Abstract
Rationale
Metabotropic glutamate 1 (mGlu1) receptor antagonists were reported to induce cognitive deficits in several animal models using aversive learning procedures.
Objective
The present study aimed to further characterize behavioral effects of mGlu1 receptor antagonists using appetitively motivated tasks that evaluate working memory, timing, and impulsivity functions.
Materials and methods
Separate groups of adult male Wistar rats were trained to perform four food-reinforced operant tasks: delayed non-matching to position (DNMTP), differential reinforcement of low rates of responding 18 s (DRL 18-s), signal duration discrimination (2-s vs 8-s bisection), and tolerance to delay of reward. Before the tests, rats were pretreated with (3-ethyl-2-methyl-quinolin-6-yl)-(4-methoxy-cyclohexyl)-methanone methanesulfonate (EMQMCM; 2.5–10 mg/kg, i.p.; JNJ16567083).
Results
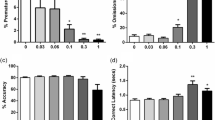
In DNMTP task, EMQMCM produced delay-dependent increases in performance accuracy so that, at 10 mg/kg dose level, percentage of correct lever choices was enhanced at 8- and 16-s delays. In DRL task, at all three tested doses, response rates were higher, and reinforcement rates were lower than under control conditions. In signal duration discrimination tasks, EMQMCM did not have any specific effects on temporal control. In tolerance to delay of reward, EMQMCM (5 and 10 mg/kg) facilitated choice of the lever associated with large reward at longer delay levels.
Conclusions
Blockade of mGlu1 receptors improves working memory and reduces impulsive choice at the doses that have no effects on time perception but appear to facilitate impulsive action.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiba A, Chen C, Herrup K, Rosenmund C, Stevens CF, Tonegawa S (2004) Reduced hippocampal long-term potentiation and context-specific learning deficit in associative learning in mGluR1 mutant mice. Cell 79:365–375
Aultman JM, Moghaddam B (2001) Distinct contributions of glutamate and dopamine receptors to temporal aspects of rodent working memory using a clinically relevant task. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 153:353–364
Ballard TM, Mcallister KH (2000) The NMDA antagonist EAA 494 does not impair working memory in an operant DNMTP task in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:725–730
Belozertseva IV, Kos T, Popik P, Danysz W, Bespalov AY (2007) Antidepressant-like effects of mGluR1 and mGluR5 antagonists in the rat forced swim and the mouse tail suspension tests. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 17:172–179
Britton KT, Koob GF (1989) Effects of corticotropin releasing factor, desipramine and haloperidol on a DRL schedule of reinforcement. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 32:967–970
Cardinal RN, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2000) The effects of d-amphetamine, chlordiazepoxide, alpha-flupenthixol and behavioural manipulations on choice of signalled and unsignalled delayed reinforcement in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152:362–375
Cheng RK, MacDonald CJ, Meck WH (2006) Differential effects of cocaine and ketamine on time estimation: Implications for neurobiological models of interval timing. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85:114–122
Christoffersen GR, Christensen LH, Hammer P, Vang M (1999) The class I metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist, AIDA, improves short-term and impairs long-term memory in a spatial task for rats. Neuropharmacology 38:817–823
Clissold DB, Karbon EW, Ferkany JW, Hartman T, Pontecorvo MJ (1992) Effects of the strychnine-insensitive glycine receptor antagonist and sigma agents on working memory performance comparison with dizocilpine and scopolamine. Behav Pharmacol 3:393–402
Danysz W, Wroblewski JT, Costa E (1988) Learning impairment in rats by N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 27:653–656
Dravolina OA, Danysz W, Bespalov AY (2006) Effects of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists on the behavioral sensitization to motor effects of cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 187:397–404
Evenden JL (1999) Varieties of impulsivity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 146:348–361
