Abstract
Rationale
The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor has been recently identified as an important mediator of impulsive choice, as assessed in delay discounting. Although discounting is independently influenced by sensitivity to reinforcer magnitude and delayed reinforcement, few studies have examined how NMDA receptor ligands differentially affect these parameters.
Objectives
The current study examined the effects of various NMDA receptor ligands on sensitivity to reinforcer magnitude and delayed reinforcement in a delay-discounting procedure.
Methods
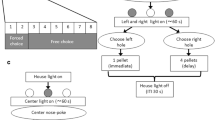
Following behavioral training, rats received treatments of the following NMDA receptor ligands: the uncompetitive antagonists ketamine (0, 1.0, 5.0, or 10.0 mg/kg; i.p.), MK-801 (0, 0.003, 0.01, or 0.03 mg/kg; s.c.), and memantine (0, 2.5, 5.0, or 10.0 mg/kg; i.p.), the competitive antagonist CGS 19755 (0, 5.0, 10.0, or 20.0 mg/kg; s.c.), the non-competitive NR2B subunit-selective antagonist ifenprodil (0, 1.0, 3.0, or 10.0 mg/kg; i.p), and the partial agonist D-cycloserine (0, 3.25, 15.0, or 30.0 mg/kg; s.c.).
Results
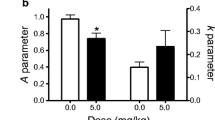
When an exponential model was used to describe discounting, CGS 19755 (5.0 mg/kg) increased impulsive choice without altering sensitivity to reinforcer magnitude. Conversely, ketamine (10.0 mg/kg), memantine (5.0 mg/kg), and ifenprodil (10.0 mg/kg) decreased sensitivity to reinforcer magnitude without altering impulsive choice. MK-801 and D-cycloserine did not alter delay-discounting performance, although two-way ANOVA analyses indicated D-cycloserine (15.0 mg/kg) decreased impulsive choice.
Conclusions
The behavioral changes observed in delay discounting following administration of NMDA receptor antagonists do not always reflect an alteration in impulsive choice. These results emphasize the utility in employing quantitative methods to assess drug effects in delay discounting.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriani W, Rea M, Baviera M, Invernizzi W, Carli M, Ghirardi O, Caprioli A, Laviola G (2004) Acetyl-L-carnitine reduces impulsive behaviour in adolescent rats. Psychopharmacology 176:296–304
Ahn WY, Rass O, Fridberg DJ, Bishara AJ, Forsyth JK, Breier A, Busemeyer JR, Hetrick WP, Bolbecker AR, O’Donnell BF (2011) Temporal discounting of rewards in patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. J Abnorm Psychol 120:911–921
Ainslie G (1975) Specious reward: a behavioral theory of impulsiveness and impulse control. Psychol Bull 82:463–496
Ainslie G, Herrnstein RJ (1981) Preference reversal and delayed reinforcement. Anim Learn Behav 9:476–482
Albein-Urios N, Martinez-González JM, Lozano O, Verdejo-Garcia A (2014) Monetary delay discounting in gambling and cocaine dependence with personality comorbidities. Addict Behav 39:1658–1662
Alessandri B, Bättig K, Welzl H (1989) Effects of ketamine on tunnel maze and water maze performance in the rat. Behav Neural Biol 52:194–212
Al-Khaled M, Heldmann M, Bolstorff I, Hagenah J, Münte TF (2015) Intertemporal choice in Parkinson’s disease and restless legs syndrome. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21:1330–1335
Aparicio CF, Elcoro M, Alonso-Alvarez B (2015) A long-term study of the impulsive choices of Lewis and Fischer 344 rats. Learn Behav 43:251–271
Archer T, Garcia D (2016) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: focus upon aberrant N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors systems. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 29:295–311
Baarendse PJJ, Vanderschuren LJMJ (2012) Dissociable effects of monoamine reuptake inhibitors on distinct forms of impulsive behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 219:313–326
Ben-Shahar OM, Szumlinksi KK, Lominac KD, Cohen A, Gordon E, Ploense KL, DeMartini J, Bernstein N, Rudy NM, Nabhan AN, Sacramento A, Pagano K, Carosso GA, Woodward N (2012) Extended access to cocaine self-administration results in reduced glutamate function within the medial prefrontal cortex. Addict Biol 17:746–757
Bezzina G, Cheung THC, Asgari K, Hampson CL, Body S, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E, Deakin JFW, Anderson IM (2007) Effects of quinolinic acid-induced lesions of the nucleus accumbens core on inter-temporal choice: a quantitative analysis. Psychopharmacology 195:71–84
Bezzina G, Body S, Cheung THC, Hampson CL, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E, Anderson IM, Deakin JFW (2008) Effect of disconnecting the orbital prefrontal cortex from the nucleus accumbens core on inter-temporal choice behaviour: a quantitative analysis. Behav Brain Res 191:272–279
Bezzina G, Body S, Cheung THC, Body S, Deakin JFW, Anderson IM, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E (2009) Quantitative analysis of the effect of lesions of the subthalamic nucleus on intemporal choice: further evidence for enhancement of the incentive value of food reinforcers. Behav Pharmacol 20:437–446
