Abstract
The loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta) is a cosmopolitan sea turtle species and is listed by IUCN as Vulnerable globally. The Southwest Atlantic is an important regional management unit of C. caretta worldwide due to the distinctive mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) lineage promoted by recent radiation within the Atlantic-Mediterranean region. However, due to the low resolution of mtDNA, the population structure of C. caretta SWA has not been well understood in the previous studies using only mtDNA. Our study encloses data from literature and a long-term genetic survey (1999 to 2021) distributed through four great nesting areas for the Southwest Atlantic to assess the genetic diversity and the population structure of the C. caretta, using both mtDNA and 15 microsatellite loci. The results demonstrate that the genetic diversity indexes of the Southwest Atlantic C. caretta reflect distinct compositions at a population level due to variation at an individual level. The SSRs results identified well-established and significant spatial population structure between nesting areas. Unique genetic patterns were identified for those females from studied areas of the Southwest Atlantic, and it may be related to their philopatric behavior and high relatedness. Thus, this study deeply evaluated the molecular ecology of Southwest Atlantic C. caretta and provides, for the first time, a fine-scale and long-term resolution of the genetic diversity and population structure due to the use of microsatellite data that must be considered for further studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
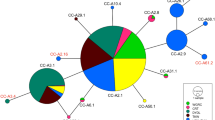
Sequences associated with the D-loop haplotypes (Cc-A4.5, Cc-A4.4, and Cc-A4.6) are deposited at GenBank by accession numbers MZ466566–MZ466568.
References
Abreu-Grobois FA, Horrocks JA, Formia A, Dutton P, LeRoux R, Vélez-Zuazo X, Soares L, Meylán P (2006) New mtDNA Dloop primers which work for a variety of marine turtle species may increase the resolution of mixed stock analysis. In: Frick MA et al. (ed) Proceedings of the 26th Annual Symposium on Sea Turtle Biology Book of Abstracts, Island of Crete: Greece, 179 pp
Adamack AT, Gruber B (2014) PopGenReport: simplifying basic population genetic analyses in R. Methods Ecol Evol 5:384–387. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12158
Almeida CA, de Oliveira AF, Pacheco AA, Lopes RP, Neves AA, de Queiroz MELR (2018) Characterization and evaluation of sorption potential of the iron mine waste after Samarco dam disaster in Doce River basin–Brazil. Chemosphere 209:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.071
Baltazar-Soares M, Klein JD, Correia SM, Reischig T, Taxonera A, Roque SM, Dos Passos L, Durão J, Lomba JP, Dinis H, Cameron SJK, Stiebens VA, Eizaguirre C (2020) Distribution of genetic diversity reveals colonization patterns and philopatry of the loggerhead sea turtles across geographic scales. Sci Rep 10:18001. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-74141-6
Bandelt H-J, Forster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16:37–48
Barreto J, Thomé JC, Baptistotte C, Rieth D, Marcovaldi MÂ, Marcovaldi GGD et al (2019) Reproductive longevity of the loggerhead sea turtle, Caretta caretta, in Espírito Santo, Brazil. Mar Turt Newsl 157: 10–12. http://www.seaturtle.org/mtn/archives/mtn157/mtn157-3.shtml
Bjorndal KA, Bolten AB (2008) Annual variation in source contributions to a mixed stock: implications for quantifying connectivity. Mol Ecol 17:2185–2193
Bonecker ACT, de Castro MS, Costa PG, Bianchini A, Bonecker SLC (2019) Larval fish assemblages of the coastal area affected by the tailings of the collapsed dam in southeast Brazil. Reg Stud Mar Sci 32:100848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2019.100848
Bowem BW, Bass AL, Soares L, Toonen RJ (2005) Conservation implications of complex population structure: lessons from the loggerhead turtle (Caretta caretta). Mol Ecol 14:2389–2402
Bowen BW, Kamezaki N, Limpus CJ, Hughes GR, Meylan AB, Avise JC (1994) Global phylogeography of the loggerhead turtle (Caretta caretta) as indicated by mitochondrial DNA haplotypes. Evol 48:1820–1828
Brasil (2022) Portaria MMA nº 148 de 07 de junho de 2022. Altera os Anexos da Portaria nº 443, de 17 de dezembro de 2014, da Portaria nº 444, de 17 de dezembro de 2014, e da Portaria nº 445, de 17 de dezembro de 2014, referentes à atualização da Lista Nacional de Espécies Ameaçadas de Extinção. Diário Oficial da União de 08.06.2022, Edição 108, Seção 1, p 74. available at: https://www.icmbio.gov.br/cepsul/images/stories/legislacao/Portaria/2020/P_mma_148_2022_altera_anexos_P_mma_443_444_445_2014_atualiza_especies_ameacadas_extincao.pdf
Brown AHD (1970) The estimation of Wright’s fixation index from genotypic frequencies. Genetica 41:399–406
