Abstract
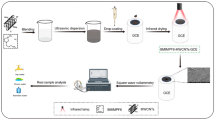
A novel smartphone-based electrochemical cell sensor was developed to evaluate the toxicity of heavy metal ions, such as cadmium (Cd2+), lead (Pb2+), and mercury (Hg2+) ions on Hep G2 cells. The cell sensor was fabricated with reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/molybdenum sulfide (MoS2) composites to greatly improve the biological adaptability and amplify the electrochemical signals. Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) was employed to measure the electrical signals induced by the toxicity of heavy metal ions. The results showed that Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+ significantly reduced the viability of Hep G2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The IC50 values obtained by this method were 49.83, 36.94, and 733.90 μM, respectively. A synergistic effect was observed between Cd2+ and Pb2+ and between Hg2+ and Pb2+, and an antagonistic effect was observed between Cd2+ and Hg2+, and an antagonistic effect at low doses and an additive effect at high doses were found in the ternary mixtures of Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+. These electrochemical results were confirmed via MTT assay, SEM and TEM observation, and flow cytometry. Therefore, this new electrochemical cell sensor provided a more convenient, sensitive, and flexible toxicity assessment strategy than traditional cytotoxicity assessment methods.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu Y, Liang X, Niyungeko C, Zhou J, Xu J, Tian G. A review of the identification and detection of heavy metal ions in the environment by voltammetry. Talanta. 2018;178:324–38.
Kim J-J, Kim Y-S, Kumar V. Heavy metal toxicity: an update of chelating therapeutic strategies. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2019;54:226–31.
Rebelo FM, Caldas ED. Arsenic, lead, mercury and cadmium: toxicity, levels in breast milk and the risks for breastfed infants. Environ Res. 2016;151:671–88.
Hamida S, Ouabdesslam L, Ladjel A, Escudero M, Anzano J. Determination of cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc in pilchard sardines from the Bay of Boumerdés by atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Lett. 2018;51(16):2501–8.
Ramdani S, Amar A, Belhsaien K, El Hajjaji S, Ghalem S, Zouahri A, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk of roadside soils in Tlemcen (Algeria) using flame-atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Lett. 2018;51(15):2468–87.
Jaswal BBS, Rai PK, Singh T, Zorba V, Singh VK. Detection and quantification of heavy metal elements in gallstones using X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Xray Spectrom. 2019;48(3):178–87.
Mohamed R, Zainudin BH, Yaakob AS. Method validation and determination of heavy metals in cocoa beans and cocoa products by microwave assisted digestion technique with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2020;303:125392.
Wang L, Peng X, Fu H, Huang C, Li Y, Liu Z. Recent advances in the development of electrochemical aptasensors for detection of heavy metals in food. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;147:111777.
Cui Z, Luan X, Jiang H, Li Q, Xu G, Sun C, et al. Application of a bacterial whole cell biosensor for the rapid detection of cytotoxicity in heavy metal contaminated seawater. Chemosphere. 2018;200:322–9.
Lauri A, Soliman D, Omar M, Stelzl A, Ntziachristos V, Westmeyer GG. Whole-cell photoacoustic sensor based on pigment relocalization. ACS Sens. 2019;4(3):603–12.
Gupta N, Renugopalakrishnan V, Liepmann D, Paulmurugan R, Malhotra BD. Cell-based biosensors: recent trends, challenges and future perspectives. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;141:111435.
Jeon H, Lee E, Kim D, Lee M, Ryu J, Kang C, et al. Cell-based biosensors based on intein-mediated protein engineering for detection of biologically active signaling molecules. Anal Chem. 2018;90(16):9779–86.
Jiang D, Ge P, Wang L, Jiang H, Yang M, Yuan L, et al. A novel electrochemical mast cell-based paper biosensor for the rapid detection of milk allergen casein. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;130:299–306.
Jiang D, Liu Y, Jiang H, Rao S, Fang W, Wu M, et al. A novel screen-printed mast cell-based electrochemical sensor for detecting spoilage bacterial quorum signaling molecules (N-acyl-homoserine-lactones) in freshwater fish. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;102:396–402.
Cardoso RM, Kalinke C, Rocha RG, Dos Santos PL, Rocha DP, Oliveira PR, et al. Additive-manufactured (3D-printed) electrochemical sensors: a critical review. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1118:73–91.
Shin J, Kim S, Yoon T, Joo C, Jung H-I. Smart Fatigue Phone: real-time estimation of driver fatigue using smartphone-based cortisol detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;136:106–11.
Deng W, Dou Y, Song P, Xu H, Aldalbahi A, Chen N, et al. Lab on smartphone with interfaced electrochemical chips for on-site gender verification. J Electroanal Chem. 2016;777:117–22.