Bickel WK, Koffarnus MK, Moody L, Wilson AG (2014) The behavioral- and neuro-economic process of temporal discounting: a candidate behavioral marker of addiction. Neuropharmacology 76:518–527
Blasio A, Narayan AR, Kaminski BJ, Steardo L, Sabino V, Cottone P (2012) A modified adjusting delay task to assess impulsive choice between isocaloric reinforcers in non-deprived male rats: effects of 5-HT2A/C and 5-HT1A receptor agonists. Psychopharmacology 219:377–386
Boyce S, Wyatt A, Webb JK, O’Donnell R, Mason G, Rigby M, Sirinathsinghji D, Hill RG, Rupniak NM (1999) Selective NMDA NR2B antagonists induce antinociception without motor dysfunction: correlation with restricted localisation of NR2B subunit in dorsal horn. Neuropharmacology 38:611–623
Cardinal RN, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2000) The effects of d-amphetamine, chlordiazepoxide, α-flupenthixol and behavioural manipulations on choice of signalled and unsignalled delayed reinforcement in rats. Psychopharmacology 152:362–375
Chang JP, Lane HY, Tsai GE (2014) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) dysregulation. Curr Pharm Des 20:5180–5185
Chenard BL, Shalaby IA, Koe BK, Rounau RT, Butler TW, Prochiniak MA, Schmidt AW, Fox CB (1991) Separation of α1 adrenergic and N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist activity in a series of ifenprodil compounds. J Med Chem 34:3085–3090
Cosenza M, Nigro G (2015) Wagering the future: cognitive distortions, impulsivity, delay discounting, and time perspective in adolescent gambling. J Adolesc 45:56–66
Cottone P, Iemolo A, Narayan AR, Kwak J, Momaney D, Sabino V (2013) The uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists ketamine and memantine preferentially increase the choice for a small, immediate reward in low-impulsive rats. Psychopharmacology 226:127–138
Dix S, Gilmour G, Potts S, Smith JW, Tricklebank M (2010) A within-subject cognitive battery in the rat: differential effects of NMDA receptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology 212:227–242
Doyle KM, Feerick S, Kirkby DL, Eddleston A, Higgins GA (1998) Comparison of various N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists in a model of short-term memory and on overt behaviour. Behav Pharmacol 9:671–681
Evenden JL, Ryan CN (1996) The pharmacology of impulsive behaviour in rats: the effects of drugs on response choice with varying delays of reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 128:161–170
Evenden JL, Ryan CN (1999) The pharmacology of impulsive behaviour in rats VI: the effects of ethanol and selective serotoninergic drugs on response choice with varying delays of reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 146:413–421
Evens R, Stankevich Y, Dshemuchadse M, Storch A, Wolz M, Reichmann H, Schlaepfer TE, Goschke T, Lueken U (2015) The impact of Parkinson’s disease and subthalamic deep brain stimulation on reward processing. Neuropsychologia 75:11–19
Floresco SB, Tse MT, Ghods-Sharifi S (2008) Dopaminergic and glutamatergic regulation of effort- and delay-based decision making. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1966–1979
Fox AT, Hand DJ, Reilly MP (2008) Impulsive choice in a rodent model of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Behav Brain Res 187:146–152
Fraser CM, Cooke MJ, Fisher A, Thompson ID, Stone TW (1996) Interactions between ifenprodil and dizocilpine on mouse behaviour in models of anxiety and working memory. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 6:311–316
Garcia LS, Comim CM, Valvassori SS, Réus GZ, Stertz L, Kapczinski F, Gavioli EC, Quevedo J (2009) Ketamine treatment reverses behavioral and physiological alterations induced by chronic mild stress in rats. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:450–455
Griffin WC III, Haun HL, Hazelbaker CL, Ramachandra VS, Becker HC (2014) Increased extracellular glutamate in the nucleus accumbens promotes excessive ethanol drinking in ethanol dependent mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:707–717
Hand DJ, Fox AT, Reilly MP (2009) Differential effects of d-amphetamine on impulsive choice in spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto rats. Behav Pharmacol 20:549–553
Harder JA, Aboobaker AA, Hodgetts TC, Ridley RM (1998) Learning impairments induced by glutamate blockade using dizocilpine (MK-801) in monkeys. Br J Pharmacol 125:1013–1018
Heerey EA, Robinson BM, McMahon RP, Gold JM (2007) Delay discounting in schizophrenia. Cogn Neuropsychiatry 12:213–221
Henderson G, Johnson JW, Ascher P (1990) Competitive antagonists and partial agonists at the glycine modulatory site of the mouse N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J Physiol 430:189–212
Higgins GA, Silenieks LB, MacMillan C, Sevo J, Zeeb FD, Thevarkunnel S (2016) Enhanced attention and impulsive action following NMDA receptor GluN2B-selective antagonist pretreatment. Behav Brain Res 311:1-14.
