Abstract
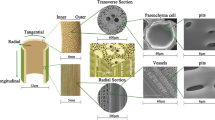
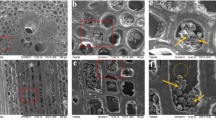
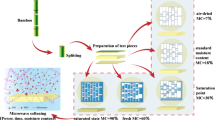
Bamboo is known to be a sustainable material with fast growth and high mechanical properties, while the high hygroscopicity and low-dimensional stability limit its further utilization in the construction sector. Thus, a novel dual modification method combining maleic anhydride and tung oil heat treatment was firstly applied to bamboo, and an orthogonal experiment was designed to investigate the influence of the processing parameter on the physical properties of bamboo, including weight change rate (WCR), moisture excluding efficiency (MEE) and anti-swelling efficiency (ASE). Furthermore, the morphological characteristics, chemical structure and water status of modified bamboo were also studied. The results showed that a parameter combination of maleic anhydride pretreatment at 80 °C for 3 h and tung oil heat treatment at 140 °C for 3 h was considered as an optimized process. The MEE and ASE (volume) of the modified bamboo could reach approximately 80 and 60%, respectively. Maleic anhydride was deposited on the cell wall and the reaction sites were grafted onto the bamboo by esterification. A portion of tung oil could be impregnated into the bamboo and occluded the water channel, such as vessels and pits, and the chemical linkage between the modified bamboo and tung oil was then established during heat treatment through the Diels–Alder reaction. Additionally, the dual modification method not only changed the water distribution of bamboo, but also shortened the spin–spin relaxation time (T2) of the bound water and free water.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida G, Gagné S, Hernández RE (2006) A NMR study of water distribution in hardwoods at several equilibrium moisture contents. Wood Sci Technol 41:293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-006-0116-3
Bickford WG, DuPrée F, Mack CH, O’Connor RT (1953) The infrared spectra and the structural relationships between alpha- and beta-eleostearic acids and their maleic anhydride adducts. J Am Oil Chem Soc 30:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02633774
Biermann U, Butte W, Eren T, Haase D, Metzger JO (2007) Regio- and stereoselective Diels-Alder additions of maleic anhydride to conjugated triene fatty acid methyl esters. Eur J Org Chem 2007:3859–3862. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.200700243
Can A, Sivrikaya H (2016) Dimensional stabilization of wood treated with tall oil dissolved in different solvents. Maderas-Cienc Tecnol 18:317–324. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0718-221x2016005000029
Chen W, Yu H, Liu Y, Hai Y, Zhang M, Chen P (2011) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibers from four plant cellulose fibers using a chemical-ultrasonic process. Cellulose 18:433–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9497-z
Chen J, Wang Y, Cao J, Wang W (2020) Improved water repellency and dimensional stability of wood via impregnation with an epoxidized linseed oil and carnauba wax complex emulsion. Forests 11:271. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11030271
Cheng D, Li T, Smith GD, Xu B, Li Y (2018) The properties of moso bamboo heat-treated with silicon oil. Eur J Wood Prod 76:1273–1278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-018-1301-4
Cui W, Li X, Zhou S, Weng J (2007) Investigation on process parameters of electrospinning system through orthogonal experimental design. J Appl Polym Sci 103:3105–3112. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.25464
Fredriksson M, Thygesen LG (2017) The states of water in Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) studied by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (LFNMR) relaxometry: assignment of free-water populations based on quantitative wood anatomy. Holzforschung 71:77–90. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2016-0044
Gao Y, Xu K, Peng H, Jiang J, Zhao R, Lu J (2019) Effect of heat treatment on water absorption of chinese fir using TD-NMR. Appl Sci 9:78. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/9/1/78.
