Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the ability of quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE)-MRI and readout segmentation of long variable echo-trains diffusion-weighted imaging (RESOLVE-DWI) in differentiating parotid tumors (PTs) with different histological types.
Methods
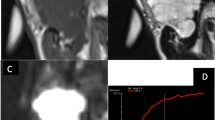
In this retrospective study, 123 patients with 145 histologically proven PTs who underwent both RESOLVE-DWI and DCE-MRI were enrolled including 51 pleomorphic adenomas (PAs), 52 Warthin’s tumors (WTs), 27 other benign neoplasms (OBNs), and 15 malignant tumors (MTs). Quantitative parameters of DCE-MRI (Ktrans, Kep, and Ve) and the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of lesions were calculated and analyzed. Kruskal–Wallis tests with Dunn-Bonferroni correction, logistic regression analyses, and receiver operating characteristic curve were used for statistical analyses.
Results
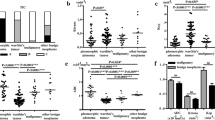
PAs exhibited a lowest Ktrans among these four PTs. WTs demonstrated the highest Kep and lowest Ve values. WTs and MTs showed lower ADCmin values than PAs and OBNs. The combination of Kep and Ve provided 98.1% sensitivity, 85% specificity, and 98.7% accuracy for differentiating WTs from the other three PTs. The ADCmin cutoff value of ≤ 0.826 yielded 80.0% sensitivity, 92.3% specificity, and 90.3% accuracy for the differentiation of MTs from PAs and OBNs. Ktrans with a cutoff value of ≤ 0.185 achieved a sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 84.3, 70.4, and 79.5%, respectively, for discriminating PAs from OBNs.
Conclusion
The combination of quantitative DCE-MRI and RESOLVE-DWI is beneficial for characterizing four histological types of PTs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Upton DC, McNamar JP, Connor NP, Harari PM, Hartig GK (2007) Parotidectomy: ten-year review of 237 cases at a single institution. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136(5):788–792
Freling N, Crippa F, Maroldi R (2016) Staging and follow-up of high-grade malignant salivary gland tumours: the role of traditional versus functional imaging approaches - a review. Oral Oncol 60:157–166
Witt RL (2002) The significance of the margin in parotid surgery for pleomorphic adenoma. Laryngoscope 112(12):2141–2154
Sciubba JJ, Brannon RB (1982) Myoepithelioma of salivary glands: report of 23 cases. Cancer 49(3):562–572
Bradley PT, Paleri V, Homer JJ (2012) Consensus statement by otolaryngologists on the diagnosis and management of benign parotid gland disease. Clin Otolaryngol 37(4):300–304
Zbaren P, Vander Poorten V, Witt RL, Woolgar JA, Shaha AR, Triantafyllou A, Takes RP, Rinaldo A, Ferlito A (2013) Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid: formal parotidectomy or limited surgery? Am J Surg 205(1):109–118
Magnano M, Gervasio CF, Cravero L, Machetta G, Lerda W, Beltramo G, Orecchia R, Ragona R, Bussi M (1999) Treatment of malignant neoplasms of the parotid gland. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121(5):627–632
Prades JM, Oletski A, Faye MB, Dumollard JM, Timoshenko AP, Veyret C, Peoc’h M, Martin C (2007) Parotid gland masses: diagnostic value of MR imaging with histopathologic correlations. Morphologie 91(292):44–51
Yousem DM, Kraut MA, Chalian AA (2000) Major salivary gland imaging. Radiology 216(1):19–29
Freling NJ, Molenaar WM, Vermey A, Mooyaart EL, Panders AK, Annyas AA, Thijn CJ (1992) Malignant parotid tumors: clinical use of MR imaging and histologic correlation. Radiology 185(3):691–696
Elmokadem AH, Abdel Khalek AM, Abdel Wahab RM, Tharwat N, Gaballa GM, Elata MA, Amer T (2019) Diagnostic accuracy of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for differentiation between parotid neoplasms. Can Assoc Radiol J 70(3):264–272
Yabuuchi H, Fukuya T, Tajima T, Hachitanda Y, Tomita K, Koga M (2003) Salivary gland tumors: diagnostic value of gadolinium-enhanced dynamic MR imaging with histopathologic correlation. Radiology 226(2):345–354
Kitamoto E, Chikui T, Kawano S, Ohga M, Kobayashi K, Matsuo Y, Yoshiura T, Obara M, Honda H, Yoshiura K (2015) The application of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and diffusion-weighted MRI in patients with maxillofacial tumors. Acad Radiol 22(2):210–216
