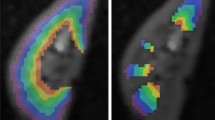
Abstract
Objectives
To compare the sensitivity and early temporal changes of diffusion parameters obtained from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI), q-space analysis (QSA) and bi-exponential modelling in hyperacute stroke patients.
Materials and methods
A single investigational acquisition allowing the four diffusion analyses was performed on seven hyperacute stroke patients with a 3T system. The percentage change between ipsi- and contralateral regions were compared at admission and 24 h later. Two out of the seven patients were imaged every 6 h during this period.
Results
Kurtoses from both DKI and QSA were the most sensitive of the tested diffusion parameters in the few hours following ischemia. An early increase–maximum–decrease pattern of evolution was highlighted during the 24-h period for all parameters proportional to diffusion coefficients. A similar pattern was observed for both kurtoses in only one of two patients.
Conclusion
Our comparison was performed using identical diffusion encoding timings and on patients in the same stage of their condition. Although preliminary, our findings confirm those of previous studies that showed enhanced sensitivity of kurtosis. A fine time mapping of diffusion metrics in hyperacute stroke patients was presented which advocates for further investigations on larger animal or human cohorts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones D (2011) Diffusion MRI: theory, methods and applications. Oxford University Press, New York
Le Bihan D (2011) Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging: introduction and concepts. In: Jones D (ed) Diffusion MRI: theory, methods and applications. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 57–78
Moseley ME, Kucharczyk J, Mintorovitch J, Cohen Y, Kurhanewicz J, Derugin N, Asgari H, Norman D (1990) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of acute stroke: correlation with T2-weighted and magnetic susceptibility-enhanced MR imaging in cats. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 11(3):423–429
Wu O, Nentwich L, Chutinet A (2011) Diffusion in acute stroke. In: Jones D (ed) Diffusion MRI: theory, methods and applications. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 518–528
Basser PJ, Özarslan E (2011) Anisotropic diffusion: from the apparent diffusion coefficient to the apparent diffusion tensor. In: Jones D (ed) Diffusion MRI: theory, methods and applications. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 79–91
Callaghan P (1991) Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance microscopy. Oxford University Press, New York
Callaghan P (2011) Translational dynamics and magnetic resonance: principles of pulsed gradient spin echo NMR. Oxford University Press, New York
Jensen J, Helpern J, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K (2005) Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(6):1432–1440
Kiselev V (2011) The cumulant expansion: an overarching mathematical framework for understanding diffusion NMR. In: Jones D (ed) Diffusion MRI: theory, methods and applications. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 152–168
Westin CF, Knutsson H, Pasternak O, Szczepankiewicz F, Ozarslan E, Van Westen D, Mattisson C, Bogren M, O’Donnell LJ, Kubicki M, Topgaard D, Nilsson M (2016) Q-space trajectory imaging for multidimensional diffusion MRI of the human brain. Neuroimage 135:345–362
Jensen JH, Helpern JA (2010) MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed 23(7):698–710
Niendorf T, Dijkhuizen R, Norris D, Van Lookeren Campagne M, Nicolay K (1996) Biexponential diffusion attenuation in various states of brain tissue: implications for diffusion weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med 36(6):847–857
Kiselev VG, Il’yasov KA (2007) Is the “biexponential diffusion” biexponential? Magn Reson Med 57(3):464–469
Welch KMA, Windham J, Knight RA, Nagesh V, Hugg JW, Jacobs M, Peck D, Booker P, Dereski MO, Levine SR (1995) A model to predict the histopathology of human stroke using diffusion and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 26(11):1983–1989
Jensen J, Falangola M, Hu C, Tabesh A, Rapalino O, Lo C, Helpern J (2011) Preliminary observations of increased diffusional kurtosis in human brain following recent cerebral infarction. NMR Biomed 24(5):452–457
