Abstract
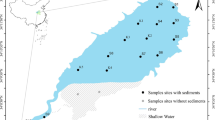
Sequential extraction was used to study the mobility and ecological risk of chemical fractions of six heavy metals in sediments collected from the Pearl River Delta (PRE) in China. Results revealed that residual fractions (F4) were the dominant forms for Cr and Ni in surface sediments, indicating that they were primarily stable in nature and had low bioavailability and ecotoxicity. Cd had a high environmental risk owing to its higher availability in acid-soluble fraction (F1), whereas Pb occurred predominantly in the reducible fraction (F2) in surface sediments. The profile variations of bioavailable fractions were generally consistent with socioeconomic development in the Pearl River Delta (PRD). A decreasing trend after 2006 suggested a reduction in heavy metal bioavailable fractions owing to the removal of heavy polluting industries and the effective control of sewage discharge. The risk assessment code suggested that the high mobility of Cd posed an extremely high risk and a threat to the aquatic environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amor RB, Yahyaoui A, Abidi M, Chouba L, Gueddari M (2019) Bioavailability and assessment of metal contamination in surface sediments of Rades-Hamam Lif coast, around Meliane River (Gulf of Tunis, Tunisia, Mediterranean Sea). J Chem 2019:11
Appleby PG, Oldfield F (1978) The calculation of lead-210 dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment. CATENA 5:1–8
Arisekar U, Shakila RJ, Shalini R, Jeyasekaran G, Keerthana M, Arumugam N, Almansour AI, Perumal K (2022) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals using geochemical normalization factors in the aquatic sediments. Chemosphere 294:133708
Cai K, Li C, Na S (2019) Spatial distribution, pollution source, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric depositions: a case study from the sustainable city of Shijiazhuang, China. Atmosphere 10(4):222
Chakraborty P, Chakraborty S, Ramteke D, Chennuri K (2014) Kinetic speciation and bioavailability of copper and nickel in mangrove sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 88(1–2):224–230
Chen SS, Li X, Zou CY, Zhu GW (2001) An analysis of the changes and evolvements on the foreshore and deep channels of lingding bay in Pearl river estuary. Remote Sens Land Resour 13:25–27
Chen B, Fan D, Guo Z, Liang W, Li W (2014) Heavy metals distribution patterns and sedimentary fluxes in fine-grained sediments in the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent areas. Acta Oceanol Sin 36:101–110
Gao L, Wang Z, Shan J, Chen J, Tang C, Yi M (2017) Aquatic environmental changes and anthropogenic activities reflected by the sedimentary records of the Shima River. South China Environ Pollut 224(MAY):70–81
Gnanachandrasamy G, Wang S, Mo L, Zou J, Zhou Y (2020) Distribution determination, risk assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in mangrove wetland sediments from Qi’ao Island, South China. Reg Stud Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2019.100961
Hei L, Jin P, Zhu X, Ye W, Yang Y (2016) Characteristics of speciation of heavy metals in municipal sewage sludge of Guangzhou as fertilizer. Procedia Environ Sci 31:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.031
Jia J, Wang YH, Huang QH, Dai Q, Yang YD (2019) Temporal and spatial characteristics of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in Pearl river Estuary and its influencing factors. Huan jing ke xue= Huanjing kexue 40(2):625–632
Karbassi AR, Shankar R (2005) Geochemistry of two sediment cores from the west coast of India. Int J Environ Sci Technol 1(4):307–316
Ke X, Gui S, Huang H, Zhang H, Wang C, Guo W (2017) Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 175:473
Li Q, Wu Z, Chu B, Zhang N, Cai S, Fang J (2007) Heavy metals in coastal wetland sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ Pollut 149(2):158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.01.006
Li Q, Wang Y, Li Y, Li L, Tang M, Hu W, Chen L, Ai S (2022) Speciation of heavy metals in soils and their immobilization at micro-scale interfaces among diverse soil components. Sci Total Environ 825:153862
Liao J, Deng S, Liu X, Lin H, Wei C (2020a) Influence of soil evolution on the heavy metal risk in three kinds of intertidal zone of the Pearl River Estuary. Land Degrad Dev 32:583–589
Lin Q, Liu E, Zhang E, Li K, Shen J (2016) Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China. CATENA 145:193–203
Liu EF, Shen J, Yang LY, Zhu YX, Sun QY, Wang JJ (2007) Chemical fractionation and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in the sediment of Nansihu lake and its main inflow rivers, China. Environ Sci 28(6):1377–1383
Liu X, Jia Q, Zhao Q, Cui B, Bai J (2016) Spatial and temporal dynamics of heavy metal pollution and source identification in sediment cores from the short-term flooding riparian wetlands in a Chinese delta. Environ Pollut 219:379–388
