
Peinado H, Portillo F, Cano A (2004) Transcriptional regulation of cadherins during development and carcinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol 48:365–375
Herranz N, Pasini D, Diaz VM, Franci C, Gutierrez A, Dave N, Escriva M, Hernandez-Munoz I, Di Croce L, Helin K, Garcia de Herreros A, Peiro S (2008) Polycomb complex 2 is required for E-cadherin repression by the Snail1 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 28:4772–4781
Lin Y, Wu Y, Li J, Dong C, Ye X, Chi YI, Evers BM, Zhou BP (2010) The SNAG domain of Snail1 functions as a molecular hook for recruiting lysine-specific demethylase 1. EMBO J 29:1803–1816
Gallagher TL, Arribere JA, Geurts PA, Exner CR, McDonald KL, Dill KK, Marr HL, Adkar SS, Garnett AT, Amacher SL, Conboy JG (2011) Rbfox-regulated alternative splicing is critical for zebrafish cardiac and skeletal muscle functions. Dev Biol 359:251–261
van Oevelen C, Bowman C, Pellegrino J, Asp P, Cheng J, Parisi F, Micsinai M, Kluger Y, Chu A, Blais A, David G, Dynlacht BD (2010) The mammalian Sin3 proteins are required for muscle development and sarcomere specification. Mol Cell Biol 30:5686–5697
Liu M, Pile LA (2017) The transcriptional corepressor SIN3 directly regulates genes involved in methionine catabolism and affects histone methylation, linking epigenetics and metabolism. J Biol Chem 292:1970–1976
Braeutigam C, Rago L, Rolke A, Waldmeier L, Christofori G, Winter J (2014) The RNA-binding protein Rbfox2: an essential regulator of EMT-driven alternative splicing and a mediator of cellular invasion. Oncogene 33:1082–1092
Strobl-Mazzulla PH, Bronner ME (2012) A PHD12-Snail2 repressive complex epigenetically mediates neural crest epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol 198:999–1010
Salomonis N, Nelson B, Vranizan K, Pico AR, Hanspers K, Kuchinsky A, Ta L, Mercola M, Conklin BR (2009) Alternative splicing in the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into cardiac precursors. PLoS Comput Biol 5:e1000553
Feng Y, Valley MT, Lazar J, Yang AL, Bronson RT, Firestein S, Coetzee WA, Manley JL (2009) SRp38 regulates alternative splicing and is required for Ca(2+) handling in the embryonic heart. Dev Cell 16:528–538
Yang J, Hung LH, Licht T, Kostin S, Looso M, Khrameeva E, Bindereif A, Schneider A, Braun T (2014) RBM24 is a major regulator of muscle-specific alternative splicing. Dev Cell 31:87–99
Wang H, Chen Y, Li X, Chen G, Zhong L, Chen G, Liao Y, Liao W, Bin J (2016) Genome-wide analysis of alternative splicing during human heart development. Sci Rep 6:35520
van den Hoogenhof MM, Pinto YM, Creemers EE (2016) RNA splicing: regulation and dysregulation in the heart. Circ Res 118:454–468
Brauch KM, Karst ML, Herron KJ, de Andrade M, Pellikka PA, Rodeheffer RJ, Michels VV, Olson TM (2009) Mutations in ribonucleic acid binding protein gene cause familial dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:930–941
Beraldi R, Li X, Martinez Fernandez A, Reyes S, Secreto F, Terzic A, Olson TM, Nelson TJ (2014) Rbm20-deficient cardiogenesis reveals early disruption of RNA processing and sarcomere remodeling establishing a developmental etiology for dilated cardiomyopathy. Hum Mol Genet 23:3779–3791
Genomes Project C, Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker RE, Kang HM, Marth GT, McVean GA (2012) An integrated map of genetic variation from 1092 human genomes. Nature 491:56–65
Freud LR, McElhinney DB, Marshall AC, Marx GR, Friedman KG, Del Nido PJ, Emani SM, Lafranchi T, Silva V, Wilkins-Haug LE, Benson CB, Lock JE, Tworetzky W (2014) Fetal aortic valvuloplasty for evolving hypoplastic left heart syndrome: postnatal outcomes of the first 100 patients. Circulation 130:638–645
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funding from NIH U01-HL098180, R01-HL132024, S10-OD010340 (CWL), and Children’s Heart Foundation (LJM and DWB) and Junior Cooperative Society (DWB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All studies were pursued under animal protocols approved by the University of Pittsburgh and the Jackson Laboratory Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were carried out with informed consent under a human study protocol approved by the University of Pittsburgh Institutional Review Board and in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagi, H., Liu, X., Gabriel, G.C. et al. The Genetic Landscape of Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome. Pediatr Cardiol 39, 1069–1081 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-018-1861-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-018-1861-4