Ho M-Y, Mobini S, Chian T-J, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E (1999) Theory and method in the quantitative analysis of “impulsive choice” behaviour: implications for psychopharmacology. Psychopharmacology 146:362–372
Huskinson SL, Anderson KG (2013) Effects of different fixed-ratio requirements on delay discounting in rats. Behav Process 100:18–22
Isherwood SN, Pekcec A, Nicholson JR, Robbins TW, Dalley JW (2015) Dissociable effects of mGluR5 allosteric modulation on distinct forms of impulsivity in rats: interaction with NMDA receptor antagonism. Psychopharmacology 232:3327–3344
Jackson JN, MacKillop J (2016) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and monetary delay discounting: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging 1:316–325
Jensen V, Rinholm JE, Johansen TJ, Medin T, Storm-Mathisen J, Sagvolden T, Hvalby O, Bergersen LH (2009) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit dysfunction at hippocampal glutamatergic synapses in an animal model of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuroscience 158:353–364
Johnson JW, Ascher P (1987) Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature 325:529–531
Kalivas PW (2009) The glutamate homeostasis hypothesis of addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:561–572
Khan AM, Currás MC, Dao J, Jamal FA, Turkowski CA, Goel RK, Gillard ER, Wolfsohn SD, Stanley BG (1999) Lateral hypothalamic NMDA receptor subunits NR2A and/or NR2B mediate eating: immunochemical/behavioral evidence. Am J Phys 276:R880–R891
Kheramin S, Body S, Mobini S, Ho M-Y, Velázquez-Martinez DN, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E, Deakin JFW, Anderson IM (2002) Effects of quinolinic acid-induced lesions of the orbital prefrontal cortex on inter-temporal choice: a quantitative analysis. Psychopharmacology 165:9–17
Koffarnus MN, Newman AH, Grundt P, Rice KC, Woods JH (2011) Effects of selective dopaminergic compounds on a delay-discounting task. Behav Pharmacol 22:300–311
Kos T, Nikiforuk A, Rafa D, Popik P (2011) The effects of NDMA receptor antagonists on attentional set-shifting task performance in mice. Psychopharmacology 214:911–921
Lalonde R, Joyal CC (1993) Effects of ketamine and L-glutamic acid diethyl ester on spatial and nonspatial learning tasks in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:539–545
Lesch KP, Merker S, Reif A, Novak M (2013) Dances with black widow spiders: dysregulation of glutamate signalling enters center stage in ADHD. Eur Neuropharmacol 23:479–491
Li JT, Su YA, Guo CM, Feng Y, Yang Y, Huang RH, Si TM (2011) Persisting cognitive deficits induced by low-dose, subchronic treatment with MK-801 in adolescent rats. Eur J Pharmacol 652:65–72
Liu YP, Wilkinson LS, Robbins TW (2004) Effects of acute and chronic buspirone on impulsive choice and efflux of 5-HT and dopamine in hippocampus, nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 173:175–185
Ma Y-Y, Yu P, Guo C-Y, Cui C-L (2011) Effects of ifenprodil on morphine-induced conditioned place preference and spatial learning and memory in rats. Neurochem Res 36:383–391
Maguire DR, Henson C, France CP (2014) Effects of amphetamine on delay discounting in rats depend on the manner in which delay is varied. Neuropharmacol 87:173–179
Mikolajczak P, Okulicz-Kozaryn I, Polanska A, Szczawinska K, Bobkiewicz-Kozlowska T (2002) Effect of multiple ifenprodil or spermidine treatment on social recognition in rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 13:61–67
Miller EM, Pomerleau F, Huetti P, Gerhardt GA, Glaser PE (2014) Aberrant glutamate signaling in the prefrontal cortex and striatum of the spontaneously hypertensive rat model of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychopharmacology 231:3019–3029
Monaghan DT, Jane DE (2009) Pharmacology of NMDA receptors. In: Van Dongen AM (ed) Biology of the NMDA receptor. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 257–281
Myerson J, Green L, Warusawitharana M (2001) Area under the curve as a measure of discounting. J Exp Anal Behav 76(2):235–243