Hui ES, Fieremans E, Jensen JH, Tabesh A, Feng W, Bonilha L, Spampinato MV, Adams R, Helpern JA (2012) Stroke assessment with diffusional kurtosis imaging. Stroke 43(11):2968–2973
Grinberg F, Ciobanu L, Farrher E, Shah NJ (2012) Diffusion kurtosis imaging and log-normal distribution function imaging enhance the visualisation of lesions in animal stroke models. NMR Biomed 25(11):1295–1304
Cheung JS, Wang E, Lo EH, Sun PZ (2012) Stratification of heterogeneous diffusion MRI ischemic lesion with kurtosis imaging: evaluation of mean diffusion and kurtosis MRI mismatch in an animal model of transient focal ischemia. Stroke 43(8):2252–2254
Wu Y, Kim J, Chan ST, Zhou IY, Guo Y, Igarashi T, Zheng H, Guo G, Sun PZ (2016) Comparison of image sensitivity between conventional tensor-based and fast diffusion kurtosis imaging protocols in a rodent model of acute ischemic stroke. NMR Biomed 29(5):625–630
Weber RA, Hui ES, Jensen JH, Nie X, Falangola MF, Helpern JA, Adkins DL (2015) Diffusional kurtosis and diffusion tensor imaging reveal different time-sensitive stroke-induced microstructural changes. Stroke 46(2):545–550
Umesh Rudrapatna S, Wieloch T, Beirup K, Ruscher K, Mol W, Yanev P, Leemans A, Van der Toorn A, Dijkhuizen RM (2014) Can diffusion kurtosis imaging improve the sensitivity and specificity of detecting microstructural alterations in brain tissue chronically after experimental stroke? Comparisons with diffusion tensor imaging and histology. Neuroimage 97:363–373
Hui ES, Du F, Huang S, Shen Q, Duong TQ (2012) Spatiotemporal dynamics of diffusional kurtosis, mean diffusivity and perfusion changes in experimental stroke. Brain Res 1451:100–109
Taoka T, Fujioka M, Kashiwagi Y, Obata A, Rokugawa T, Hori M, Masutani Y, Aoki S, Naganawa S, Abe K (2016) Time course of diffusion kurtosis in cerebral infarctions of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion rat model. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 25(3):610–617
Zhang S, Yao Y, Shi J, Tang X, Zhao L, Zhu W (2016) The temporal evolution of diffusional kurtosis imaging in an experimental middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model. Magn Reson Imaging 34(7):889–895
Taoka T, Fujioka M, Sakamoto M, Miyasaka T, Akashi T, Ochi T, Hori S, Uchikoshi M, Xu J, Kichikawa K (2014) Time course of axial and radial diffusion kurtosis of white matter infarctions: period of pseudonormalization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35(8):1509–1514
Hori M, Motosugi U, Fatima Z, Kumagai H, Ikenaga S, Ishigame K, Aoki S, Onodera T, Yagi K, Araki T (2011) A comparison of mean displacement values using high b value q-space diffusion-weighted MRI with conventional apparent diffusion coefficient in patients with stroke. Acad Radiol 18(7):837–841
Brugières P, Thomas P, Maraval A, Hosseini H, Combes C, Chafiq A, Ruel L, Breil S, Peschanski M, Gaston A (2004) Water diffusion compartmentation at high b values in ischemic brain. Am J Neuroradiol 25(5):692–698
Grinberg F, Farrher E, Ciobanu L, Geffroy F, Le Bihan D, Shah NJ (2014) Non-Gaussian diffusion imaging for enhanced contrast of brain tissue affected by ischemic stroke. PLoS One 9(2):e89225. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089225
Schwarcz A, Bogner P, Meric P, Correze J-L, Berente Z, Pál J, Gallyas F, Doczi T, Gillet B, Beloeil J-C (2004) The existence of biexponential signal decay in magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging appears to be independent of compartmentalization. Magn Reson Med 51(2):278–285
Latt J, Nilsson M, van Westen D, Wirestam R, Stahlberg F, Brockstedt S (2009) Diffusion-weighted MRI measurements on stroke patients reveal water-exchange mechanisms in sub-acute ischaemic lesions. NMR Biomed 22(6):619–628
Baron CA, Kate M, Gioia L, Butcher K, Emery D, Budde M, Beaulieu C (2015) Reduction of diffusion-weighted imaging contrast of acute ischemic stroke at short diffusion times. Stroke 46(8):2136–2141
Mitra PP, Halperin BI (1995) Effects of finite gradient-pulse widths in pulsed-field-gradient diffusion measurements. J Magn Reson Ser A 113(1):94–101
Mitra P, Latour L, Kleinber R, Sotak C (1995) Pulsed field gradient measurements of restricted diffusion and the return-to-origin probability. J Magn Reson A 114(1):47–58
