Abstract
Purpose
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is related to impairment in various white matter (WM) pathways. Utility of the recently developed two-compartment model of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) to analyse axial diffusivity of WM is restricted by several limitations. The present study aims to validate the utility of model-free DKI in the evaluation of WM alterations in ASD and analyse the potential relationship between DKI-evident WM alterations and personality scales.
Methods
Overall, 15 participants with ASD and 15 neurotypical (NT) controls were scanned on a 3 T magnetic resonance (MR) scanner, and scores for autism quotient (AQ), systemising quotient (SQ) and empathising quotient (EQ) were obtained for both groups. Multishell diffusion-weighted MR data were acquired using two b-values (1000 and 2000 s/mm2). Differences in mean kurtosis (MK), radial kurtosis (RK) and axial kurtosis (AK) between the groups were evaluated using tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS). Finally, the relationships between the kurtosis indices and personality quotients were examined.
Results
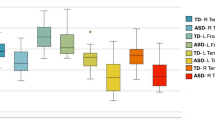
The ASD group demonstrated significantly lower AK in the body and splenium of corpus callosum than the NT group; however, no other significant differences were identified. Negative correlations were found between AK and AQ or SQ, predominantly in WM areas related to social–emotional processing such as uncinate fasciculus, inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus, and inferior and superior longitudinal fasciculi.
Conclusions
Model-free DKI and its indices may represent a novel, objective method for detecting the disease severity and WM alterations in patients with ASD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wise EA, Smith MD, Rabins PV (2017) Aging and autism spectrum disorder: a naturalistic, longitudinal study of the comorbidities and behavioral and neuropsychiatric symptoms in adults with ASD. J Autism Dev Disord 47(6):1708–1715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-017-3095-3
American Psychiatric Association., American Psychiatric Association. DSM-5 Task Force (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, D.C
Clemm von Hohenberg C, Wigand MC, Kubicki M, Leicht G, Giegling I, Karch S, Hartmann AM, Konte B, Friedl M, Ballinger T, Eckbo R, Bouix S, Jager L, Shenton ME, Rujescu D, Mulert C (2013) CNTNAP2 polymorphisms and structural brain connectivity: a diffusion-tensor imaging study. J Psychiatr Res 47(10):1349–1356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2013.07.002
McFadden K, Minshew NJ (2013) Evidence for dysregulation of axonal growth and guidance in the etiology of ASD. Front Hum Neurosci 7:671. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00671
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J 66(1):259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80775-1
Ikuta T, Shafritz KM, Bregman J, Peters BD, Gruner P, Malhotra AK, Szeszko PR (2014) Abnormal cingulum bundle development in autism: a probabilistic tractography study. Psychiatry Res 221(1):63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2013.08.002
Libero LE, Burge WK, Deshpande HD, Pestilli F, Kana RK (2016) White matter diffusion of major fiber tracts implicated in autism spectrum disorder. Brain Connect 6(9):691–699. https://doi.org/10.1089/BrainConnect.2016.0442
McGrath J, Johnson K, O'Hanlon E, Garavan H, Leemans A, Gallagher L (2013) Abnormal functional connectivity during visuospatial processing is associated with disrupted organisation of white matter in autism. Front Hum Neurosci 7:434. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00434
Travers BG, Tromp do PM, Adluru N, Lange N, Destiche D, Ennis C, Nielsen JA, Froehlich AL, Prigge MB, Fletcher PT, Anderson JS, Zielinski BA, Bigler ED, Lainhart JE, Alexander AL (2015) Atypical development of white matter microstructure of the corpus callosum in males with autism: a longitudinal investigation. Mol Autism 6:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-015-0001-8
Jou RJ, Reed HE, Kaiser MD, Voos AC, Volkmar FR, Pelphrey KA (2016) White matter abnormalities in autism and unaffected siblings. J Neuropsychiatr Clin Neurosci 28(1):49–55. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.neuropsych.15050109