Liu C, Yin J, Hu L, Zhang B (2020) Spatial distribution of heavy metals and associated risks in sediment of the urban river flowing into the Pearl River Estuary, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 78(4):622–630
Liu Q, Yang P, Hu Z, Shu Q, Chen Y (2022) Identification of the sources and influencing factors of the spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments along the northern Jiangsu coast. Ecol Indic 137:108716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108716
Loring DH, Rantala R (1992) Manual for the geochemical analysis of marine sediments and suspended particulate matter. Earth Sci Rev 32(4):235–283
Lou C, Liu X, Nie Y, Emslie SD (2015) Fractionation distribution and preliminary ecological risk assessment of As, Hg and Cd in ornithogenic sediments from the Ross Sea region, East Antarctica. Sci Total Environ 538:644–653
Lu G, Zhao L, Jiao Z, Song M, Duan S (2016) Distribution and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Soil Sediment Contam Int J 25:101–116
Mo L, Zhou Y, Gopalakrishnana G, Li X (2020) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of toxic metals in agricultural soils from endemic nasopharyngeal carcinoma region in South China. Open Geosci 12(1):568–579
Najamuddin PT, Sanusi HS, Nurjaya IW (2016) Seasonal distribution and geochemical fractionation of heavy metals from surface sediment in a tropical estuary of Jeneberang River, Indonesia. Mar Pollut Bull 111(1–2):456–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.106
Omuku P, Abugu H, Edeme S, Umeobika U (2016) Metal distribution along the major roads of trans-amadi industrial complex port Harcourt, Nigeria. Int Res J Pure Appl Chem 10(4):1–11
Park MK, Choi SD (2021) Monitoring and risk assessment of arsenic species and metals in the Taehwa River in Ulsan, the largest industrial city in South Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 172:112862
Qi S, Leipe T, Rueckert P, Di Z, Harff J (2010) Geochemical sources, deposition and enrichment of heavy metals in short sediment cores from the Pearl River Estuary. South China J Mar Syst 82(9):S28–S42
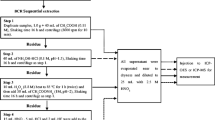
Rauret G, López-Sánchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monit 1:57–61
Riso R, Mastin M, Aschehoug A, Davy R, Devesa J, Laes-Huon A, Waeles M, Dulaquais G (2021) Distribution, speciation and composition of humic substances in a macro-tidal temperate estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 255:107360
Sert I, Eftelioglu M, Ozel FE (2017) Historical evolution of heavy metal pollution and recent records in Lake Karagl sediment cores using 210Pb models, western Turkey. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 314:2155–2169
Shepard FP (1954) Nomenclature based on sand-silt-clay ratios. J Sediment Res 24(3):151–158
Shu-Qing FU, Wei ZQ, Yuan SX, Xiong HX, Guo YH (2019) Heavy metal pollution features and potential ecological risk assessment in sediments and soils of the Pearl River Estuary. J Saf Environ
Singh KP, Mohan D, Singh VK, Malik A (2005) Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—a tributary of the Ganges, India. J Hydrol 312(1–4):14–27
Song M, Yin P, Zhao L, Jiao Z, Duan S, Lu G (2016) Distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Soil Sediment Contam Int J 25(2):101–116
Sun C, Zhang Z, Cao H, Xu M, Xu L (2019) Concentrations, speciation, and ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediment of the Songhua River in an urban area with petrochemical industries. Chemosphere 219:538–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.040
Sundaray SK, Nayak BB, Lin S, Bhatta D (2011a) Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—a case study: Mahanadi basin, India. J Hazard Mater 186(2–3):1837–1846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.081
Tack F, Mozo JE, Verloo MG (2008) Cadmium uptake by cucumber plants as affected by fluctuations in nutrient solution cadmium concentration during growth. Commun Soil Sci Plan Anal 29:3015–3021
Wang S, Jia Y, Wang S, Wang X, Wang H, Zhao Z, Liu B (2010a) Fractionation of heavy metals in shallow marine sediments from Jinzhou Bay, China. J Environ Sci (China) 22(1):23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(09)60070-x
Wang S, Jia Y, Wang S, Wang X, Wang H, Zhao Z, Liu B (2010b) Fractionation of heavy metals in shallow marine sediments from Jinzhou Bay, China. J Environ Sci China 22(1):23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60070-X
Wijaya AR, Ouchi AK, Tanaka K, Shinjo R, Ohde S (2012) Metal contents and Pb isotopes in road-side dust and sediment of Japan. J Geochem Explor 118:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.04.009