Morais S, Tortajada-Genaro LA, Maquieira Á, Gonzalez Martinez M-Á. Biosensors for food allergy detection according to specific IgE levels in serum. Trends Anal Chem. 2020;127.
Minnetti E, Chiariotti P, Paone N, Garcia G, Vicente H, Violini L, et al. A smartphone integrated hand-held gap and flush measurement system for in line quality control of car body assembly. Sensors. 2020;20(11):3300.
Lu L, Jiang Z, Hu Y, Zhou H, Liu G, Chen Y, et al. A portable optical fiber SPR temperature sensor based on a smart-phone. Opt Express. 2019;27(18):25420–7.
Jiang D, Zhu P, Jiang H, Ji J, Sun X, Gu W, et al. Fluorescent magnetic bead-based mast cell biosensor for electrochemical detection of allergens in foodstuffs. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;70:482–90.
Ramaraj S, Sakthivel M, Chen S-M, Elshikh MS, Chen T-W, Yu M-C, et al. Electrochemical sensing of anti-inflammatory agent in paramedical sample based on FeMoSe2 modified SPCE: comparison of various preparation methods and morphological effects. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1083:88–100.
Yin S, Li C, Wang S, Ren X, Zeng L, Zhang L. The construction of a 2D MoS2-based binder-free electrode with a honeycomb structure for enhanced electrochemical performance. Dalton Trans. 2020;49(24):8036–40.
Mazaheri A, Lee M, Van Der Zant HS, Frisenda R, Castellanos-Gomez A. MoS2-on-paper optoelectronics: drawing photodetectors with van der Waals semiconductors beyond graphite. Nanoscale. 2020;12(37):19068–74.
Ye Y, Guo H, Sun X. Recent progress on cell-based biosensors for analysis of food safety and quality control. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;126:389–404.
Xiao P, Mao J, Ding K, Luo W, Hu W, Zhang X, et al. Solution-processed 3D RGO–MoS2/pyramid Si heterojunction for ultrahigh detectivity and ultra-broadband photodetection. Adv Mater. 2018;30(31):1801729.
Geleta GS, Zhao Z, Wang Z. A novel reduced graphene oxide/molybdenum disulfide/polyaniline nanocomposite-based electrochemical aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin B 1. Analyst. 2018;143(7):1644–9.
Qi H, Yue S, Bi S, Ding C, Song W. Isothermal exponential amplification techniques: from basic principles to applications in electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;110:207–17.
Law S, Leung AW, Xu C. Folic acid-modified celastrol nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, anticancer activity in 2D and 3D breast cancer models. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020;48(1):542–59.
Gu W, Zhu P, Jiang D, He X, Li Y, Ji J, et al. A novel and simple cell-based electrochemical impedance biosensor for evaluating the combined toxicity of DON and ZEN. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;70:447–54.
Liu Q, Xu S, Niu C, Li M, He D, Lu Z, et al. Distinguish cancer cells based on targeting turn-on fluorescence imaging by folate functionalized green emitting carbon dots. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;64:119–25.
Zhang Y, Liu J-M, Yan X-P. Self-assembly of folate onto polyethyleneimine-coated CdS/ZnS quantum dots for targeted turn-on fluorescence imaging of folate receptor overexpressed cancer cells. Anal Chem. 2013;85(1):228–34.
Xia S, Zhu P, Pi F, Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang J, et al. Development of a simple and convenient cell-based electrochemical biosensor for evaluating the individual and combined toxicity of DON, ZEN, and AFB1. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;97:345–51.
Chen C, Wang Y, Zhao X, Qian Y, Wang Q. Combined toxicity of butachlor, atrazine and λ-cyhalothrin on the earthworm Eisenia fetida by combination index (CI)-isobologram method. Chemosphere. 2014;112:393–401.
Wang Y, Ni Y. Molybdenum disulfide quantum dots as a photoluminescence sensing platform for 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol detection. Anal Chem. 2014;86(15):7463–70.
Jiang H, Yang J, Wan K, Jiang D, Jin C. Miniaturized paper-supported 3D cell-based electrochemical sensor for bacterial lipopolysaccharide detection. ACS Sens. 2020;5(5):1325–35.
Wang X, Zhu P, Pi F, Jiang H, Shao J, Zhang Y, et al. A sensitive and simple macrophage-based electrochemical biosensor for evaluating lipopolysaccharide cytotoxicity of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;81:349–57.
Funding
This work was supported by The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFC1606801), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20180160), Special Program of the State Administration for Market Regulation (2019YJ047), and Science and Technology Program of Nanjing Administration for Market Regulation (Kj2019042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(PDF 1386 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, D., Sheng, K., Gui, G. et al. A novel smartphone-based electrochemical cell sensor for evaluating the toxicity of heavy metal ions Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+ in rice. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 4277–4287 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03379-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03379-4