Pugliese L, Catani M, Ameis S, Dell'Acqua F, Thiebaut de Schotten M, Murphy C, Robertson D, Deeley Q, Daly E, Murphy DG (2009) The anatomy of extended limbic pathways in Asperger syndrome: a preliminary diffusion tensor imaging tractography study. Neuroimage 47(2):427–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.014
Thomas C, Humphreys K, Jung KJ, Minshew N, Behrmann M (2011) The anatomy of the callosal and visual-association pathways in high-functioning autism: a DTI tractography study. Cortex 47(7):863–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2010.07.006
Pardini M, Elia M, Garaci FG, Guida S, Coniglione F, Krueger F, Benassi F, Emberti Gialloreti L (2012) Long-term cognitive and behavioral therapies, combined with augmentative communication, are related to uncinate fasciculus integrity in autism. J Autism Dev Disord 42(4):585–592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-011-1281-2
Aoki Y, Yoncheva YN, Chen B, Nath T, Sharp D, Lazar M, Velasco P, Milham MP, Di Martino A (2017) Association of white matter structure with autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 74(11):1120–1128. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.2573
Catani M, Jones DK, Daly E, Embiricos N, Deeley Q, Pugliese L, Curran S, Robertson D, Murphy DG (2008) Altered cerebellar feedback projections in Asperger syndrome. Neuroimage 41(4):1184–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.041
Cooper M, Thapar A, Jones DK (2015) ADHD severity is associated with white matter microstructure in the subgenual cingulum. Neuroimage Clin 7:653–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.02.012
Ke X, Tang T, Hong S, Hang Y, Zou B, Li H, Zhou Z, Ruan Z, Lu Z, Tao G, Liu Y (2009) White matter impairments in autism, evidence from voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging. Brain Res 1265:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.02.013
Langen M, Leemans A, Johnston P, Ecker C, Daly E, Murphy CM, Dell’acqua F, Durston S, Consortium A, Murphy DG (2012) Fronto-striatal circuitry and inhibitory control in autism: findings from diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cortex 48(2):183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2011.05.018
Basser PJ, Jones DK (2002) Diffusion-tensor MRI: theory, experimental design and data analysis - a technical review. NMR Biomed 15(7–8):456–467. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.783
Chung AW, Seunarine KK, Clark CA (2016) NODDI reproducibility and variability with magnetic field strength: a comparison between 1.5 T and 3 T. Hum Brain Mapp 37(12):4550–4565. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23328
Kamagata K, Zalesky A, Hatano T, Ueda R, Di Biase MA, Okuzumi A, Shimoji K, Hori M, Caeyenberghs K, Pantelis C, Hattori N, Aoki S (2017) Gray matter abnormalities in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: evaluation by diffusional kurtosis imaging and neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging. Hum Brain Mapp. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23628
Fieremans E, Jensen JH, Helpern JA (2011) White matter characterization with diffusional kurtosis imaging. Neuroimage 58(1):177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.006
Alexander AL, Lee JE, Lazar M, Field AS (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics 4(3):316–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2007.05.011
Hui ES, Cheung MM, Qi L, Wu EX (2008) Towards better MR characterization of neural tissues using directional diffusion kurtosis analysis. NeuroImage 42(1):122–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.04.237
Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K (2005) Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(6):1432–1440. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20508
Zhu J, Zhuo C, Qin W, Wang D, Ma X, Zhou Y, Yu C (2015) Performances of diffusion kurtosis imaging and diffusion tensor imaging in detecting white matter abnormality in schizophrenia. Neuroimage Clin 7:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2014.12.008