Burritt RL, Christ KL (2018) Water risk in mining: Analysis of the Samarco dam failure. J Clean Prod 178:196–205
Cameron SJ, Baltazar-Soares M, and Eizaguirre C (2019) Region-specific magnetic fields structure sea turtle populations. bioRxiv, 630152. https://doi.org/10.1101/630152
Cantor M, Barreto AS, Taufer RM, Giffoni B, Castilho PV, Maranho A et al (2020) High incidence of sea turtle stranding in the southwestern Atlantic Ocean. ICES J Mar Sci 77:1864–1878. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsaa073
Canzanella S, Danese A, Mandato M, Lucifora G, Riverso C, Federico G, Gallo P, Esposito M (2021) Concentrations of trace elements in tissues of loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta) from the tyrrhenian and the Ionian coastlines (Calabria, Italy). Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:26545–26557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12499-4
Carreras C, Pascual M, Cardona L, Aguilar A, Margaritoulis D, Rees A et al (2007) The genetic structure of the loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta) in the mediterranean as revealed by nuclear and mitochondrial DNA and its conservation implications. Conserv Genet 8:761–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-006-9224-8
Carreras C, Pascual M, Tomás J, Marco A, Hochscheid S, Castillo JJ et al (2018) Sporadic nesting reveals long distance colonisation in the philopatric loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta). Sci Rep 8:1435. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19887-w
Casale P and Tucker AD (2017) Caretta caretta (amended version of 2015 assessment). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: .T3897A119333622. https://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T3897A119333622.en. Downloaded on 03 April 2021.
Clusa M, Carreras C, Pascual M, Gaughran SJ, Piovano S, Avolio D et al (2016) Potential bycatch impact on distinct sea turtle populations is dependent on fishing ground rather than gear type in the Mediterranean Sea Mar Biol 163:1–10
Clusa M, Carreras C, Cardona L, Demetropoulos A, Margaritoulis D, Rees AF, Hamza AA, Khalil M, Levy Y, Turkozan O, Aguilar A, Pascual M (2018) Philopatry in loggerhead turtles Caretta caretta: beyond the gender paradigm. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 588:201–213. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps12448
Coimbra KTO, Alcântara E, de Souza Filho CR (2020) Possible contamination of the Abrolhos reefs by Fundao dam tailings, Brazil-New constraints based on satellite data. Sci Total Environ 733:138101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138101
Colman LP, Lara PH, Bennie J, Broderick AC, de Freitas JR, Marcondes A et al (2020) Assessing coastal artificial light and potential exposure of wildlife at a national scale: the case of marine turtles in Brazil. Biodivers Conserv 29:1135–1152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-019-01928-z
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Duchene S, Frey A, Alfaro-Núñez A, Dutton PH, Gilbert MTP, Morin PA (2012) Marine turtle mitogenome phylogenetics and evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 65:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.06.010
Dutton PH, Roden SE, Stewart KR, LaCasella E, Tiwari M, Formia A, Thomé JC, Livingstone SR, Eckert E, Chacon-Chaverri D, Rivalan P, Allman P (2013) Population stock structure of leatherback turtles (Dermochelys coriacea) in the Atlantic revealed using mtDNA and microsatellite markers. Conserv Genet 14:625–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-013-0456-0
Erb V, Wyneken J (2019) Nest-to-Surf Mortality of Loggerhead Sea Turtle (Caretta caretta) Hatchlings on Florida’s East Coast. Front Mar Sci 6:271. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2019.00271
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/131.2.479
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform 1:47–50
Fernandes GW, Goulart FF, Ranieri BD, Coelho MS, Dales K, Boesche N et al (2016) Deep into the mud: ecological and socio-economic impacts of the dam breach in Mariana, Brazil. Nat Conservacao 14:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncon.2016.10.003
FitzSimmons NN, Pittard SD, McIntyre N, Jensen MP, Guinea M, Hamann M et al (2020) Phylogeography, genetic stocks, and conservation implications for an Australian endemic marine turtle. Aquat Conserv 30:440–460. https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.3270
Freire JB, Sousa RM, Taufner K, Carneiro MT, Filgueiras HR, Lenz D, Ferreira PD, Endringer CD (2021) Metals in eggs and hatchlings of Dermochelys coriacea (Testudines) in Espírito Santo, Brazil and their relation to hatching and emergence success. Mar Ecol 42:e12633. https://doi.org/10.1111/maec.12633