Navarrete A, Flores-Machorro FX, Téllez-Ballesteros RI, Alfaro-Romero A, Balderas JL, Reyes A (2014) Study on action mechanism of 1-(4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl)piperazine (MMPP) in acquisition, formation, and consolidation of memory in mice. Drug Dev Res 75:59–67
Niciu MJ, Henter ID, Sanacora G, Zarate CA Jr (2014) Glial abnormalities in substance use disorders and depression: does shared glutamatergic dysfunction contribute to comorbidity? World J Biol Psychiatry 15:2–16
Oliveira L, Green L, Myerson J (2014) Pigeons’ delay discounting functions established using a concurrent-chains procedure. J Exp Anal Behav 102:151–161
Parada J, Czuczwar SJ, Turski WA (1992) NBQX does not affect learning and memory tasks in mice: a comparison with D-CPPene and ifenprodil. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 1:67–71
Pattij T, Vanderschuren LJ (2008) The neuropharmacology of impulsive behaviour. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:192–199
Perlov E, Phillipsen A, Hesslinger B, Buechert M, Ahrendts J, Feige B, Bubl E, Hennig J, Ebert D, Tebartz van Elst L (2007) Reduced cingulate glutamate/glutamine-to-creatine ratios in adult patients with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder—a magnet resonance spectroscopy study. J Psychiatry Res 41:934–941
Perry JL, Larson EB, German JP, Madden GJ, Carroll ME (2005) Impulsivity (delay discounting) as a predictor of acquisition of IV cocaine self-administration in female rats. Psychopharmacology 178:193–201
Petry NM (2001) Pathological gamblers, with and without substance use disorders, discount delayed rewards at high rates. J Abnorm Psychol 110:482–487
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D (2007) Linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, pp. 1–89
Popik P, Kos T, Zhang Y, Bisaga A (2011) Memantine reduces consumption of highly palatable food in a rat model of binge eating. Amino Acids 40:477–485
Rapanelli M, Frick LR, Bernardez-Vidal M, Zanutto BS (2013) Different MK-801 administration schedules induce mild to severe learning impairments in an operant conditioning task: role of buspirone and risperidone in ameliorating these cognitive deficits. Behav Brain Res 257:156–165
Schwager AL, Haack AK, Taha SA (2014) Impaired flexibility in decision making in rats after administration of the pharmacological stressor yohimbine. Psychopharmacology 231:3941–3952
Simon NW, Mendez IA, Setlow B (2007) Cocaine exposure causes long-term increases in impulsive choice. Behav Neurosci 121:543–549
Slezak JM, Anderson KG (2009) Effects of variable training, signaled and unsignaled delays, and d-amphetamine on delay-discounting functions. Behav Pharmacol 20:424–436
Smith KL, Rao RR, Velázquez-Sánchez C, Valenza M, Giuliano C, Everitt BJ, Sabino V, Cottone P (2015) The uncompetitive N-methyl-D-asparate antagonist memantine reduces binge-like eating, food-seeking behavior, and compulsive eating: role of the nucleus accumbens shell. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:1163–1171
St. Onge JR, Chiu YC, Florescro SB (2010) Differential effects of dopaminergic manipulations on risky choice. Psychopharmacology 211:209–221
Stanis JJ, Burns RM, Sherrill LK, Gulley JM (2008) Disparate cocaine-induced locomotion as a predictor of choice behavior in rats trained in a delay-discounting task. Drug Alcohol Dep 98:54–62
Sukhotina IA, Dravolina OA, Novitskaya Y, Zvartau EE, Danysz W, Bespalov AY (2008) Effects of mGlu1 receptor blockade on working memory, time estimation, and impulsivity in rats. Psychopharmacology 196:211–220
Talpos JC, Fletcher AC, Circelli C, Tricklebank MD, Dix SL (2012) The pharmacological sensitivity of a touchscreen-based visual discrimination task in the rat using simple and perceptually challenging stimuli. Psychopharmacology 221:437–449
Tang AH, Franklin SR (1983) Disruption of brightness discrimination in a shock avoidance task by phencyclidine and its antagonism in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 225:503–508