Fieremans E, Benitez A, Jensen JH, Falangola MF, Tabesh A, Deardorff RL, Spampinato MV, Babb JS, Novikov DS, Ferris SH, Helpern JA (2013) Novel white matter tract integrity metrics sensitive to Alzheimer disease progression. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34(11):2105–2112. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3553
Steven AJ, Zhuo J, Melhem ER (2014) Diffusion kurtosis imaging: an emerging technique for evaluating the microstructural environment of the brain. AJR Am J Roentgenol 202(1):W26–W33. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.13.11365
Das SK, Wang JL, Bing L, Bhetuwal A, Yang HF (2017) Regional values of diffusional kurtosis estimates in the healthy brain during normal aging. Clin Neuroradiol 27(3):283–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-015-0490-z
Davenport EM, Apkarian K, Whitlow CT, Urban JE, Jensen JH, Szuch E, Espeland MA, Jung Y, Rosenbaum DA, Gioia GA, Powers AK, Stitzel JD, Maldjian JA (2016) Abnormalities in diffusional kurtosis metrics related to head impact exposure in a season of high school varsity football. J Neurotrauma 33(23):2133–2146. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2015.4267
Duchene G, Peeters F, Peeters A, Duprez T (2017) A comparative study of the sensitivity of diffusion-related parameters obtained from diffusion tensor imaging, diffusional kurtosis imaging, q-space analysis and bi-exponential modelling in the early disease course (24 h) of hyperacute (6 h) ischemic stroke patients. MAGMA 30(4):375–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-017-0612-5
Gao J, Feng ST, Wu B, Gong N, Lu M, Wu PM, Wang H, He X, Huang B (2015) Microstructural brain abnormalities of children of idiopathic generalized epilepsy with generalized tonic-clonic seizure: a voxel-based diffusional kurtosis imaging study. J Magn Reson Imaging 41(4):1088–1095. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24647
Qi XX, Shi DF, Ren SX, Zhang SY, Li L, Li QC, Guan LM (2018) Histogram analysis of diffusion kurtosis imaging derived maps may distinguish between low and high grade gliomas before surgery. Eur Radiol 28(4):1748–1755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5108-1
Kamiya K, Okada N, Sawada K, Watanabe Y, Irie R, Hanaoka S, Suzuki Y, Koike S, Mori H, Kunimatsu A, Hori M, Aoki S, Kasai K, Abe O (2018) Diffusional kurtosis imaging and white matter microstructure modeling in a clinical study of major depressive disorder. NMR Biomed 31(7):e3938. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.3938
Kamagata K, Tomiyama H, Hatano T, Motoi Y, Abe O, Shimoji K, Kamiya K, Suzuki M, Hori M, Yoshida M, Hattori N, Aoki S (2014) A preliminary diffusional kurtosis imaging study of Parkinson disease: comparison with conventional diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroradiology 56(3):251–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1327-1
Kamagata K, Tomiyama H, Motoi Y, Kano M, Abe O, Ito K, Shimoji K, Suzuki M, Hori M, Nakanishi A, Kuwatsuru R, Sasai K, Aoki S, Hattori N (2013) Diffusional kurtosis imaging of cingulate fibers in Parkinson disease: comparison with conventional diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 31(9):1501–1506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2013.06.009
Gong NJ, Chan CC, Leung LM, Wong CS, Dibb R, Liu C (2017) Differential microstructural and morphological abnormalities in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from cortical and deep gray matter. Hum Brain Mapp 38(5):2495–2508. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23535
Lazar M, Miles LM, Babb JS, Donaldson JB (2014) Axonal deficits in young adults with high functioning autism and their impact on processing speed. Neuroimage Clin 4:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2014.01.014
Sui YV, Donaldson J, Miles L, Babb JS, Castellanos FX, Lazar M (2018) Diffusional kurtosis imaging of the corpus callosum in autism. Mol Autism 9:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-018-0245-1
Alexander DC, Dyrby TB, Nilsson M, Zhang H (2017) Imaging brain microstructure with diffusion MRI: practicality and applications. NMR Biomed 32:e3841. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.3841