Frossard A, Vieira LV, Carneiro MTWD, Gomes LC, Chippari-Gomes AR (2020) Accumulation of trace metals in eggs and hatchlings of Chelonia mydas. J Trace Elem Med Bio 62:126654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126654
Gallego-García N, Forero-Medina G, Vargas-Ramírez M, Caballero S, Shaffer HB (2018) Landscape genomic signatures indicate reduced gene flow and forest-associated adaptive divergence in an endangered neotropical turtle. Mol Ecol 28:2757–2771. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15112
Hatje V, Pedreira RM, de Rezende CE, Schettini CAF, de Souza GC, Marin DC, Hackspacher PC (2017) The environmental impacts of one of the largest tailing dam failures worldwide. Sci Rep 7:10706. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11143-x
Hawkes LA, Broderick AC, Godfrey MH, Godley BJ (2007) Investigating the potential impacts of climate change on a marine turtle population. Glob Change Biol 13:923–932. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01320.x
IBAMA (2015) Laudo técnico Preliminar: Impactos Ambientais Decorrentes do Desastre Envolvendo O Rompimento da Barragem de Fundão, Em Mariana, Minas Gerais [Preliminary Technical Report: Environmental Impacts of the Disaster Involving the Disruption of Fundão Dam in Mariana, Minas Gerais].
Jerez S, Motas M, Cánovas RA, Talavera J, Almela RM, Del Río AB (2010) Accumulation and tissue distribution of heavy metals and essential elements in loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta) from Spanish mediterranean coastline of Murcia. Chemosphere 78:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.10.062
Jombart T (2008) Adegenet: A R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 24:1403–1405. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btn129
Jombart T, Devillard S, Balloux F (2010) Discriminant analysis of principal components: a new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC Genet 11:94. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-11-94
Kalinowski ST, Wagner AP, Taper ML (2006) ML-Relate: a computer program for maximum likelihood estimation of relatedness and relationship. Mol Ecol Notes 6:576–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01256.x
Kawashima R, Ji Y, Maruyama K (2009) FreeNA: a multi-platform framework for inserting upper-layer network services. IEICE T Inf Syst 92:1923–1933. https://doi.org/10.1587/transinf.E92.D.1923
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S et al (2012) Geneious basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28:1647–1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
Keenan K, McGinnity P, Cross TF, Crozier WW, Prodöhl PA (2013) diveRsity: an R package for the estimation and exploration of population genetics parameters and their associated errors. Methods Ecol Evol 4:782–788. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12067
Kobayashi S, Wada M, Fujimoto R, Kumazawa Y, Arai K, Watanabe G, Saito T (2017) The effects of nest incubation temperature in embryos and hatchlings of the loggerhead sea turtle: implications of sex difference for survival rates during early life stages. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 486:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2016.10.020
Komoroske LM, Jensen MP, Stewart KR, Shamblin BM, Dutton PH (2017) Advances in the application of genetics in marine turtle biology and conservation. Front Mar Sci 4:156. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2017.00156
Lacerda D, dos Santos Vergilio C, da Silva Souza T, Costa LHV, Rangel TP, de Oliveira BCV et al (2020) Comparative metal accumulation and toxicogenetic damage induction in three neotropical fish species with distinct foraging habits and feeding preferences. Ecotox Environ Saf 195:110449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110449
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187
Lima EPE, Wanderlinde J, de Almeida DT, Lopez G, Goldberg DW (2012) Nesting ecology and conservation of the loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Chelonian Conserv Biol 11:249–254. https://doi.org/10.2744/CCB-0996.1
Lockley EC, Lockley EC, Fouda L, Correia SM, Taxonera A, Nash LN, Fairweather K, Reischig T, Durão J, Dinis H, Roque SM, Lomba JP, Passos L, Cameron SJK, Stiebens VA, Eizaguirre C (2020) Long-term survey of sea turtles (Caretta caretta) reveals correlations between parasite infection, feeding ecology, reproductive success and population dynamics. Sci Rep 10:18569. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-75498-4
Loisier A, Savelli MP, Arnal V, Claro F, Gambaiani D, Sénégas JB et al (2021) Genetic composition, origin and conservation of loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta) frequenting the French mediterranean coasts. Mar Biol 168:52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-021-03855-6
