Abstract
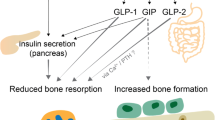
Glucagon-like peptide-1 Receptor agonists (GLP-1Ras) such as liraglutide and semaglutide have been recently approved as medications for chronic weight management in people living with obesity (PwO); GLP-1 may enhance bone metabolism and improve bone quality. However, the effects of GLP-1Ras on skeletal health remain to be determined and that's the purpose of this narrative review. Nevertheless, bone consequences of intentional weight loss interventions in PwO are well known: (i) significant weight loss induced by caloric restriction and bariatric surgery results in accelerated bone turnover and bone loss, and (ii) unlike caloric restriction interventions, PwO experience a substantial deterioration in bone microarchitecture and strength associated with an increased risk of fracture after bariatric surgery especially malabsorptive procedures. Liraglutide seems to have a positive effect on bone material properties despite significant weight loss in several rodent models. However, most of positive effects on bone mineral density and microarchitecture were observed at concentration much higher than approved for obesity care in humans. No data have been reported in preclinical models with semaglutide. The current evidence of the effects of GLP-1Ra on bone health in PwO is limited. Indeed, studies on the use of GLP-1Ra mostly included patients with diabetes who were administered a dose used in this condition, did not have adequate bone parameters as primary endpoints, and had short follow-up periods. Further studies are needed to investigate the bone impact of GLP-1Ra, dual- and triple-receptor agonists for GLP-1, glucose-dependent insulin releasing polypeptide (GIP), and glucagon in PwO.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, Paccou J.
References
Zatońska K, Psikus P, Basiak-Rasała A et al (2021) Obesity and chosen non-communicable diseases in pure poland cohort study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(5):2701
Okunogbe A, Nugent R, Spencer G, Powis J, Ralston J, Wilding J (2022) Economic impacts of overweight and obesity: current and future estimates for 161 countries. BMJ Glob Health 7(9):e009773
https://www.who.int/news/item/04-03-2022-world-obesity-day-2022-accelerating-action-to-stop-obesity. Accessed 3 June 2023
Chang SH, Stoll CR, Song J et al (2014) The effectiveness and risks of bariatric surgery: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis, 2003–2012. JAMA Surg 149:275–287
Sjöström L, Peltonen M, Jacobson P et al (2014) Association of bariatric surgery with long-term remission of type 2 diabetes and with microvascular and macrovascular complications. JAMA 311:2297–2304
Davies M, Pieber TR, Hartoft-Nielsen ML, Hansen OKH, Jabbour S, Rosenstock J (2017) Effect of oral semaglutide compared with placebo and subcutaneous semaglutide on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 318(15):1460–1470
Nauck MA, Petrie JR, Sesti G, Mannucci E, Courrèges JP, Lindegaard ML, Jensen CB, Atkin SL (2016) A phase 2, randomized, dose-finding study of the novel once-weekly human GLP-1 analog, semaglutide, compared with placebo and open-label liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 39(2):231–241
Kushner RF, Calanna S, Davies M, Dicker D, Garvey WT, Goldman B, Lingvay I, Thomsen M, Wadden TA, Wharton S, Wilding JPH, Rubino D (2020) Semaglutide 2.4 mg for the treatment of obesity: key elements of the STEP trials 1 to 5. J Obesity 28(6):1050–1061
Garvey WT, Batterhazm RL, Bhatta M, Buscemi S et al (2022) Two years effects of semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: the STEP 5 trial. Nat Med 28(10):2083–2091
Chao AM, Tronieri JS, Amaro A, Wadden TA (2023) Semaglutide for the treatment of obesity. Trends Cardiovasc Med 33(3):159–166
Lepsen EW, Lundgren JR, Hartmann B et al (2015) GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment increases bone formation and prevents bone loss in weight-reduced obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(8):2909–2917
Gautier JF, Choukem SP, Girard J (2008) Physiology of incretins (GIP and GLP-1) and abnormalities in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab 34(Suppl 2):S65-72
Hygum K, Harsløf T, Langdahl B, Starup-Linde J (2019) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and fracture risk—limitations to current knowledge. Osteoporos Int 30(8):1709–1710
