Abstract
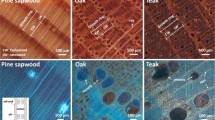
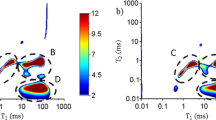
The water state of one tropical (Robinia coccinea) and two temperate (Acer saccharum and Fagus grandifolia) hardwoods was determined at different equilibrium moisture contents (EMC) during desorption at 25°C. NMR technique was used to separate different components of water in wood. The species studied presented different structures, which were apparent on the spin–spin relaxation T2 values. Three different water components were separated: slow T2 (liquid water in vessel elements), medium T2 (liquid water in fiber and parenchyma elements) and fast T2 (bound or cell wall water). The NMR results showed that even at equilibrated conditions a region exists where loss of liquid water and bound water takes place simultaneously. This region will vary according to the wood structure. Finally, liquid water was present at EMC lower than the fiber saturation point, which contradicts the concept of this point when considered as a bulk property of wood.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida G (2006) Influence de la structure du bois sur ses propriétés physico-mécaniques à des teneurs en humidité élevées. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Laval, Québec
Almeida G, Hernández RE (2006a) Changes in physical properties of tropical and temperate hardwoods below and above the fiber saturation point. Wood Sci Technol 40(3):599–613
Almeida G, Hernández RE (2006b) Changes in physical properties of yellow birch below and above the fiber saturation point. Wood Fiber Sci 38(1):74–83
Araujo CD, MacKay AL, Hailey JRT, Whittall KP (1992) Proton magnetic resonance techniques for characterization of water in wood: application to white spruce. Wood Sci Technol 26:101–113
Araujo CD, MacKay AL, Whittall KP, Hailey JRT (1993) A diffusion model for spin–spin relaxation of compartmentalized water in wood. J Magn Reson B 101(3):248–261
Araujo CD, Avramidis S, MacKay AL (1994) Behaviour of solid wood and bound water as a function of moisture content. A proton magnetic resonance study. Holzforschung 48(1):69–74
Brownstein KR, Tarr CE (1979) Importance of classical diffusion in NMR studies of water in biological cells. Phys Rev A 19(6):2446–2453
Brownstein KR (1980) Diffusion as an explanation of observed NMR behavior of water absorbed on wood. J Magn Reson 40(3):505–510
Casieri C, Senni L, Romagnoli M, Santamaria U, De Luca F (2004) Determination of moisture fraction in wood by mobile NMR device. J Magn Reson 171(2):364–372
Flibotte S, Menon RS, MacKay AL, Hailey JRT (1990) Proton magnetic resonance of western red cedar. Wood Fiber Sci 22(4):362–376
Gonzalez GC, Siau JF (1978) Longitudinal liquid permeability of American beech and eucalyptus. Wood Sci 11(2):105–110
Goulet M (1968) Phénomènes de second ordre de la sorption d’humidité dans le bois au terme d’un conditionnement de trois mois à temperature normale. Seconde partie: Essais du bois d’érable à sucre en compression radiale. Note de recherches N° 3, Département d’exploitation et utilisation des bois, Université Laval, Québec
Hart CA, Przestrzelski PJ, Wheeler FJ (1974) Entrapped lumen water in hickory during desorption. Wood Sci 6(4):356–362
Hartley ID, Kamke FA, Peemoeller H (1994) Absolute moisture content determination of aspen wood below the fiber saturation point using pulsed NMR. Holzforschung 48(6):474–479
Hernández RE (2006) Moisture sorption properties of hardwoods as affected by their extraneous substances, wood density and interlocked grain. Wood Fiber Sci (in press)
Hernández RE, Bizoň M (1994) Changes in shrinkage and tangential compression strength of sugar maple below and above the fiber saturation point. Wood Fiber Sci 26(3):360–369
Hernández RE, Pontin M (2006) Shrinkage of three tropical hardwoods below and above the fiber saturation point. Wood Fiber Sci 38(3):474−483
Hsi E, Hossfeld R, Bryant RG (1977) Nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation study of water adsorbed on mill northern white-cedar. J Colloid Interface Sci 62:389–395
Labbé N, De Jéso B, Lartigue J-C, Daudé G, Pétraud M, Ratier M (2002) Moisture content and extractive materials in maritime pine wood by low field 1H NMR. Holzforschung 56:25–31
Menon RS, Mackay AL, Hailey JRT, Bloom M, Burgess AE, Swanson JS (1987) An NMR determination of the physiological water distribution in wood during drying. J Appl Polym Sci 33(4):1141–1155
Merela M, Sepe A, Oven P, Serša I (2005) Three-dimensional in vivo magnetic resonance microscopy of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) wood. Magma 18(4):171–174
Naderi N, Hernández RE (1997) Effect of a re-wetting treatment on the dimensional changes of sugar maple wood. Wood Fiber Sci 29(4):340–344
Panshin AJ, de Zeeuw C (1980) Textbook of wood technology, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Rosenkilde A, Glover P (2002) High resolution measurement of the surface layer moisture content during drying of wood using a novel magnetic resonance imaging technique. Holzforschung 56(3):312–317
Riggin MT, Sharp AR, Kaiser R, Schneider MH (1979) Transverse NMR relaxation of water in wood. J Appl Polym Sci 23(11):3147–3154
Siau JF (1995) Wood: Influence of moisture on physical properties. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, VA
Tiemann HD (1906) Effect of moisture upon the strength and stiffness of wood. USDA Forest Service, Bulletin 70
Wen YH, Kalff J, Peters RH (1999) Pharmacokinetic modeling in toxicology: a critical perspective. Environ Rev 7:1–18
Wheeler EA (1982) Ultrastructural characteristics of red maple (Acer rubrum L.) wood. Wood Fiber Sci 14(1):43–53
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development of Brazil (CNPq) and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almeida, G., Gagné, S. & Hernández, R.E. A NMR study of water distribution in hardwoods at several equilibrium moisture contents. Wood Sci Technol 41, 293–307 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-006-0116-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-006-0116-3