Lopez GG, Saliés EDC, Lara PH, Tognin F, Marcovaldi MA, Serafini TZ (2015) Coastal development at sea turtles nesting ground: efforts to establish a tool for supporting conservation and coastal management in northeastern Brazil. Ocean Coast Manage 116:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2015.07.027
López-Mendilaharsu M, Giffoni B, Monteiro D, Prosdocimi L, Vélez-Rubio GM, Fallabrino A et al (2020) Multiple-threats analysis for loggerhead sea turtles in the southwest Atlantic Ocean. Endanger Species Res 41:183–196. https://doi.org/10.3354/esr01025
Luschi P, Casale P (2014) Movement patterns of marine turtles in the mediterranean sea: a review. Ital J Zool 81:478–495. https://doi.org/10.1080/11250003.2014.963714
Lynch M, Ritland K (1999) Estimation of pairwise relatedness with molecular markers. Genetics 152:1753–1766. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/152.4.1753
Magris RA, Marta-Almeida M, Monteiro JAF, Ban NC (2019) A modeling approach to assess the impact of land mining on marine biodiversity: assessment in coastal catchments experiencing catastrophic events (SW Brazil). Sci Total Environ 659:828–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.238
Marcovaldi MA, Chaloupka M (2007) Conservation status of the loggerhead sea turtle in Brazil: an encouraging outlook. Endanger Species Res 3:133–143. https://doi.org/10.3354/esr003133
Marcovaldi MÂ, Lopez GG, Soares LS, Lima EH, Thomé JC, Almeida AP (2010) Satellite-tracking of female loggerhead turtles highlights fidelity behavior in northeastern Brazil. Endanger Species Res 12:263–272. https://doi.org/10.3354/esr00308
Marcovaldi MA, López-Mendilaharsu M, Santos AS, Lopez GG, Godfrey MH, Tognin F et al (2016) Identification of loggerhead male producing beaches in the south Atlantic: implications for conservation. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 477:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2016.01.001
Marcovaldi MÂ, Santos AS, Lara PH, López-Mendilaharsu M (2017) Novel Research Techniques Provide New Insights to the Sea Turtle Life Cycle. Advances in Marine Vertebrate Research in Latin America. Springer, Cham, pp 169–195
Marcovaldi MA, Sales G, Thomé JC, da Silva ACCD, Gallo BM, Lima EHSM et al (2006) Sea turtles and fishery interactions in Brazil: identifying and mitigating potential conflicts. Mar Turt Newsl 112: 4–8. http://www.seaturtle.org/mtn/archives/mtn112/mtn112p4.shtml
Martín-del-Campo R, Calderón-Campuzano MF, Rojas-Lleonart I, Briseño-Dueñas R, García-Gasca A (2021) Congenital malformations in sea turtles: puzzling interplay between genes and environment. Animals 11:444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020444
Matsuzawa Y, Kamezaki N, Ishihara T, Omuta K, Takeshita H, Goto K et al (2016) Fine-scale genetic population structure of loggerhead turtles in the Northwest Pacific. Endanger Species Res 30:83–93. https://doi.org/10.3354/esr00724
McCallum ML (2021) Turtle biodiversity losses suggest coming sixth mass extinction. Biodivers Conserv 30:1257–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-021-02140-8
McClellan CM, Read AJ (2007) Complexity and variation in loggerhead sea turtle life history. Biol Lett 3:592–594. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2007.0355
Medeiros L, Monteiro DS, Botta S, Proietti MC, Secchi ER (2019) Origin and foraging ecology of male loggerhead sea turtles from southern Brazil revealed by genetic and stable isotope analysis. Mar Biol 166:76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-019-3524-2
Miguel C, Costa PG, Bianchini A, Luzardo OLP, Vianna MRM, de Deus Santos MR (2022) Health condition of chelonia mydas from a foraging area affected by the tailings of the collapsed dam in southeast Brazil. Sci Total Environ 821:153353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153353
Mills LS, Allendorf EW (1996) The one-migrant-per-generation rule in conservation and management. Conserv Biol 6:1509–1518. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1739.1996.10061509.x
Monteiro CC, Carmo HM, Santos AJ, Corso G, Sousa-Lima RS (2019) First record of bioacoustic emission in embryos and hatchlings of hawksbill sea turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata). Chelonian Conserv Biol 18:273–278. https://doi.org/10.2744/CCB-1382.1
Monzón-Argüello C, Rico C, Naro-Maciel E, Varo-Cruz N, López P, Marco A, López-Jurado LF (2010) Population structure and conservation implications for the loggerhead sea turtle of the Cape Verde Islands. Conserv Genet 11:1871–1884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-010-0079-7
Moore MK, Ball RM (2002) Multiple paternity in loggerhead turtle (Caretta Caretta) nests on melbourne beach, florida: a microsatellite analysis. Mol Ecol 11:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01426.x
Naro-Maciel E, Becker JH, Lima EH, Marcovaldi MA, DeSalle R (2007) Testing dispersal hypotheses in foraging green sea turtles (Chelonia mydas) of Brazil. J Hered 98:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esl050