Wakabayashi A, Tojo Y, Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S (2004) The autism-Spectrum quotient (AQ) Japanese version: evidence from high-functioning clinical group and normal adults. Shinrigaku Kenkyu 75(1):78–84
Baron-Cohen S, Richler J, Bisarya D, Gurunathan N, Wheelwright S (2003) The systemizing quotient: an investigation of adults with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism, and normal sex differences. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 358(1430):361–374. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2002.1206
Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S (2004) The empathy quotient: an investigation of adults with Asperger syndrome or high functioning autism, and normal sex differences. J Autism Dev Disord 34(2):163–175
Andersson JL, Sotiropoulos SN (2016) An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage 125:1063–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.019
Tabesh A, Jensen JH, Ardekani BA, Helpern JA (2011) Estimation of tensors and tensor-derived measures in diffusional kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Med 65(3):823–836. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22655
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B 103(3):247–254
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, Watkins KE, Ciccarelli O, Cader MZ, Matthews PM, Behrens TE (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31(4):1487–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.024
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM (2012) Fsl. Neuroimage 62(2):782–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015
Mori S, Wakana S, Van Zijl PCM (2005) MRI atlas of human white matter. 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Winkler AM, Ridgway GR, Webster MA, Smith SM, Nichols TE (2014) Permutation inference for the general linear model. Neuroimage 92:381–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.01.060
Smith SM, Nichols TE (2009) Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. Neuroimage 44(1):83–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.061
Follin C, Svard D, van Westen D, Bjorkman-Burtscher IM, Sundgren PC, Fjalldal S, Latt J, Nilsson M, Johanson A, Erfurth EM (2019) Microstructural white matter alterations associated to neurocognitive deficits in childhood leukemia survivors treated with cranial radiotherapy - a diffusional kurtosis study. Acta Oncol:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2019.1571279
Cheng JX, Zhang HY, Peng ZK, Xu Y, Tang H, Wu JT, Xu J (2018) Divergent topological networks in Alzheimer's disease: a diffusion kurtosis imaging analysis. Transl Neurodegener 7:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-018-0115-y
Veraart J, Poot DH, Van Hecke W, Blockx I, Van der Linden A, Verhoye M, Sijbers J (2011) More accurate estimation of diffusion tensor parameters using diffusion kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Med 65(1):138–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22603
Jensen JH, Helpern JA (2010) MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed 23(7):698–710. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1518
Hui ES, Fieremans E, Jensen JH, Tabesh A, Feng W, Bonilha L, Spampinato MV, Adams R, Helpern JA (2012) Stroke assessment with diffusional kurtosis imaging. Stroke 43(11):2968–2973. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.657742
Raab P, Hattingen E, Franz K, Zanella FE, Lanfermann H (2010) Cerebral gliomas: diffusional kurtosis imaging analysis of microstructural differences. Radiology 254(3):876–881. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.09090819
Wu EX, Cheung MM (2010) MR diffusion kurtosis imaging for neural tissue characterization. NMR Biomed 23(7):836–848. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1506
Falangola MF, Guilfoyle DN, Tabesh A, Hui ES, Nie X, Jensen JH, Gerum SV, Hu C, LaFrancois J, Collins HR, Helpern JA (2014) Histological correlation of diffusional kurtosis and white matter modeling metrics in cuprizone-induced corpus callosum demyelination. NMR Biomed 27(8):948–957. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.3140
Hu VW, Nguyen A, Kim KS, Steinberg ME, Sarachana T, Scully MA, Soldin SJ, Luu T, Lee NH (2009) Gene expression profiling of lymphoblasts from autistic and nonaffected sib pairs: altered pathways in neuronal development and steroid biosynthesis. PLoS One 4(6):e5775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005775