Gao J, Qu L, Qian J, Wang Z, Li Y, Yi S, He Z (2020) Effects of combined acid-alkali and heat treatment on the physiochemical structure of moso bamboo. Sci Rep 10:6760. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63907-7
Ghorbani M, Shahmirzadi AN, Amininasab SM (2017) Physical and morphological properties of combined treated wood polymer composites by maleic anhydride and methyl methacrylate. J Wood Chem Technol 37:443–450. https://doi.org/10.1080/02773813.2017.1310902
Guo Y, Zhang M, Xiao Z, Chen H, Xie Y (2018) Vaporization heat of bound water in wood chemically modified via grafting and crosslinking patterns by DSC and NMR analysis. Holzforschung 72:1043–1049. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2017-0210
Guo F, Zhang X, Yang R, Salmén L, Yu Y (2021) Hygroscopicity, degradation and thermal stability of isolated bamboo fibers and parenchyma cells upon moderate heat treatment. Cellulose 28:8867–8876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04050-y
Hao X, Wang Q, Wang Y, Han X, Yuan C, Cao Y, Lou Z, Li Y (2021) The effect of oil heat treatment on biological, mechanical and physical properties of bamboo. J Wood Sci 67:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10086-021-01959-7
He Z, Qian J, Qu L, Yan N, Yi S (2019) Effects of tung oil treatment on wood hygroscopicity, dimensional stability and thermostability. Ind Crops Prod 140:111647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111647
He M, Xu D, Li C, Ma Y, Dai X, Pan X, Fan J, He Z, Gui S, Dong X, Li Y (2020) Cell wall bulking by maleic anhydride for wood durability improvement. Forests 11:367. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11040367
Hone T, Cahill L, Robinson A, Korde C, Taylor D (2020) The splitting of bamboo in response to changes in humidity and temperature. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 111:103990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2020.103990
Huang Y, Pang L, Wang H, Zhong R, Zeng Z, Yang J (2013) Synthesis and properties of UV-curable tung oil based resins via modification of Diels-Alder reaction, nonisocyanate polyurethane and acrylates. Prog Org Coat 76:654–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2012.12.005
Huang J, Yuan T, Ye X, Man L, Zhou C, Hu Y, Zhang C, Yang Z (2018) Study on the UV curing behavior of tung oil: mechanism, curing activity and film-forming property. Ind Crops Prod 112:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.10.061
Humar M, Lesar B (2013) Efficacy of linseed- and tung-oil-treated wood against wood-decay fungi and water uptake. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 85:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.07.011
Iwamoto Y, Itoh T, Minato K (2005) Vapor phase reaction of wood with maleic anhydride (II): mechanism of dimensional stabilization. J Wood Sci 51:601–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10086-005-0712-0
Kondratyeva E, Safiullin K, Motygullin I, Klochkov A, Tagirov M, Reita V (2016) Thermal modification of wood and a complex study of its properties by magnetic resonance and other methods. Wood Sci Technol 50:895–916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-016-0825-1
Labbé N, De Jéso B, Lartigue JC, Daudé G, Pétraud M, Ratier M (2006) Time-domain 1H NMR characterization of the liquid phase in greenwood. Holzforschung 60:265–270. https://doi.org/10.1515/HF.2006.043
Lacerda TM, Carvalho AJF, Gandini A (2014) Two alternative approaches to the Diels-Alder polymerization of tung oil. RSC Adv 4:26829–26837. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra03416c
Lee SH, Ashaari Z, Lum WC, Halip JA, Ang AF, Tan LP, Chin KL, Tahir PM (2018) Thermal treatment of wood using vegetable oils: areview. Constr Build Mater 181:408–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.06.058
Li A, Li K (2015) Pressure-sensitive adhesives based on tung oil. RSC Adv 5:85264–85271. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA15144A
Li J, Ma E (2021) Characterization of water in wood by time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (TD-NMR): a review. Forests 12:886. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070886
Li Y, Dong X, Liu Y, Li J, Wang F (2011) Improvement of decay resistance of wood via combination treatment on wood cell wall: Swell-bonding with maleic anhydride and graft copolymerization with glycidyl methacrylate and methyl methacrylate. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65:1087–1094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.08.009