Wijaya AR, Ouchi AK, Tanaka K, Cohen MD, Sirirattanachai S, Shinjo R, Ohde S (2013) Evaluation of heavy metal contents and Pb isotopic compositions in the Chao Phraya River sediments: Implication for anthropogenic inputs from urbanized areas, Bangkok. J Geochem Explor 126–127:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.12.009
Wu Q, Zhou H, Tam NFY, Tian Y, Tan Y, Zhou S, Li Q, Chen Y, Leung JYS (2016) Contamination, toxicity and speciation of heavy metals in an industrialized urban river: implications for the dispersal of heavy metals. Mar Pollut Bull 104(1–2):153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.01.043
Wu S, Han R, Yang H, Wang Q, Bi F, Wang Y (2017) A century-long trend of metal pollution in the Sheyang River, on the coast of Jiangsu (China), reconstructed from sedimentary record. Chem Ecol 33(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2016.1246544
Xiao R, Bai J, Lu Q, Zhao Q, Gao Z, Wen X, Liu X (2015) Fractionation, transfer, and ecological risks of heavy metals in riparian and ditch wetlands across a 100-year chronosequence of reclamation in an estuary of China. Sci Total Environ 517:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.052
Xiao L, Guan D, Peart MR, Chen Y, Li Q (2017) The influence of bioavailable heavy metals and microbial parameters of soil on the metal accumulation in rice grain. Chemosphere 185:868–878
Yang C, Peng XZ, Wang ZD, Hollebone B, Brown CE, Yang ZY, Landriault M (2011) Fingerprinting analysis and characterization of hydrocarbons in sediment cores from the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ Forensics 12(1):49–62
Ye Z, Chen J, Gao L, Liang Z, Gnanachandrasamy G (2020) 210Pb dating to investigate the historical variations and identification of different sources of heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Mar Pollut Bull 150:110670
Zeng X, Xiao Z, Zhang G, Wang A, Li Z, Liu Y, Wang H, Zeng Q, Liang Y, Zou D (2018) Speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in pyrolytic biochar of swine and goat manures. J Anal Appl Pyrol 132:82–93
Zhai Y, Chen H, Xu BB, Xiang B, Chen Z, Li C, Zeng G (2014) Influence of sewage sludge-based activated carbon and temperature on the liquefaction of sewage sludge: yield and composition of bio-oil, immobilization and risk assessment of heavy metals. Bioresource Technol 159:72–79
Zhang T, Li Y (2020) Spatial distribution, fractions and risk assessment of five heavy metals in the sediments of Jialing River: a tributary of the Yangtze. Environ Earth Sci 79(19):464
Zhang C, Peng P, Song J, Liu C, Peng J (2012) Utilization of modified BCR procedure for the chemical speciation of heavy metals in Chinese soil reference material. Ecol Environ Sci 21(11):1881–1884
Zhang G, Bai J, Xiao R, Zhao Q, Jia J, Cui B, Liu X (2017a) Heavy metal fractions and ecological risk assessment in sediments from urban, rural and reclamation-affected rivers of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 184:278–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.155
Zhang G, Bai J, Xiao R, Zhao Q, Jia C (2017) Heavy metal fractions and ecological risk assessment in sediments from urban, rural and reclamation-affected rivers of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 184:278–288
Zhang L, Songjun XU, Difeng FU (2018) Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in the Pearl River Estuary Wetland Soil. Trop Geomorphol 39:20–25
Zhang J, Mo L, Li X, Zhu Y , Hu B, Zhang L (2022) Distributions, historical variations, and geochemical fractions of toxic trace metals and their ecological risks in sediments of the Nanliu river Estuary, South China. Ecol Indic 145:1–10
Zhu X, Yu W, Li F, Liu C, Ma J, Yan J, Wang Y, Tian R (2021) Spatio-temporal distribution and source identification of heavy metals in particle size fractions of road dust from a typical industrial district. Sci Total Environ 780:146357
Zhu X, Yu W, Li F, Liu C, Tian R (2021) Spatio-temporal distribution and source identification of heavy metals in particle size fractions of road dust from a typical industrial district. Sci Total Environ 184:278–288
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41771027 and 41701585), APN (CRRP2019-09MY-Onodera), Startup Project of Doctor scientific research, Huizhou University (2020JB074).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 41771027, Jianyao Chen, 41701585, Lei Gao, APN, CRRP2019-09MY-Onodera, Shin-ichi Onodera, Startup Project of Doctor scientific research, Huizhou University, 2020JB074, Zhiping Ye.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Z., Chen, J., Liang, Z. et al. Spatial and Temporal Variations and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Fractions in Sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 84, 389–399 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-023-00995-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-023-00995-2