Anitha A, Nakamura K, Yamada K, Suda S, Thanseem I, Tsujii M, Iwayama Y, Hattori E, Toyota T, Miyachi T, Iwata Y, Suzuki K, Matsuzaki H, Kawai M, Sekine Y, Tsuchiya K, Sugihara G, Ouchi Y, Sugiyama T, Koizumi K, Higashida H, Takei N, Yoshikawa T, Mori N (2008) Genetic analyses of roundabout (ROBO) axon guidance receptors in autism. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B(7):1019–1027. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.30697
Sbacchi S, Acquadro F, Calo I, Cali F, Romano V (2010) Functional annotation of genes overlapping copy number variants in autistic patients: focus on axon pathfinding. Current genomics 11(2):136–145. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920210790886880
Melin M, Carlsson B, Anckarsater H, Rastam M, Betancur C, Isaksson A, Gillberg C, Dahl N (2006) Constitutional downregulation of SEMA5A expression in autism. Neuropsychobiology 54(1):64–69. https://doi.org/10.1159/000096040
Kalkman HO (2012) A review of the evidence for the canonical Wnt pathway in autism spectrum disorders. Mol Autism 3(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-2392-3-10
Hussman JP, Chung RH, Griswold AJ, Jaworski JM, Salyakina D, Ma D, Konidari I, Whitehead PL, Vance JM, Martin ER, Cuccaro ML, Gilbert JR, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (2011) A noise-reduction GWAS analysis implicates altered regulation of neurite outgrowth and guidance in autism. Mol Autism 2(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-2392-2-1
Morgan JT, Chana G, Pardo CA, Achim C, Semendeferi K, Buckwalter J, Courchesne E, Everall IP (2010) Microglial activation and increased microglial density observed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in autism. Biol Psychiatry 68(4):368–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.05.024
Zikopoulos B, Barbas H (2010) Changes in prefrontal axons may disrupt the network in autism. J Neurosci 30(44):14595–14609. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2257-10.2010
Travers BG, Adluru N, Ennis C, Tromp do PM, Destiche D, Doran S, Bigler ED, Lange N, Lainhart JE, Alexander AL (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging in autism spectrum disorder: a review. Autism Res 5(5):289–313. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1243
Hardan AY, Pabalan M, Gupta N, Bansal R, Melhem NM, Fedorov S, Keshavan MS, Minshew NJ (2009) Corpus callosum volume in children with autism. Psychiatry Res 174(1):57–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2009.03.005
Wolff JJ, Gerig G, Lewis JD, Soda T, Styner MA, Vachet C, Botteron KN, Elison JT, Dager SR, Estes AM, Hazlett HC, Schultz RT, Zwaigenbaum L, Piven J, Network I (2015) Altered corpus callosum morphology associated with autism over the first 2 years of life. Brain 138(Pt 7):2046–2058. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awv118
Meyza KZ, Defensor EB, Jensen AL, Corley MJ, Pearson BL, Pobbe RL, Bolivar VJ, Blanchard DC, Blanchard RJ (2013) The BTBR T+ tf/J mouse model for autism spectrum disorders-in search of biomarkers. Behav Brain Res 251:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2012.07.021
Aylward EH, Minshew NJ, Field K, Sparks BF, Singh N (2002) Effects of age on brain volume and head circumference in autism. Neurology 59(2):175–183
Gibbard CR, Ren J, Seunarine KK, Clayden JD, Skuse DH, Clark CA (2013) White matter microstructure correlates with autism trait severity in a combined clinical-control sample of high-functioning adults. Neuroimage Clin 3:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2013.07.007
Roine U, Salmi J, Roine T, Wendt TN, Leppamaki S, Rintahaka P, Tani P, Leemans A, Sams M (2015) Constrained spherical deconvolution-based tractography and tract-based spatial statistics show abnormal microstructural organization in Asperger syndrome. Mol Autism 6:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-2392-6-4
Wheelwright S, Baron-Cohen S, Goldenfeld N, Delaney J, Fine D, Smith R, Weil L, Wakabayashi A (2006) Predicting autism Spectrum quotient (AQ) from the systemizing quotient-revised (SQ-R) and empathy quotient (EQ). Brain Res 1079(1):47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2006.01.012
Lundqvist LO, Lindner H (2017) Is the autism-spectrum quotient a valid measure of traits associated with the autism spectrum? A Rasch validation in adults with and without autism spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 47(7):2080–2091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-017-3128-y
Beacher FD, Minati L, Baron-Cohen S, Lombardo MV, Lai MC, Gray MA, Harrison NA, Critchley HD (2012) Autism attenuates sex differences in brain structure: a combined voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR 33(1):83–89. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2880
Sotiropoulos SN, Jbabdi S, Xu J, Andersson JL, Moeller S, Auerbach EJ, Glasser MF, Hernandez M, Sapiro G, Jenkinson M, Feinberg DA, Yacoub E, Lenglet C, Van Essen DC, Ugurbil K, Behrens TE, WU-MH C (2013) Advances in diffusion MRI acquisition and processing in the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage 80:125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.057
Ameis SH, Fan J, Rockel C, Voineskos AN, Lobaugh NJ, Soorya L, Wang AT, Hollander E, Anagnostou E (2011) Impaired structural connectivity of socio-emotional circuits in autism spectrum disorders: a diffusion tensor imaging study. PLoS One 6(11):e28044. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028044
Billeci L, Calderoni S, Tosetti M, Catani M, Muratori F (2012) White matter connectivity in children with autism spectrum disorders: a tract-based spatial statistics study. BMC Neurol 12:148. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-12-148
Itahashi T, Yamada T, Nakamura M, Watanabe H, Yamagata B, Jimbo D, Shioda S, Kuroda M, Toriizuka K, Kato N, Hashimoto R (2015) Linked alterations in gray and white matter morphology in adults with high-functioning autism spectrum disorder: a multimodal brain imaging study. Neuroimage Clin 7:155–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2014.11.019
Bakhtiari R, Zurcher NR, Rogier O, Russo B, Hippolyte L, Granziera C, Araabi BN, Nili Ahmadabadi M, Hadjikhani N (2012) Differences in white matter reflect atypical developmental trajectory in autism: a tract-based spatial statistics study. Neuroimage Clin 1(1):48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2012.09.001
Kamagata K, Motoi Y, Tomiyama H, Abe O, Ito K, Shimoji K, Suzuki M, Hori M, Nakanishi A, Sano T, Kuwatsuru R, Sasai K, Aoki S, Hattori N (2013) Relationship between cognitive impairment and white-matter alteration in Parkinson’s disease with dementia: tract-based spatial statistics and tract-specific analysis. Eur Radiol 23(7):1946–1955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2775-4
Acknowledgements
We thank Yuki Takenaka and Mana Kuramochi for their research assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP16H06280, the MEXT-Supported Program for the Private University Research Branding Project and ImPACT Program of Council for Science, Technology and Innovation (Cabinet Office, Government of Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in reports involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants before evaluation.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
Comparison of AK between the ASD and NT groups using uncorrected P-value of 0.05. TBSS analyses show significantly decreased AK in three clusters of white matter in the ASD group compared with the NT group. In TBSS, blue-light blue voxels represent lower AK, and arrows show the peak of each cluster. The FA skeleton with an FA > 0.2 is shown in green. To facilitate visualisation, the results are thickened using the fill script implemented in FSL. AK axial kurtosis, ASD autism spectrum disorder, FA fractional anisotropy, FSL FMRIB software library, NT neurotypical control, PFWE family-wise error-corrected P value, ROI range of interest, TBSS tract-based spatial statistic (PNG 235 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hattori, A., Kamagata, K., Kirino, E. et al. White matter alterations in adult with autism spectrum disorder evaluated using diffusion kurtosis imaging. Neuroradiology 61, 1343–1353 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02238-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02238-5