Assaf Y, Ben-Bashat D, Chapman J, Peled S, Biton IE, Kafri M, Segev Y, Hendler T, Korczyn AD, Graif M, Cohen Y (2002) High b value q-space analyzed diffusion-weighted MRI: application to multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Med 47(1):115–126
Lätt J, Nilsson M, Wirestam R, Johansson E, Larsson E-M, Stȧhlberg F, Brockstedt S (2008) In vivo visualization of displacement-distribution-derived parameters in q-space imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 26(1):77–87
Gudbjartsson H, Patz S (1995) The rician distribution of noisy MRI data. J Sci Comput 34(6):910–914
Veraart J, Sijbers J, Sunaert S, Leemans A, Jeurissen B (2013) Weighted linear least squares estimation of diffusion MRI parameters: strengths, limitations, and pitfalls. Neuroimage 81:335–346
Osborne M, Smyth G (1995) A modified Prony algorithm for exponential function fitting. J Sci Comput 16(1):119–138
Peeters F, Rommel D, Abarca-Quinones J, Grégoire V, Duprez T (2012) Early (72-h) detection of radiotherapy-induced changes in an experimental tumor model using diffusion-weighted imaging, diffusion tensor imaging, and Q-space imaging parameters: a comparative study. J Magn Reson Imaging 35(2):409–417
Sun PZ, Wang Y, Mandeville E, Chan S-T, Lo EH, Ji X (2014) Validation of fast diffusion kurtosis MRI for imaging acute ischemia in a rodent model of stroke. NMR Biomed 27(11):1413–1418
Fukunaga I, Hori M, Masutani Y, Hamasaki N, Sato S, Suzuki Y, Kumagai F, Kosuge M, Hoshito H, Kamagata K, Shimoji K, Nakanishi A, Aoki S, Senoo A (2013) Effects of diffusional kurtosis imaging parameters on diffusion quantification. Radiol Phys Technol 6(2):343–348
Le Bihan D (2007) The ‘wet mind’: water and functional neuroimaging. Phys Med Biol 52(7):R57
Nakagawa S (2004) A farewell to Bonferroni: the problems of low statistical power and publication bias. Behav Ecol 15(6):1044–1045
Beauchamp N, Ulug A, Passe T, Van Zijl PCM (1998) MR diffusion imaging in stroke: review and controversies. Imag Thera Techno 18(5):1269–1283
Glenn GR, Helpern JA, Tabesh A, Jensen JH (2015) Quantitative assessment of diffusional kurtosis anisotropy. NMR Biomed 28(4):448–459
Budde MD, Frank JA (2010) Neurite beading is sufficient to decrease the apparent diffusion coefficient after ischemic stroke. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(32):14472–14477
Novikov DS, Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Fieremans E (2014) Revealing mesoscopic structural universality with diffusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(14):5088–5093
An H, Ford AL, Vo K, Powers WJ, Lee J-M, Lin W (2011) Signal evolution and infarction risk for ADC lesions in acute ischemic stroke are both time and perfusion dependent. Stroke 42(5):1276–1281
Nilsson M, Szczepankiewicz F, van Westen D, Hansson O (2015) Extrapolation-based references improve motion and eddy-current correction of high b value DWI data: application in Parkinson’s disease Dementia. PLoS One 10(11):e0141825. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0141825
Ben-Amitay S, Jones DK, Assaf Y (2012) Motion correction and registration of high b value diffusion weighted images. Magn Reson Med 67(6):1694–1702
Acknowledgements
Grant Support
This work was funded by the Fond National de la Recherche Scientifique of Belgium (FNRS-FWO). Grants number: FNRS 3.4.625.06.F
Authors’ contribution
Gaëtan Duchêne: data analysis, Frank Peeters: protocol development and data analysis, André Peeters: data collection, Thierry Duprez: data collection and project development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors involved in the present study declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Research involving human participants
All procedures performed in the present study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of our institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants—or their legal decision-maker substitutes—included in the present study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duchêne, G., Peeters, F., Peeters, A. et al. A comparative study of the sensitivity of diffusion-related parameters obtained from diffusion tensor imaging, diffusional kurtosis imaging, q-space analysis and bi-exponential modelling in the early disease course (24 h) of hyperacute (6 h) ischemic stroke patients. Magn Reson Mater Phy 30, 375–385 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-017-0612-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-017-0612-5