Abstract
Background
Post-burn hypertrophic scar and keloid are challenging problems. Intense pulsed light (IPL) vascular filter (550–1200nm) has a similar effect to the pulsed dye laser 585nm in management of the same cutaneous applications.
Methods
This prospective comparative study was conducted on 34 patients with post-burn hypertrophic scars and keloid. The lesions were irradiated, using an IPL filter 550–1100 nm, 20 ms pulse duration, and fluence of 34 J/cm2. Sessions done every 2 weeks over a period of 6 months. The follow-up was scheduled for 1 month and 6 months. Evaluation methods were both subjective by the Vancouver scar scale (VSS) and objective by the skin imaging analysis system.
Results
Patients received 12 sessions. Erythema was the first sign to show improvement after the second session while itching was the first symptom which showed improvement followed by pain and finally improvement in the range of movement. The improvement of the VSS was higher in the hypertrophic scars than the keloid group (P˂ 0.001).
Conclusions
IPl proved its efficacy in the treatment of post-burn hypertrophic scars and keloid. However, the improvement in the pliability and erythema in hypertrophic scar was higher than in keloids.
Level of evidence: Level IV, Therapeutic




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erol OO, Gurlek A, Agaoglu G, Topcuoglu E, Oz H (2008) Treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids using intense pulsed light (IPL). Aesthet Plast Surg 32(6):902–909
Piccolo D, Di Marcantonio D, Crisman G, Cannarozzo G, Sannino M, Chiricozzi A et al (2014) Unconventional use of intense pulsed light. Biomed Res Int 2014:618206
Hultman CS, Friedstat JS, Edkins RE (2015) Effcacy of intense pulsed light for the treatment of burn scar dyschromias: a pilot study to assess patient satisfaction, safety, and willingness to pay. Ann Plast Surg 74(Suppl 4):S204–S208
Al-Mohamady Ael S, Ibrahim SM, Muhammad MM (2016) Pulsed dye laser versus long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloid: a comparative randomized split-scar trial. J Cosmet Laser Ther 18(4):208–212
Hultman CS, Edkins RE, Lee CN, Calvert CT, Cairns BA (2012) Shine on: review of laser-and light-based therapies for the treatment of burn scars. Dermatol Res Pract 2012:243651
Brown JJ, Bayat A (2009) Genetic susceptibility to raised dermal scarring. Br J Dermatol. 161:8–18
Gauglitz GG, Korting HC, Pavicic T, Ruzicka T, Jeschke MG (2011) Hypertrophic scarring and keloids: pathomechanisms and current and emerging treatment strategies. Mol Med 17(1-2):113–125
Cartier H, Patarin M, Prost ALP (2020) Use of intense pulsed light in the treatment of scars. In: Fodor L, Ullmann Y (eds) Aesthetic Applications of Intense Pulsed Light. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22829-3_15
Sarkar A, Dewangan YK, Bain J, Rakshit P, Dhruw K, Basu SK et al (2014) Effect of intense pulsed light on immature burn scars: a clinical study. Indian J Plast Surg 47:381–385
Abalí M, Bravo B, Zylbersztejn D (2014) Intense pulsed light in the treatment of scars caused by burns. Surg Cosmet Dermatol 6(1):2631
Elmelegy NG, Hegazy AM, Sadaka MS, Abdeldaim DE (2018) Electrophotobiomodulation in the treatment of facial post-burn hypertrophic scars in pediatric patients. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 31(2):127–132
Fu X, Dong J, Wang S et al (2019) Advances in the treatment of traumatic scars with laser, intense pulsed light, radiofrequency, and ultrasound. Burn Trauma 7:1
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the National Institute of Laser Enhanced Sciences Cairo Univeristy (NIELS-EC-CU 23/6/10).
Consent to participate
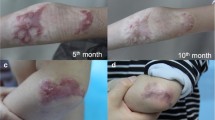
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for sharing their data and for publication of the images in Figs. 1a, b and 2a, b.
Conflict of interest
Abeer Attia Tawfik and Rama Ahmad Ali declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tawfik, A.A., Ali, R.A. Intense pulsed light in the management of post-burn keloid and hypertrophic scar: a comparative study. Eur J Plast Surg 46, 1323–1329 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-023-02103-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-023-02103-y