Yabuuchi H, Matsuo Y, Kamitani T, Setoguchi T, Okafuji T, Soeda H, Sakai S, Hatakenaka M, Nakashima T, Oda Y et al (2008) Parotid gland tumors: can addition of diffusion-weighted MR imaging to dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging improve diagnostic accuracy in characterization? Radiology 249(3):909–916
Habermann CR, Arndt C, Graessner J, Diestel L, Petersen KU, Reitmeier F, Ussmueller JO, Adam G, Jaehne M (2009) Diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging of primary parotid gland tumors: is a prediction of different histologic subtypes possible? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(3):591–596
Coudert H, Mirafzal S, Dissard A, Boyer L, Montoriol PF (2021) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of parotid tumors: a systematic review. Diagn Interv Imaging 102(3):121–130
Chikui T, Obara M, Simonetti AW, Ohga M, Koga S, Kawano S, Matsuo Y, Kamintani T, Shiraishi T, Kitamoto E et al (2012) The principal of dynamic contrast enhanced MRI, the method of pharmacokinetic analysis, and its application in the head and neck region. Int J Dent 2012:480659
Sumi M, Van Cauteren M, Sumi T, Obara M, Ichikawa Y, Nakamura T (2012) Salivary gland tumors: use of intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging for assessment of diffusion and perfusion for the differentiation of benign from malignant tumors. Radiology 263(3):770–777
Koyasu S, Iima M, Umeoka S, Morisawa N, Porter DA, Ito J, Le Bihan D, Togashi K (2014) The clinical utility of reduced-distortion readout-segmented echo-planar imaging in the head and neck region: initial experience. Eur Radiol 24(12):3088–3096
Porter DA, Heidemann RM (2009) High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn Reson Med 62(2):468–475
Leach MO, Morgan B, Tofts PS, Buckley DL, Huang W, Horsfield MA, Chenevert TL, Collins DJ, Jackson A, Lomas D et al (2012) Imaging vascular function for early stage clinical trials using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 22(7):1451–1464
Tofts PS, Brix G, Buckley DL, Evelhoch JL, Henderson E, Knopp MV, Larsson HB, Lee TY, Mayr NA, Parker GJ et al (1999) Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T(1)-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J Magn Reson Imaging 10(3):223–232
Patella F, Franceschelli G, Petrillo M, Sansone M, Fusco R, Pesapane F, Pompili G, Ierardi AM, Saibene AM, Moneghini L et al (2018) A multiparametric analysis combining DCE-MRI- and IVIM -derived parameters to improve differentiation of parotid tumors: a pilot study. Future Oncol 14(28):2893–2903
Patella F, Sansone M, Franceschelli G, Tofanelli L, Petrillo M, Fusco M, Nicolino GM, Buccimazza G, Fusco R, Gopalakrishnan V et al (2020) Quantification of heterogeneity to classify benign parotid tumors: a feasibility study on most frequent histotypes. Future Oncol 16(12):763–778
Xu Z, Zheng S, Pan A, Cheng X, Gao M (2019) A multiparametric analysis based on DCE-MRI to improve the accuracy of parotid tumor discrimination. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46(11):2228–2234
Park JY, Shin HJ, Shin KC, Sung YS, Choi WJ, Chae EY, Cha JH, Kim HH (2015) Comparison of readout segmented echo planar imaging (EPI) and EPI with reduced field-of-VIew diffusion-weighted imaging at 3t in patients with breast cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 42(6):1679–1688
Yeom KW, Holdsworth SJ, Van AT, Iv M, Skare S, Lober RM, Bammer R (2013) Comparison of readout-segmented echo-planar imaging (EPI) and single-shot EPI in clinical application of diffusion-weighted imaging of the pediatric brain. AJR Am J Roentgenol 200(5):W437-443
Xu X, Wang Y, Hu H, Su G, Liu H, Shi H, Wu F (2017) Readout-segmented echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging in the assessment of orbital tumors: comparison with conventional single-shot echo-planar imaging in image quality and diagnostic performance. Acta Radiol 58(12):1457–1467
Zhao M, Liu Z, Sha Y, Wang S, Ye X, Pan Y, Wang S (2016) Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging in the evaluation of sinonasal lesions: a comprehensive comparison of image quality in single-shot echo-planar imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 34(2):166–172
Wisner DJ, Rogers N, Deshpande VS, Newitt DN, Laub GA, Porter DA, Kornak J, Joe BN, Hylton NM (2014) High-resolution diffusion-weighted imaging for the separation of benign from malignant BI-RADS 4/5 lesions found on breast MRI at 3T. J Magn Reson Imaging 40(3):674–681