Thomas MK, Nikooienejad A, Bray R et al (2021) Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide improves beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 106(2):388–396
Jastreboff AM, Kaplan LM, Frías JP et al (2023) Triple–hormone-receptor agonist retatrutide for obesity—A phase 2 trial. N Engl J Med 389:514–526
Gadde KM, Martin CK, Berthoud HR, Heymsfield SB (2018) Obesity: pathophysiology and management. J Am Coll Cardiol 71(1):69–84
Pasquali R, Casanueva F, Haluzik M et al (2020) European society of endocrinology clinical practice guideline: endocrine work-up in obesity. Eur J Endocrinol 182(1):G1–G32
Ryan DH, Lingvay I, Colhoum HM, Denfield J et al (2020) Semaglutide effects on cardiovascular outcomes in people with overweight or obesity (Select) rationale and design. Am J Heart 229:61–69
Kadawaki T, Isendahl JK, Khalid U, Lee SW et al (2022) Semaglutide once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, with or without type 2 diabetes in an east Asian population (STEP 6): a randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00008-0
Rubino DM, Grenway FL, Khalid O, Oeil PM et al (2022) Effect of weekly subcutaneous Semaglutide vs daily Liraglutide on body weight in adults with overweight or obesity without diabetes. The step 8 randomized clinical study. JAMA 327(2):138–150
Weghuber D, Barett T, Barrientos-Pérez M, Gies I et al (2022) Once-weekly semaglutide in adolescents with obesity. N Engl J Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2208601
Schlienger JL, Monnier L (2023) Co-agonistes des récepteurs du GIP et du GLP-1: une innovation thérapeutique majeure dans le traitement du diabète de type 2. Med Mal Metab 17:49–57
Enebo LB, Berthelsen KK, Kankam M, Lund MT et al (2022) Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of concomitant administration of multiple doses of cagrilintide with semaglutide 2.4 mg for weight management: a randomised, controlled, phase 1b trial. Lancet 397:1736–1748
Lau DCW, Erichsen L, Francisco AM, Satylganova A et al (2022) Once-weekly cagrilintide for weight management in people with overweight and obesity: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled and active-controlled, dose-finding phase 2 trial. Lancet. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01751-7
Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, Wharton S, Connery L, Alves B, Kiyosue A, Zhang S, Liu B, Bunck MC, Stefanski A, SURMOUNT-1 Investigators (2022) Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med 387(3):205–216
Lespessailles E, Paccou J, Javier RM et al (2010) GRIO scientific committee. obesity, bariatric surgery, and fractures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 104:4756–4768
Paccou J, Caiazzo R, Lespessailles E, Cortet B (2022) Bariatric surgery and osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int 110:576–591
Jensen VFH, Mølck AM, Dalgaard M, McGuigan FE, Akesson KE (2021) Changes in bone mass associated with obesity and weight loss in humans: applicability of animal models. Bone 145:115781
Papageorgiou M, Biver E (2023) Bone consequences of intentional weight loss in overweight or obese patients. Rev Med Suisse 19:756–760
Armamento-Villareal R, Aguirre L, Waters DL, Napoli N, Qualls C, Villareal DT (2020) Effect of aerobic or resistance exercise, or both, on bone mineral density and bone metabolism in obese older adults while dieting: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Miner Res 35:430–439
Pines A (2012) Weight loss, weight regain and bone health. Climacteric 15:317–319
Zibellini J et al (2015) Does diet-induced weight loss lead to bone loss in overweight or obese adults? A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. J Bone Miner Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2564
Uusi-Rasi K et al (2010) Three-month weight reduction does not compromise bone strength in obese premenopausal women. Bone. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2009.10.013
Uusi-Rasi K et al (2009) Influence of weight reduction on muscle performance and bone mass, structure and metabolism in obese premenopausal women. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 9:72–80
Villareal DT, Shah K, Banks MR, Sinacore DR, Klein S (2008) Effect of weight loss and exercise therapy on bone metabolism and mass in obese older adults: a one-year randomized controlled trial. J Clin Endoc Metab. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-1473
Papageorgiou M, Kerschan-Schindl K, Sathyapalan T, Pietschmann P (2020) Is weight loss harmful for skeletal health in obese older adults? Gerontology 66(1):2–14
Lv QB et al (2015) The relationship between weight change and risk of hip fracture: meta-analysis of prospective studies. Sci Rep 5:16030
Ensrud KE, Ewing SK, Stone KL et al (2003) Intentional and unintentional weight loss increase bone loss and hip fracture risk in older women. J Am Geriatr Soc 51(12):1740–1747
Compston JE, Wyman A, FitzGerald G et al (2016) Increase in fracture risk following unintentional weight loss in postmenopausal women: the global longitudinal study of osteoporosis in women. J Bone Miner Res 31(7):1466–1472
Crandall CJ, Yildiz VO, Wactawski-Wende J et al (2015) Postmenopausal weight change and incidence of fracture: post hoc findings from women’s health initiative observational study and clinical trials. BMJ 27(350):h25
Schafer AL, Kazakia GJ, Vittinghoff E et al (2018) Effects of gastric bypass surgery on bone mass and microarchitecture occur early and particularly impact postmenopausal women: bone mass and microarchitecture after gastric bypass surgery. J Bone Miner Res 33:975–986
Shanbhogue VV, Støving RK, Frederiksen KH et al (2017) Bone structural changes after gastric bypass surgery evaluated by HR-pQCT: a two-year longitudinal study. Eur J Endocrinol 176:685–693
Paccou J, Martignène N, Lespessailles E et al (2020) Gastric bypass but not sleeve gastrectomy increases risk of major osteoporotic fracture: french population-based cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 35:1415–1423
Khalid SI, Omotosho PA, Spagnoli A, Torquati A (2020) Association of bariatric surgery with risk of fracture in patients with severe obesity. JAMA Netw Open 3:e207419
Paccou J et al (2022) Bariatric surgery and skeletal health: a narrative review and position statement for management by the European calcified tissue society (ECTS). Bone 154:116236
Gagnon C, Schafer AL (2018) Bone health after bariatric surgery. JBMR Plus 2(3):121–133
Paccou J, Thuillier D, Courtalin M, Pigny P, Labreuche J, Cortet B, Pattou F (2022) A comparison of changes in bone turnover markers after gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, and their association with markers of interest. Surg Obes Relat Dis 18(3):373–383
Beavers KM, Greene KA, Yu EW (2020) Management of endocrine disease: bone complications of bariatric surgery: updates on sleeve gastrectomy, fractures, and interventions. Eur J Endocrinol 183(5):R119–R132
Yamada C, Yamada Y, Tsukiyama K, Yamada K, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Tanaka K, Drucker DJ, Seino Y, Inagaki N (2008) The murine glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is essential for control of bone resorption. Endocrinology 149:574–579
Bjerre Knudsen L, Madsen LW, Andersen S, Almholt K, de Boer AS, Drucker DJ, Gotfredsen C, Egerod FL, Hegelund AC, Jacobsen H, Jacobsen SD, Moses AC, Molck AM, Nielsen HS, Nowak J, Solberg H, Thi TD, Zdravkovic M, Moerch U (2010) Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists activate rodent thyroid C-cells causing calcitonin release and C-cell proliferation. Endocrinology 151:1473–1486
Hegedus L, Moses AC, Zdravkovic M, Le Thi T, Daniels GH (2011) GLP-1 and calcitonin concentration in humans: lack of evidence of calcitonin release from sequential screening in over 5000 subjects with type 2 diabetes or nondiabetic obese subjects treated with the human GLP-1 analog, liraglutide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:853–860
Mabilleau G, Mieczkowska A, Irwin N, Flatt PR, Chappard D (2013) Optimal bone mechanical and material properties require a functional glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. J Endocrinol 219:59–68
Gaudin-Audrain C, Irwin N, Mansur S, Flatt PR, Thorens B, Basle M, Chappard D, Mabilleau G (2013) Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor deficiency leads to modifications of trabecular bone volume and quality in mice. Bone 53:221–230
Mieczkowska A, Irwin N, Flatt PR, Chappard D, Mabilleau G (2013) Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor deletion leads to reduced bone strength and quality. Bone 56:337–342
Mieczkowska A, Mansur S, Bouvard B, Flatt PR, Thorens B, Irwin N, Chappard D, Mabilleau G (2015) Double incretin receptor knock-out (DIRKO) mice present with alterations of trabecular and cortical micromorphology and bone strength. Osteoporos Int 26:209–218
Gao L, Li SL, Li YK (2018) Liraglutide promotes the osteogenic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells via regulating the expression of Smad2/3 through PI3K/Akt and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways. DNA Cell Biol 37:1031–1043
Wu X, Li S, Xue P, Li Y (2017) Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, facilitates osteogenic proliferation and differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells through phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT), extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)1/2, and cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathways involving beta-catenin. Exp Cell Res 360:281–291
Wu X, Li S, Xue P, Li Y (2018) Liraglutide inhibits the apoptosis of MC3T3-e1 cells induced by serum deprivation through cAMP/PKA/beta-catenin and PI3K/AKT/GSK3beta signaling pathways. Mol Cells 41:234–243
Li Y, Fu H, Wang H, Luo S, Wang L, Chen J, Lu H (2020) GLP-1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human ADSCs via the Wnt/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol 515:110921
Pang Y, Yuan X, Guo J, Wang X, Yang M, Zhu J, Wang J (2019) The effect of liraglutide on the proliferation, migration, and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res 54:106–114
Zhai S, Liu C, Vimalraj S, Subramanian R, Abullais SS, Arora S, Saravanan S (2023) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor promotes osteoblast differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and bone formation in a zebrafish scale regeneration model. Peptides 163:170974
Zhang Y, Yuan X, Wu Y, Pei M, Yang M, Wu X, Pang Y, Wang J (2020) Liraglutide regulates bone destruction and exhibits anti-inflammatory effects in periodontitis in vitro and in vivo. J Dent 94:103310
Li Z, Li S, Wang N, Xue P, Li Y (2020) Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, suppresses osteoclastogenesis through the inhibition of NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways via GLP-1R. Biomed Pharmacother 130:110523
Knudsen LB, Hastrup S, Underwood CR, Wulff BS, Fleckner J (2012) Functional importance of GLP-1 receptor species and expression levels in cell lines. Regul Pept 175:21–29
Lu N, Sun H, Yu J, Wang X, Liu D, Zhao L, Sun L, Zhao H, Tao B, Liu J (2015) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist Liraglutide has anabolic bone effects in ovariectomized rats without diabetes. PLoS ONE 10:e0132744
Pal S, Maurya SK, Chattopadhyay S, Pal China S, Porwal K, Kulkarni C, Sanyal S, Sinha RA, Chattopadhyay N (2019) The osteogenic effect of liraglutide involves enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis in osteoblasts. Biochem Pharmacol 164:34–44
Langlois JA, Mussolino ME, Visser M, Looker AC, Harris T, Madans J (2001) Weight loss from maximum body weight among middle-aged and older white women and the risk of hip fracture: the NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study. Osteoporos Int 12:763–768
Shires R, Aivioli LV, Bergfeld MA, Fallon MD, Slatopolsky E, Teitelbaum SL (1980) Effects of semistarvation on skeletal homeostasis. Endocrinology 107:1530–1535
Talbott SM, Cifuentes M, Dunn MG, Shapses SA (2001) Energy restriction reduces bone density and biomechanical properties in aged female rats. J Nutr 131:2382–2387
Pereira M, Jeyabalan J, Jorgensen CS, Hopkinson M, Al-Jazzar A, Roux JP, Chavassieux P, Orriss IR, Cleasby ME, Chenu C (2015) Chronic administration of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists improves trabecular bone mass and architecture in ovariectomised mice. Bone 81:459–467
Yang L, Yang J, Pan T, Zhong X (2019) Liraglutide increases bone formation and inhibits bone resorption in rats with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. J Endocrinol Invest 42:1125–1131
Bouvard B, Gallois Y, Legrand E, Audran M, Chappard D (2013) Glucocorticoids reduce alveolar and trabecular bone in mice. Joint Bone Spine 80:77–81
Mansur SA, Mieczkowska A, Bouvard B, Flatt PR, Chappard D, Irwin N, Mabilleau G (2015) Stable incretin mimetics counter rapid deterioration of bone quality in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Cell Physiol 230:3009–3018