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. P Natl A Sci 70:3321–3323. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.70.12.3321
Nei M (1977) F-statistics and analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Ann Hum Genet 41:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.1977.tb01918.x
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. PNAS 76:5269–5273. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269
Orlóci L (2013) Multivariate analysis in vegetation research. Springer
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2005.01155.x
Pike DA (2013) Forecasting range expansion into ecological traps: climate-mediated shifts in sea turtle nesting beaches and human development. Glob Change Biol 19:3082–3092. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12282
Rees AF, Alfaro-Shigueto J, Barata PCR, Bjorndal KA, Bolten AB, Bourjea J, Godley BJ (2016) Are we working towards global research priorities for management and conservation of sea turtles? Endanger Species Res 31:337–382. https://doi.org/10.3354/esr00801
Reid BN, Naro-Maciel E, Hahn AT, FitzSimmons NN, Gehara M (2019) Geography best explains global patterns of genetic diversity and postglacial co-expansion in marine turtles. Mol Ecol 28:3358–3370. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15165
Reis EC, Soares LS, Vargas SM, Santos FR, Young RJ, Bjorndal KA, Bolten AB, Lôbo-Hajdu G (2010) Genetic composition, population structure and phylogeography of the loggerhead sea turtle: colonization hypothesis for the Brazilian rookeries. Conserv Genet 11:1467–1477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-009-9975-0
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Santos RG, Martins AS, da Nobrega FJ, Horta PA, Pinheiro HT, Torezani E et al (2011) Coastal habitat degradation and green sea turtle diets in Southeastern Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 62:1297–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.03.004
Segura FR, Nunes EA, Paniz FP, Paulelli ACC, Rodrigues GB, Braga GUL, dos Pedreira Filho W, R., Barbosa Jr, F., Cerchiaro, G., Silva, F.F., Batista, B.L., (2016) Potential risks of the residue from Samarco’s mine dam burst (Bento Rodrigues, Brazil). Environ Pollut 218:813–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.005
Shamblin BM, Faircloth BC, Dodd M, Wood-Jones ALICIA, Castleberry SB, Carroll JP, Nairn CJ (2007) Tetranucleotide microsatellites from the loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta Caretta). Mol Ecol Resour 7:784–787. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01701.x
Shamblin BM, Faircloth BC, Dodd MG, Bagley DA, Ehrhart LM, Dutton PH, Frey A, Nairn CJ (2009) Tetranucleotide markers from the loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta Caretta) and their cross-amplification in other marine turtle species. Conserv Genet 10:577–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-008-9573-6
Shamblin BM, Dodd MG, Williams KL, Frick MG, Bell R, Nairn CJ (2011) Loggerhead turtle eggshells as a source of maternal nuclear genomic DNA for population genetic studies. Mol Ecol Resour 11:110–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02910.x
Shamblin BM, Bolten AB, Bjorndal KA, Dutton PH, Nielsen JT, Abreu-Grobois FA et al (2012) Expanded mitochondrial control region sequences increase resolution of stock structure among North Atlantic loggerhead turtle rookeries. Mar Ecol Progress Ser 469:145–160. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09980
Shamblin BM, Bolten AB, Abreu-Grobois FA, Bjorndal KA, Cardona L, Carreras C, Nel R (2014) Geographic patterns of genetic variation in A broadly distributed marine vertebrate: new insights into loggerhead turtle stock structure from explanded mitochondrial Dna sequences. PLoS ONE 9:E85956. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085956
Slatkin M (1995) A measure of population subdivision based on microsatellite allele frequencies. Genetics 139(1):457–462
Soares LS, Bjorndal KA, Bolten AB, Wayne ML, Castilhos JC, Weber MI et al (2021) Reproductive output, foraging destinations, and isotopic niche of olive ridley and loggerhead sea turtles, and their hybrids, in Brazil. Endanger Species Res 44:237–251. https://doi.org/10.3354/esr01095
Stewart KR, LaCasella EL, Jensen MP, Epperly SP, Haas HL, Stokes LW, Dutton PH (2019) Using mixed stock analysis to assess source populations for at-sea bycaught juvenile and adult loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta) in the north-west Atlantic. Fish Fish 20:239–254. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12336
Team RDC (2021) R Programming. R Development Core Team. https://www.r-project.org/
Thompson J, Gibson T, and Higgens D (1996) Clustal W version 1.6. EMBL: 1.