Li Y, Wu Q, Li J, Liu Y, Wang X-M, Liu Z (2012) Improvement of dimensional stability of wood via combination treatment: swelling with maleic anhydride and grafting with glycidyl methacrylate and methyl methacrylate. Holzforschung 66:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1515/HF.2011.123
Li L, Liu G, Zhang C, Ou Q, Zhang L, Zhao X (2013) Discrimination of bamboo using FTIR spectroscopy and statistical analysis. Spectrosc Spectral Anal 33:3221–3225. https://doi.org/10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)12-3221-05
Li S, Han K, Li J, Li M, Lu C (2017) Preparation and characterization of super activated carbon produced from gulfweed by KOH activation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 243:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.02.052
Li J, Chen Y, Xu J, Ren D, Yu H, Guo F, Wu Z (2018) The influence of media treatments on color changes, dimensional stability, and cracking behavior of bamboo scrimber. Int J Polym Sci 2018:6068589. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6068589
Li J, Ma E, Yang T (2019) Differences between hygroscopicity limit and cell wall saturation investigated by LF-NMR on southern pine (Pinus spp.). Holzforschung 73:911–921. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2018-0257
Liu W, Zheng Y, Hu X, Han X, Chen Y (2019) Interfacial bonding enhancement on the epoxy adhesive joint between engineered bamboo and steel substrates with resin pre-coating surface treatment. Wood Sci Technol 53:785–799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-019-01109-9
Meng Fd, Yu Yl, Zhang Ym, Yu Wj, Gao Jm (2016) Surface chemical composition analysis of heat-treated bamboo. Appl Surf Sci 371:383–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.015
Mohebby B, Kevily H, Kazemi-Najafi S (2014) Oleothermal modification of fir wood with a combination of soybean oil and maleic anhydride and its effects on physico-mechanical properties of treated wood. Wood Sci Technol 48:797–809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-014-0640-5
Passarini L, Zelinka SL, Glass SV, Hunt CG (2017) Effect of weight percent gain and experimental method on fiber saturation point of acetylated wood determined by differential scanning calorimetry. Wood Sci Technol 51:1291–1305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-017-0963-0
Qi X, Chu J, Jia L, Kumar A (2019) Influence of different pretreatments on the structure and hydrolysis behavior of bamboo: a comparative study. Materials 12:2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162570
Schönemann A, Edwards HGM (2011) Raman and FTIR microspectroscopic study of the alteration of Chinese tung oil and related drying oils during ageing. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:1173–1180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4855-0
Siimer K, Kaljuvee T, Christjanson P, Lasn I (2006) Curing of urea-formaldehyde resins on a wood substrate. J Therm Anal Calorim 84:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-7185-7
Singh AP, Causin V, Nuryawan A, Park BD (2014) Morphological, chemical and crystalline features of urea–formaldehyde resin cured in contact with wood. Eur Polym J 56:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.04.014
Sun Y, Lin L (2010) Hydrolysis behavior of bamboo fiber in formic acid reaction System. J Agric Food Chem 58:2253–2259. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf903731s
Tamburini D, Sardi D, Spepi A, Duce C, Tinè MR, Colombini MP, Bonaduce I (2016) An investigation into the curing of urushi and tung oil films by thermoanalytical and mass spectrometric techniques. Polym Degrad Stab 134:251–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.10.015
Tang T, Chen X, Zhang B, Liu X, Fei B (2019a) Research on the physico-mechanical properties of moso bamboo with thermal treatment in tung oil and its influencing factors. Materials 12:599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12040599
Tang T, Zhang B, Liu X, Wang W, Chen X, Fei B (2019b) Synergistic effects of tung oil and heat treatment on physicochemical properties of bamboo materials. Sci Rep 9:12824. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49240-8