Gravius A, Pietraszek M, Schafer D, Schmidt WJ, Danysz W (2005) Effects of mGlu1 and mGlu5 receptor antagonists on negatively reinforced learning. Behav Pharmacol 16:113–121
Gravius A, Barberi C, Schafer D, Schmidt WJ, Danysz W (2006) The role of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in acquisition and expression of contextual and auditory fear conditioning in rats—a comparison. Neuropharmacology 51:1146–1155
Heale V, Harley C (1990) MK-801 and APV impair acquisition, but not retention, of the Morris milk maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 36:145–149
Higgins GA, Enderlin M, Haman M, Fletcher PJ (2003) The 5-HT2A receptor antagonist M100,907 attenuates motor and ‘impulsive-type’ behaviours produced by NMDA receptor antagonism. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 170:309–319
Kos T, Popik P, Pietraszek M, Schafer D, Danysz W, Dravolina O, Blokhina E, Galankin T, Bespalov AY (2006) Effect of 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist MDL 72222 on behaviors induced by ketamine in rats and mice. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 16:297–310
Lesage ASJ, Bischoff F, Van Beijsterveldt L, Meert T, Steckler T, Ashton D (2002) Novel, centrally active mGluR1 antagonists: in vitro and in vivo pharmacology. Neuropharmacology 43:295
Maciejak P, Taracha E, Lehner M, Szyndler J, Bidzinski A, Skorzewska A, Wislowska A, Zienowicz M, Plaznik A (2003) Hippocampal mGluR1 and consolidation of contextual fear conditioning. Brain Res Bull 62:39–45
Maricq AV, Church RM (1983) The differential effects of haloperidol and methamphetamine on time estimation in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 79:10–15
McAuley JD, Miller JP, Pang KCH (2006) Modeling the effects of the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 on timing in rats. Behav Neurosci 120:1163–1168
Meck WH (1986) Affinity for the dopamine D2 receptor predicts neuroleptic potency in decreasing the speed of an internal clock. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:1185–1189
Meck WH (1996) Neuropharmacology of timing and time perception. Cogn Brain Res 3:227–242
Meck WH (2006) Neuroanatomical localization of an internal clock: A functional link between mesolimbic, nigrostriatal, and mesocortical dopaminergic systems. Brain Res 1109:93–107
Naie K, Manahan-Vaughan D (2005) Pharmacological antagonism of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 regulates long-term potentiation and spatial reference memory in the dentate gyrus of freely moving rats via N-methyl-d-aspartate and metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent mechanisms. Eur J Neurosci 21:411–421
O’Donnell JM, Seiden LS (1983) Differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate 72-second schedule: selective effects of antidepressant drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:80–88
O’Donnell JM, Marek GJ, Seiden LS (2005) Antidepressant effects assessed using behavior maintained under a differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate (DRL) operant schedule. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:785–798
Packard MG, Teather LA (1997) Posttraining injections of MK-801 produce a time-dependent impairment of memory in two water maze tasks. Neurobiol Learn Mem 68:42–50
Petersen S, Bomme C, Baastrup C, Kemp A, Christoffersen GR (2002) Differential effects of mGluR1 and mGluR5 antagonism on spatial learning in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:381–389
Pietraszek M, Sukhanov I, Maciejak P, Szyndler J, Gravius A, Wislowska A, Plaznik A, Bespalov AY, Danysz W (2005a) Anxiolytic-like effects of mGlu1 and mGlu5 receptor antagonists in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 514:25–34
Pietraszek M, Gravius A, Schafer D, Weil T, Trifanova D, Danysz W (2005b) mGluR5, but not mGluR1, antagonist modifies MK-801-induced locomotor activity and deficit of prepulse inhibition. Neuropharmacology 49:73–85
Richards JB, Sabol KE, Seiden LS (1993) DRL interresponse-time distributions: quantification by peak deviation analysis. J Exp Anal Behav 60:361–385
Riedel G, Wetzel W, Reymann KG (1996) Comparing the role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in long-term potentiation and in learning and memory. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 20:761–789
Sloan HL, Good M, Dunnett SB (2006) