Abstract
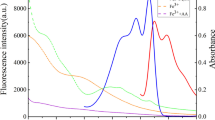
Human urine phosphorus (existing in the form of phosphate) is a biomarker for the diagnosis of several diseases such as kidney disease, hyperthyroidism, and rickets. Therefore, the selective detection of phosphate in urine samples is crucial in the field of clinical diagnosis. Herein, we reported the phosphatase-like catalytic activity of few-layered h-BNNS for the first time. As the phosphatase-like activity of few-layered h-BNNS could be effectively inhibited by phosphate, a selective fluorescent method for the detection of phosphate was proposed. The linear range for phosphate detection is 0.5–10 µM with a detection limit of 0.33 µM. The fluorescent method was then explored for the detection of human urine phosphorus in real samples. The results obtained by the proposed method were consistent with those of the traditional method, indicating that the present method has potential application for urine phosphorus detection in clinical disease diagnosis.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Gu N, et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2(9):577–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.260.
Wu J, Wang X, Wang Q, Lou Z, Li S, Zhu Y, et al. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(4):1004–76. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cs00457a.
Zhang R, Yan X, Fan K. Nanozymes inspired by natural enzymes. Acc Mater Res. 2021;2(7):534–47. https://doi.org/10.1021/accountsmr.1c00074.
Li S, Zhang Y, Wang Q, Lin A, Wei H. Nanozyme-enabled analytical chemistry. Anal Chem. 2022;94(1):312–23. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04492.
Zhang J, Wang J, Liao J, Lin Y, Zheng C, Liu J. In situ fabrication of nanoceria with oxidase-like activity at neutral pH: mechanism and boosted bio-nanozyme cascades. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(42):50236–45. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c14831.
Chao D, Dong Q, Yu Z, Qi D, Li M, Xu L, et al. Specific nanodrug for diabetic chronic wounds based on antioxidase-mimicking MOF-818 nanozymes. J Am Chem Soc. 2022;144(51):23438–47. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c09663.
Xu W, Song W, Kang Y, Jiao L, Wu Y, Chen Y, et al. Axial ligand-engineered single-atom catalysts with boosted enzyme-like activity for sensitive immunoassay. Anal Chem. 2021;93(37):12758–66. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c02842.
Zhang C, Chen C, Zhao D, Kang G, Liu F, Yang F, et al. Multienzyme cascades based on highly efficient metal-nitrogen-carbon nanozymes for construction of versatile bioassays. Anal Chem. 2022;94(8):3485–93. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04018.
Dong K, Xu C, Ren J, Qu X. Chiral nanozymes for enantioselective biological catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022;61(43): e202208757. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202208757.
Huang Y, Ren J, Qu X. Nanozymes: classification, catalytic mechanisms, activity regulation, and applications. Chem Rev. 2019;119(6):4357–412. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00672.
Chang J, Yu L, Hou T, Hu R, Li F. Direct and specific detection of glyphosate using a phosphatase-like nanozyme-mediated chemiluminescence strategy. Anal Chem. 2023;95(9):4479–85. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05198.
Wu Y, Huang T, Luo Y, Dai L, Wang M, Xia Z, et al. Zirconium-amino acid framework as a green phosphatase-like nanozyme for the selective detection of phosphate-containing drugs. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023;59(8):1098–101. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2cc06606h.
Liu H, Liu J. Self-limited phosphatase-mimicking CeO2 nanozymes. ChemNanoMat. 2020;6(6):947–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.202000132.
Gao R, Ye N, Kou X, Shen Y, Yang H, Wu T, et al. Hierarchically mesoporous Ce-based MOFs with enhanced alkaline phosphatase-like activity for phosphorylated biomarker sensing. Chem Commun (Camb). 2022;58(91):12720–3. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2cc04895g.
Xiong Y, Su L, Ye F, Zhao S. Inhibition of NADP(H) supply by highly active phosphatase-like ceria nanozymes to boost oxidative stress and ferroptosis. Mater Today Chem. 2022; 23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2021.100672.
Dai L, Mao W, Hu L, Song J, Zhang Y, Huang T, et al. Ratiometric fluorescent sensing and imaging of intracellular pH by an AIE-active luminogen with intrinsic phosphatase-like catalytic activity. Dyes Pigments. 2022; 204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2022.110436.
Mao W, Dai L, Hu L, Song J, Huang T, Wang M. Dual-channel fluorescent imaging of reactive oxygen species in living cells based on Ce(III) modified quantum dots with oxidation triggered phosphatase-like activity. Sensor and Actuat B: Chem. 2022; 367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.132178.
Li S, Zhou Z, Tie Z, Wang B, Ye M, Du L, et al. Data-informed discovery of hydrolytic nanozymes. Nat Commun. 2022; 13 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28344-2.
Park Y-G, Nam S-N, Jang M, Min Park C, Her N, Sohn J, et al. Boron nitride-based nanomaterials as adsorbents in water: a review. Sep Purif Technol. 2022; 288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120637.
Li M, Huang G, Chen X, Yin J, Zhang P, Yao Y, et al. Perspectives on environmental applications of hexagonal boron nitride nanomaterials. Nano Today. 2022; 44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2022.101486.
Li X, Chen S, Liu Q, Luo Y, Sun X. Hexagonal boron nitride nanosheet as an effective nanoquencher for the fluorescence detection of microRNA. Chem Commun (Camb). 2021;57(65):8039–42. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cc03011f.
Kobayashi H, Fukuoka A. Hexagonal boron nitride for adsorption of saccharides. J Phys Chem C. 2017;121(32):17332–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b05077.
Pan Y, Zheng H, Li G, Li Y, Jiang J, Chen J, et al. Antibiotic-like activity of atomic layer boron nitride for combating resistant bacteria. ACS Nano. 2022;16(5):7674–88. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c11353.
Liu T, Li Y, He J, Zhang K, Hu Y, Chen X, et al. Few-layered boron nitride nanosheets as superior adsorbents for the rapid removal of lead ions from water. J Mater Sci. 2019;54(7):5366–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-03240-7.
Vatanparast M, Shariatinia Z. Hexagonal boron nitride nanosheet as novel drug delivery system for anticancer drugs: insights from DFT calculations and molecular dynamics simulations. J Mol Graph Model. 2019;89:50–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2019.02.012.
Karthikeyan P, Elanchezhiyan SS, Preethi J, Meenakshi S, Park CM. Mechanistic performance of polyaniline-substituted hexagonal boron nitride composite as a highly efficient adsorbent for the removal of phosphate, nitrate, and hexavalent chromium ions from an aqueous environment. Appl Surf Sci. 2020; 511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145543.
Li Z, Wei W, Li H, Li S, Leng L, Zhang M, et al. Low-temperature synthesis of single palladium atoms supported on defective hexagonal boron nitride nanosheet for chemoselective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde. ACS Nano. 2021;15(6):10175–84. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c02094.
Kong L, Jiao D, Wang Z, Liu Y, Shang Y, Yin L, et al. Single metal atom anchored on porous boron nitride nanosheet for efficient collaborative urea electrosynthesis: a computational study. Chem Eng J. 2023; 451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138885.
Ding Y, Torres-Davila F, Khater A, Nash D, Blair R, Tetard L. Defect engineering in boron nitride for catalysis. MRS Commun. 2018;8(3):1236–43. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.113.
Zhang Y, Du H, Ma Y, Ji L, Guo H, Tian Z, et al. Hexagonal boron nitride nanosheet for effective ambient N2 fixation to NH3. Nano Res. 2019;12(4):919–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2323-x.
Chen H, Yang Z, Zhang Z, Chen Z, Chi M, Wang S, et al. Construction of a nanoporous highly crystalline hexagonal boron nitride from an amorphous precursor for catalytic dehydrogenation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019;58(31):10626–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201904996.
Liu Z, Liu J, Mateti S, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Chen L, et al. Boron radicals identified as the source of the unexpected catalysis by boron nitride nanosheets. ACS Nano. 2019;13(2):1394–402. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b06978.
Chen H, Jiang DE, Yang Z, Dai S. Engineering nanostructured interfaces of hexagonal boron nitride-based materials for enhanced catalysis. Acc Chem Res. 2023;56(1):52–65. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00564.
Ramakrishnam Raju MV, Harris SM, Pierre VC. Design and applications of metal-based molecular receptors and probes for inorganic phosphate. Chem Soc Rev. 2020;49(4):1090–108. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cs00543a.
Zhao CX, Zhang XP, Shu Y, Wang JH. Europium-pyridinedicarboxylate-adenine light-up fluorescence nanoprobes for selective detection of phosphate in biological fluids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(20):22593–600. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c04318.
Li H, Fu F, Yang W, Ding L, Dong J, Yang Y, et al. A simple fluorescent probe for fast and sensitive detection of inorganic phosphate based on uranine@ZIF-8 composite. Sensors Actuat B: Chem. 2019; 301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127110.
Yang L, Zhang Q, Han Y, Li H, Sun S, Xu Y. The selective deprotonation of carbon quantum dots for fluorescence detection of phosphate and visualization of latent fingerprints. Nanoscale. 2021;13(30):13057–64. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nr02432a.
Wu Z, Yang H, Pan S, Liu H, Hu X. Fluorescence-scattering dual-signal response of carbon dots@ZIF-90 for phosphate ratiometric detection. ACS Sens. 2020;5(7):2211–20. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c00853.
Mashhadi Farahani S, Dadmehr M, Ali Karimi M, Korouzhdehi B, Amin Karimi M, Rajabian M. Fluorometric detection of phytase enzyme activity and phosphate ion based on gelatin supported silver nanoclusters. Food Chem. 2022;396: 133711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133711.
Funding
This work was supported by the Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0625 and cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0757) and the Chongqing Innovation Research Group Project (no. CXQT21015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Declarations
The human urine samples were provided by healthy volunteers from Dr. Min Wang’s lab. The studies have been approved by the Ethics Committee at Chongqing University and have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection featuring Nanozymes with guest editors Vipul Bansal, Sudipta Seal, and Hui Wei.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., He, Y., Zhou, G. et al. Few-layered boron nitride nanosheet as a non-metallic phosphatase nanozyme and its application in human urine phosphorus detection. Anal Bioanal Chem (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05030-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05030-w