Abstract
Background
Keloids and hypertrophic scars are extremely disturbing to patients, both physically and psychologically. This study prospectively assessed the safety and efficacy of intense pulsed light (IPL) on scars originating from burns, trauma, surgery, and acne.
Methods
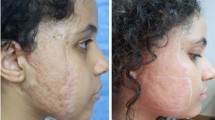
Hypertrophic scars in 109 patients, originating from surgical incisions (n = 55), traumatic cuts (traffic accidents) (n = 24), acne scars (n = 6), keloids (n = 5), and burns (n = 19), were treated using an IPL® Quantum™ device. Treatment was administered at 2–4-week intervals, and patients received an average of 8 treatments (range = 6–24). Using digital photographs, Changes in scar appearance were assessed by two physicians who were blinded to the study patients and treatments. The photographs were graded on a scale of 0 to 4 (none, minimal, moderate, good, excellent) for improvement in overall clinical appearance and reduction in height, erythema, and hardness.
Results
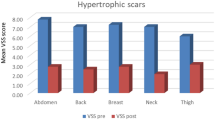
An overall clinical improvement in the appearance of scars and reductions in height, erythema, and hardness were seen in the majority of the patients (92.5%). Improvement was excellent in 31.2% of the patients, good in 25.7%, moderate in 34%, and minimal in 9.1%. Over half the patients had good or excellent improvement. In the preventive IPL treatment group, 65% had good to excellent improvement in clinical appearance. Patient satisfaction was very high.
Conclusion
This study suggests that IPL is effective not only in improving the appearance of hypertrophic scars and keloids regardless of their origin, but also in reducing the height, redness, and hardness of scars.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alster TS, Tanzi EL (2003) Hypertrophic scars and keloids: etiology and management. Am J Clin Dermatol 4:235–243
Alster TS, West TB (1997) Treatment of scars: a review. Ann Plast Surg 39:418–432
Chen MA, Davidson TM (2005) Scar management: prevention and treatment strategies. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13:242–247
Bayat A, McGrouther DA (2005) Clinical management of skin scarring. Skinmed 4:165–173
Boutli-Kasapidou F, Tsakiri A, Anagnostou E, Mourellou O (2005) Hypertrophic and keloidal scars: an approach to polytherapy. Int J Dermatol 44:324–327
Smith FR (2005) Causes of and treatment options for abnormal scar tissue. J Wound Care 14:49–52
Alster TS (1997) Laser treatment of hypertrophic scars, keloids, and striae. Dermatol Clin 15:419–429
Alster TS, Lewis AB, Rosenbach A (1998) Laser scar revision: comparison of CO2 laser vaporization with and without simultaneous pulsed dye laser treatment. Dermatol Surg 24:1299–1302
Alster TS, Tanzi EL (2005) Re: the use of pulsed dye laser for the prevention and treatment of hypertrophic scars in Chinese persons. Dermatol Surg 31:252–253; author reply 253
Lupton JR, Alster TS (2002) Laser scar revision. Dermatol Clin 20:55–65
Bellew SG, Weiss MA, Weiss RA (2005) Comparison of intense pulsed light to 595-nm long-pulsed pulsed dye laser for treatment of hypertrophic surgical scars: a pilot study. J Drugs Dermatol 4:448–452
Kontoes PP, Marayiannis KV, Vlachos SP (2003) The use of intense pulsed light in the treatment of scars. Eur J Plast Surg 25:374–377
Hedelund L, Due E, Bjerring P, Wulf HC, Haedersdal M (2006) Skin rejuvenation using intense pulsed light: a randomized controlled split-face trial with blinded response evaluation. Arch Dermatol 142:985–990
Clementoni MT, Gilardino P, Muti GF, Signorini M, Pistorale A, Morselli PG, Cavina C (2006) Intense pulsed light treatment of 1,000 consecutive patients with facial vascular marks. Aesthetic Plast Surg 30:226–232
Lemperle G, Rullan PP, Gauthier-Hazan N (2006) Avoiding and treating dermal filler complications. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:92S–107S
Yamashita T, Negishi K, Hariya T, Kunizawa N, Ikuta K, Yanai M, Wakamatsu S (2006) Intense pulsed light therapy for superficial pigmented lesions evaluated by reflectance-mode confocal microscopy and optical coherence tomography. J Invest Dermatol 126:2281–2286
Butterwick KJ, Butterwick LS, Han A (2006) Laser and light therapies for acne rosacea. J Drugs Dermatol 5:35–39
Hurwitz DJ, Holland SW (2006) The L brachioplasty: an innovative approach to correct excess tissue of the upper arm, axilla, and lateral chest. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:403–411; discussion 412–403
Allison KP, Kiernan MN, Waters RA, Clement RM (2003) Pulsed dye laser treatment of burn scars. Alleviation or irritation? Burns 29:207–213
McCraw JB, McCraw JA, McMellin A, Bettencourt N (1999) Prevention of unfavorable scars using early pulse dye laser treatments: a preliminary report. Ann Plast Surg 42:7–14
Meshkinpour A, Ghasri P, Pope K, Lyubovitsky JG, Risteli J, Krasieva TB, Kelly KM (2005) Treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids with a radiofrequency device: a study of collagen effects. Lasers Surg Med 37:343–349
Nouri K, Jimenez GP, Harrison-Balestra C, Elgart GW (2003) 585-nm pulsed dye laser in the treatment of surgical scars starting on the suture removal day. Dermatol Surg 29:65–73; discussion 73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erol, O.O., Gurlek, A., Agaoglu, G. et al. Treatment of Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids Using Intense Pulsed Light (IPL). Aesth Plast Surg 32, 902–909 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9161-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9161-7