Tanno T, Maguire DR, Hensen C, France CP (2014) Effects of amphetamine and methylphenidate on delay discounting in rats: interactions with order of delay presentation. Psychopharmacology 231:85–95
van den Bergh FS, Bloemarts E, Groenink L, Olivier B, Oosting RS (2006) Delay aversion: effects of 7-OH-DPAT, 5-HT1A/1B-receptor stimulation and D-cycloserine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85:736–743
van der Staay FJ, Rutten K, Erb C, Blokland A (2011) Effects of the cognition impairer MK-801 on learning and memory in mice and rats. Behav Brain Res 220:215–229
van Gaalen MM, van Koten R, Schoffelmeer AN, Vanderschuren LJ (2006) Critical involvement of dopaminergic neurotransmission in impulsive decision making. Biol Psychiatry 60:66–73
Venâncio C, Magalhães A, Antunes L, Summavielle T (2011) Impaired spatial memory after ketamine administration in chronic low doses. Curr Neuropharmacol 9:251–255
Ward KC, Khattak HZ, Richardson L, Lee JL, Vreugdenhil M (2013) NMDA receptor antagonists distort visual grouping in rats performing a modified two-choice visual discrimination task. Psychopharmacology 229:627–637
Weller RE, Avsar KB, Cox JE, Reid MA, White DM, Lahti AC (2014) Delay discounting and task performance consistency in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 215:286–293
Wiehler A, Bromberg U, Peters J (2015) The role of prospection in steep temporal reward discounting in gambling addiction. Front Psychiatry 6:112
Winstanley CA, Theobald DEH, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2005) Interactions between serotonin and dopamine in the control of impulsive choice in rats: therapeutic implications for impulse control disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:669–682
Winstanley CA, LaPlant Q, Theobald DEH, Green TA, Bachtell RK, Perrotti LI, DiLeone RJ, Russo SJ, Garth WJ, Self DW, Nestler EJ (2007) ΔFosB induction in orbitofrontal cortex mediates tolerance to cocaine-induced cognitive dysfunction. J Neurosci 27:10497–10507
Wooters TE, Bardo MT (2011) Methylphenidate and fluphenazine, but not amphetamine, differentially affect impulsive choice in spontaneously hypertensive, Wistar-Kyoto and Sprague-Dawley rats. Brain Res 1396:45–53
Wooters TE, Dwoskin LP, Bardo MT (2011) Discriminative stimulus effects of NMDA, AMPA, and mGluR5 glutamate receptor ligands in methamphetamine-trained rats. Behav Pharmacol 22:516–524
Yates JR, Batten SR, Bardo MT, Beckmann JS (2015) Role of ionotropic glutamate receptors in delay and probability discounting in the rat. Psychopharmacology 232:1187–1196
Yates JR, Breitenstein KA, Gunkel BT, Hughes MN, Johnson AB, Rogers KK, Sharpe SM (2016) Effects of NMDA receptor antagonists on probability discounting depend on the order of probability presentation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 150-151:31–38
Young ME, Clark MH, Goffus A, Hoane MR (2009) Mixed effects modeling of Morris water maze data: advantages and cautionary notes. Learn Motiv 40:160–177
Zeeb FD, Floresco SB, Winstanley CA (2010) Contributions of the orbitofrontal cortex to impulsive choice: interactions with basal levels of impulsivity, dopamine signalling, and reward-related cues. Psychopharmacology 211:87–98
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Cliff Brown, Kerry Breitenstein, Anthony Johnson, and Sara Sharpe for assistance in data collection. We also would like to thank Dr. Mark Bardgett for reviewing a draft of the manuscript and providing feedback. Finally, we thank the NIMH’s Chemical Synthesis and Drug Supply Program for generously providing CGS 19755.
The current study was supported by NIH grant P20GM103436, as well as a Northern Kentucky University Faculty Project Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 88 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yates, J.R., Gunkel, B.T., Rogers, K.K. et al. Effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor ligands on sensitivity to reinforcer magnitude and delayed reinforcement in a delay-discounting procedure. Psychopharmacology 234, 461–473 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4469-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4469-5