Yu J, Shi YC, Ping F, Li W, Zhang HB, He SL, Zhao Y, Xu LL, Li YX (2021) Liraglutide inhibits osteoclastogenesis and improves bone loss by downregulating trem2 in female type 1 diabetic mice: findings from transcriptomics. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 12:763646
Chen K, Wu R, Mo B, Yan X, Shen D, Chen M (2021) Comparison between liraglutide alone and liraglutide in combination with insulin on osteoporotic rats and their effect on bone mineral density. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 21:142–148
Cheng Y, Liu P, Xiang Q, Liang J, Chen H, Zhang H, Yang L (2022) Glucagon-like peptide-1 attenuates diabetes-associated osteoporosis in ZDF rat, possibly through the RAGE pathway. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 23:465
Li J, Fu LZ, Liu L, Xie F, Dai RC (2017) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist liraglutide alters bone marrow exosome-mediated miRNA signal pathways in ovariectomized rats with type 2 diabetes. Med Sci Monit 23:5410–5419
Sun HX, Lu N, Luo X, Zhao L, Liu JM (2015) Liraglutide, the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, has anabolic bone effects in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. J Diabetes 7:584–588
Wen B, Zhao L, Zhao H, Wang X (2018) Liraglutide exerts a bone-protective effect in ovariectomized rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis. Exp Ther Med 15:5077–5083
Mieczkowska A, Millar P, Chappard D, Gault VA, Mabilleau G (2020) Dapagliflozin and liraglutide therapies rapidly enhanced bone material properties and matrix biomechanics at bone formation site in a type 2 diabetic mouse model. Calcif Tissue Int 107:281–293
Iepsen EW, Lundgren JR, Hartmann B et al (2015) GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment increases bone formation and prevents bone loss in weight-reduced obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(8):2909–2917. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-1176
Hygum K, Harsløf T, Jørgensen NR, Rungby J, Pedersen SB, Langdahl BL (2020) Bone resorption is unchanged by liraglutide in type 2 diabetes patients: a randomised controlled trial. Bone 132:115197
Cai TT, Li HQ, Jiang LL, Wang HY, Luo MH, Su XF, Ma JH (2021) Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on bone mineral density in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 52-week clinical study. Biomed Res Int 17(2021):3361309
Mabilleau G, Mieczkowska A, Chappard D (2014) Use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and bone fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Diabetes 6(3):260–266
Zhang YS, Weng WY, Xie BC et al (2018) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and fracture risk: a network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Osteoporos Int 29(12):2639–2644
Zhang YS, Zheng YD, Yuan Y, Chen SC, Xie BC (2021) Effects of anti-diabetic drugs on fracture risk: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 14(12):735824
Hidayat K, Du X, Shi BM (2019) Risk of fracture with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in real-world use: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos Int 30(10):1923–1940
Su B, Sheng H, Zhang M, Bu L, Yang P, Li L, Li F, Sheng C, Han Y, Qu S, Wang J (2015) Risk of bone fractures associated with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists’ treatment: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Endocrine 48(1):107–115
Chai S, Liu F, Yang Z, Yu S, Liu Z, Yang Q, Sun F (2022) Risk of fracture with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and network meta-analysis combining 177 randomized controlled trials with a median follow-up of 26 weeks. Front Pharmacol 1(13):825417
Cheng L, Hu Y, Li YY, Cao X, Bai N, Lu TT, Li GQ, Li N, Wang AN, Mao XM (2019) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and risk of bone fracture in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 35(7):e3168
Funding
This work was supported by the French Society of Rheumatology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Julia Herrou, Guillaume Mabilleau, Jean-Michel Lecerf, Thierry Thomas, Emmanuel Biver and Julien Paccou declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Herrou, J., Mabilleau, G., Lecerf, JM. et al. Narrative Review of Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Bone Health in People Living with Obesity. Calcif Tissue Int 114, 86–97 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-023-01150-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-023-01150-8