Uller T, Olsson M (2008) Multiple paternity in reptiles: patterns and processes. Mol Ecol 17:2566–2580. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03772.x
van Oosterhout C, Hutchinson WF, Wills DP, Shipley P (2004) MICRO-CHECKER: software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol Ecol Notes 4:535–538. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2004.00684.x
Vargas SM, Barcelos AC, Rocha RG, Guimarães P, Amorim L, Martinelli A, Santos FR, Erickson J, Marcondes ACJ, Ludwig S (2022) Genetic monitoring of the critically endangered leatherback turtle (Dermochelys coriacea) in the South West Atlantic. Reg Stud Mar Sci 25:102530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2022.102530
Vergilio C, Lacerda DS, da Silva ST, de Oliveira BCV, Fioresi VS, de Souza VV et al (2021) Immediate and long-term impacts of one of the worst mining tailing dam failure worldwide (Bento Rodrigues, Minas Gerais, Brazil). Sci Total Environ 756:143697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143697
Vilaça ST, Piccinno R, Rota-Stabelli O, Gabrielli M, Benazzo A, Matschiner M et al (2021) Divergence and hybridization in sea turtles: inferences from genome data show evidence of ancient gene flow between species. Mol Ecol 30:6178–6192. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.16113
Wallace BP, DiMatteo AD, Hurley BJ, Finkbeiner EM, Bolten AB, Chaloupka MY et al (2010) Regional management units for marine turtles: a novel framework for prioritizing conservation and research across multiple scales. PLoS ONE 5:e15465. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015465
Yipel M, Tekeli İO, İşler CT, Altuğ ME (2017) Heavy metal distribution in blood, liver and kidneys of Loggerhead (Caretta caretta) and green (Chelonia mydas) sea turtles from the Northeast mediterranean sea. Mar Pollut Bull 125:487–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.08.011
Acknowledgements
The present study was carried out as part of the Aquatic Biodiversity Monitoring Program, Ambiental Area I, established by the Technical-Scientific Agreement (DOU number 30/2018) between FEST/RRDM and Renova Foundation. This study was supported in part by the IBAMA/ICMBio, the Fundação Projeto TAMAR, CAPES, FAPES, and the Federal University of Espírito Santo. We thank FEST for the scholarships, the Marcos Daniel Institute, Tommy Magalhães, and Fundação Projeto TAMAR for the fieldwork, Luciano Soares, Juliana Justino, Monique Nascimento, and the Núcleo de Genética aplicada à Conservação da Biodiversidade for technical support.
Funding
This work was supported by the IBAMA/ICMBio, Fundação Projeto Tamar, and the work of Sarah Maria Vargas was supported by Fest/RRDM and Renova Foundation, 30/2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SL and SMV designed the study; ACB, JE, LA, and PRLG carried out field and laboratory work; SL analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; SL, LM, and SMV reviewed the drafts; SMV supervised and coordinated the project; All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: C. Eizaguirre .
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ludwig, S., Amorim, L., Barcelos, A.C. et al. Going deeper into the molecular ecology of the Southwest Atlantic Caretta caretta (Testudinata: Cheloniidae), what do microsatellites reveal to us?. Mar Biol 170, 78 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-023-04212-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-023-04212-5