Ma G, Zhu LN, Su GY, Hu H, Qian W, Bu SS, Xu XQ, Wu FY (2018) Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient maps for differentiating malignant from benign parotid gland tumors. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275(8):2151–2157
Zhang Z, Song C, Zhang Y, Wen B, Zhu J, Cheng J (2019) Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) histogram analysis: differentiation of benign from malignant parotid gland tumors using readout-segmented diffusion-weighted imaging. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 48(7):20190100
Alibek S, Zenk J, Bozzato A, Lell M, Grunewald M, Anders K, Rabe C, Iro H, Bautz W, Greess H (2007) The value of dynamic MRI studies in parotid tumors. Acad Radiol 14(6):701–710
Gaddikeri S, Hippe DS, Anzai Y (2016) Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in the Evaluation of Carotid Space Paraganglioma versus Schwannoma. J Neuroimaging 26(6):618–625
Lee FK, King AD, Ma BB, Yeung DK (2012) Dynamic contrast enhancement magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) for differential diagnosis in head and neck cancers. Eur J Radiol 81(4):784–788
Yu JY, Zhang D, Huang XL, Ma J, Yang C, Li XJ, Xiong H, Zhou B, Liao RK, Tang ZY (2020) Quantitative analysis of DCE-MRI and RESOLVE-DWI for differentiating nasopharyngeal carcinoma from nasopharyngeal lymphoid hyperplasia. J Med Syst 44(4):75
Woo SH, Choi DS, Kim JP, Park JJ, Joo YH, Chung PS, Kim BY, Ko YH, Jeong HS, Kim HJ (2013) Two-phase computed tomography study of warthin tumor of parotid gland: differentiation from other parotid gland tumors and its pathologic explanation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 37(4):518–524
Furuya M, Yonemitsu Y (2008) Cancer neovascularization and proinflammatory microenvironments. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8(4):253–265
Jain RK (2005) Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307(5706):58–62
Triest WE, Fried MP, Stanievich JF (1983) Membranous basal cell adenoma of the hypopharynx. Arch Otolaryngol 109(11):774–777
Ahn SJ, An CS, Koom WS, Song HT, Suh JS (2011) Correlations of 3T DCE-MRI quantitative parameters with microvessel density in a human-colorectal-cancer xenograft mouse model. Korean J Radiol 12(6):722–730
Kim SH, Lee HS, Kang BJ, Song BJ, Kim HB, Lee H, Jin MS, Lee A (2016) Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI perfusion parameters as imaging biomarkers of angiogenesis. PLoS One 11(12):e0168632
Yabuuchi H, Kamitani T, Sagiyama K, Yamasaki Y, Hida T, Matsuura Y, Hino T, Murayama Y, Yasumatsu R, Yamamoto H (2020) Characterization of parotid gland tumors: added value of permeability MR imaging to DWI and DCE-MRI. Eur Radiol 30(12):6402–6412
Ikeda M, Motoori K, Hanazawa T, Nagai Y, Yamamoto S, Ueda T, Funatsu H, Ito H (2004) Warthin tumor of the parotid gland: diagnostic value of MR imaging with histopathologic correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25(7):1256–1262
Lee JY, Kim HJ, Kim YK, Cha J, Kim ST (2019) Basal cell adenoma and myoepithelioma of the parotid gland: patterns of enhancement at two-phase CT in comparison with Warthin tumor. Diagn Interv Radiol 25(4):285–290
Eida S, Sumi M, Sakihama N, Takahashi H, Nakamura T (2007) Apparent diffusion coefficient mapping of salivary gland tumors: prediction of the benignancy and malignancy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(1):116–121
Celebi I, Mahmutoglu AS, Ucgul A, Ulusay SM, Basak T, Basak M (2013) Quantitative diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of parotid gland masses: a study with histopathological correlation. Clin Imaging 37(2):232–238
Funding
This study was supported by the Startup Fund for scientific research of Fujian Medical University (No. 2019QH1105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
The study was approved by our institutional review committee. Due to the retrospective nature of the investigation, informed consent has been waived for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, N., Xiao, Z., Chen, Y. et al. Quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and readout segmentation of long variable echo-trains diffusion-weighted imaging in differentiating parotid gland tumors. Neuroradiology 63, 1709–1719 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02758-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02758-z