Telkki VV, Yliniemi M, Jokisaari J (2013) Moisture in softwoods: fiber saturation point, hydroxyl site content, and the amount of micropores as determined from NMR relaxation time distributions. Holzforschung 67:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2012-0057
Thygesen LG, Elder T (2008) Moisture in untreated, a cetylated, and furfurylated Norway spruce studied during drying using time domain NMR. Wood Fiber Sci 40:309–320
Thygesen LG, Ehmcke G, Barsberg S, Pilgård A (2020) Furfurylation result of Radiata pine depends on the solvent. Wood Sci Technol 54:929–942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-020-01194-1
Wang F, Shao Z (2020) Study on the variation law of bamboo fibers’ tensile properties and the organization structure on the radial direction of bamboo stem. Ind Crops Prod 152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112521
Wang W, Chen J, Cao J (2019) Using low-field NMR and MRI to characterize water status and distribution in modified wood during water absorption. Holzforschung 73:997–1004. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2018-0293
Wang Z, Li H, Yang D, Xiong Z, Sayed U, Lorenzo R, Corbi I, Corbi O, Hong C (2021) Bamboo node effect on the tensile properties of side press-laminated bamboo lumber. Wood Sci Technol 55:195–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-020-01251-9
Weiland JJ, Guyonnet R (2003) Study of chemical modifications and fungi degradation of thermally modified wood using DRIFT spectroscopy. Holz Roh Werkst 61:216–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-003-0364-y
Wu H, Xu D, Zhou Y, Gao C, Guo J, He W, He Y, Qin S (2020) Tung oil anhydride modified hemp fiber/polypropylene composites: the improved toughness, thermal stability and rheological property. Fibers Polym 21:2084–2091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-1157-1
Xu K, Lu J, Gao Y, Wu Y, Li X (2017) Determination of moisture content and moisture content profiles in wood during drying by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Drying Technol 35:1909–1918. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2017.1291519
Xu M, Wang C, Lyu G, Zhong L, Yang L, Wang Z, Qin C, Ji X, Yang G, Chen J, Xu F (2019) Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of milled wood lignin from xylose residue and corncob. Polymers-Basel 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122092
Xu L, Qian R, Zhao J, Yang W, Gao J, Wang Q, Zhu Y, Zhuo S (2021) Efficient identification of raw and ripe tung oil using headspace GC-MS. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 35:e9156. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.9156
Yan L, Cao J, Gao W, Zhou X, Zhao G (2011) Interaction between glycerin and wood at various temperatures from stress relaxation approach. Wood Sci Technol 45:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-010-0322-x
Yang TH, Lee CH, Lee CJ, Cheng Y (2016) Effects of different thermal modification media on physical and mechanical properties of moso bamboo. Constr Build Mater 119:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.04.156
Yoo Y, Youngblood JP (2017) Tung oil wood finishes with improved weathering, durability, and scratch performance by addition of cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:24936–24946. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b04931
Yuan Z, Wu X, Wang X, Zhang X, Yuan T, Liu X, Li Y (2020) Effects of one-step hot oil treatment on the physical, mechanical, and surface properties of bamboo scrimber. Molecules 25:4488. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194488
Zhang H, Li W, Xu J, Shang S, Song Z (2021) Synthesis and characterization of bio-based epoxy thermosets using rosin-based epoxy monomer. Iran Polym J 30:643–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-021-00918-9
Zhuang Y, Ren Z, Jiang L, Zhang J, Wang H, Zhang G (2018) Raman and FTIR spectroscopic studies on two hydroxylated tung oils (HTO) bearing conjugated double bonds. Spectrochim Acta, Part A 199:146–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.03.020
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China [2018YFD0600305].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Zhang, T., Zhao, X. et al. Improvement in hygroscopicity and dimensional stability of bamboo through a synthetic modification of maleic anhydride with tung oil heat treatment. Wood Sci Technol 56, 1377–1400 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-022-01410-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-022-01410-0