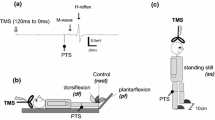
Abstract
The effect of body posture on the human soleus H-reflex via electrical stimulation of the tibial nerve at the popliteal fossa was studied. All parameters that may influence the reflex were controlled stringently. H-reflexes were elicited in three different body postures while keeping the level of background muscle activation to a minimum. The H-reflex curve relative to the M-wave curve did not change significantly in any of the body postures. However, the maximal H-reflex amplitude significantly increased in the prone position compared with the sitting (p = 0.02) and standing positions (p = 0.01). The background level of electrical activity of the soleus muscle did not significantly change during varying body postures. Together, these findings indicate that the effectiveness of the spindle primary afferent synapse on the soleus motor neuron pool changes significantly in prone position as compared to sitting and standing positions. Given that we have controlled the confounding factors excluding the head position relative to the gravity and the receptors that may be differentially activated at varying body postures such as the proprioceptors, it is concluded that the tonic activity from these receptors may presynaptically interfere with the effectiveness of the spindle primary afferent synapses on the soleus motor neurons.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aimonetti JM, Vedel J-P, Schmied A, Pagni S (2000) Distribution of presynaptic inhibition on type-identified motoneurones in the extensor carpi radialis pool in man. J Physiol 522:125—135
Aniss AM, Diener HC, Hore J, Burke D, Gandevia SC (1990) Reflex activation of muscle spindles in human pretibial muscles during standing. J Neurophysiol 64:671–679
Aniss AM, Gandevia SC, Burke D (1992) Reflex responses in active muscles elicited by stimulation of low-threshold afferents from the human foot. J Neurophysiol 67;1375–1384
Billot M, Simoneau EM, Van Hoecke J, Martin A (2010) Age-related relative increases in electromyography activity and torque according to the maximal capacity during upright standing. Eur J Appl Physiol 109:669–680
Brinkworth RSA, Tuncer M, Tucker K, Jaberzadeh S, Türker KS (2007) Standardization of H-reflex analyses. J Neurosci Meth 162:1–7
Cattagni T, Martin A, Scaglioni G (2014) Is spinal excitability of the triceps surae mainly affected by muscle activity or body position? J Neurophysiol 111:2525–2532
Dakin CJ, Heroux ME, Luu BL, Inglis JM, Blouin J-S (2016) Vestibular contribution to balance control in the medial gastrocnemius and soleus. J Neurophysiol 115:1289–1297
Fox A, Koceja D (2017) Static otolithic drive alters presynaptic inhibition in soleus motor pool. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 32:37–43
Heckman CJ, Binder MD (1988) Analysis of steady-state effective synaptic currents generated by homonymous Ia afferent fibers in motoneurons of the cat. J Neurophysiol 60:1946–1966
Knikou M (2008) The H-reflex as a probe: pathways and pitfalls. J Neurosci Meth 171:1–12
Knikou M, Rymer WZ (2003) Static and dynamic changes in body orientation modulate spinal reflex excitability in humans. Exp Brain Res 152:466–475
Kyung-Min K, Hart JM, Hertel J (2013) Influence of body position on fibularis longus and soleus Hoffmann reflexes. Gait Posture 37:138–140
Lowrey CR, Bent LR (2009) Modulation of the soleus H-reflex following galvanic vestibular stimulation and cutaneous stimulation in prone human subjects. Muscle Nerve 40:213–220
Miles TS, Türker KS (1986) Does reflex inhibition of motor units follow the “Size Principle”? Exp Brain Res 62:443–445
Morita H, Petersen N, Christensen LO, Sinkjaer T, Nielsen J (1998) Sensitivity of H-reflexes and stretch reflexes to presynaptic inhibition in humans. J Neurophysiol 80:610–620
Mynark RG (2005) Reliability of the soleus H-reflex from supine to standing in young and elderly. Clin Neurophysiol 116:1400–1404
Scarpini C, Mazzocchio R, Mondelli M, Nuti D, Rossi A (1991) Changes in alpha motoneuron excitability of the soleus muscle in relation to vestibular stimulation assessed by angular acceleration in man. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 53:100–105
Schieppati M (1987) The Hoffmann reflex: a means of assessing spinal reflex excitability and its descending control in man. Prog Neurobiol 28:345–376
Shimba S, Kawashima N, Ohta Y, Yamamoto S-I, Nakazawa K (2010) Enhanced stretch reflex excitability in the soleus muscle during passive standing posture in humans. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 20:406–412
Stein RB, Estabrooks KL, m McGie S, Roth MJ, Jones KE (2007) Quantifying the effects of voluntary contraction and inter-stimulus interval on the human soleus H-reflex. Exp Brain Res 182:309–319
Strzalkowski ND, Mildren RL, Bent LR (2015) Thresholds of cutaneous afferents related to perceptual threshold across the human foot sole. J Neurophysiol 114:2144–2151
Traccis S, Rosati G, Patraskakis S, Bissakou M, Sau GF, Aiello I (1987) Influences of neck receptors on soleus motoneuron excitability in man. Exp Neurol 95:76–84
Trimble MH (1998) Postural modulation of the segmental reflex: effect of body tilt and postural sway. Int J Neurosci 95:85–100
Trulsson M (2001) Mechanoreceptive afferents in the human sural nerve. Exp Brain Res 137:111–116
Türker KS (1988) A method for standardization of silent period measurements in human masseter muscle. J Oral Rehab 15:91–101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cecen, S., Niazi, I.K., Nedergaard, R.W. et al. Posture modulates the sensitivity of the H-reflex. Exp Brain Res 236, 829–835 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5182-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5182-x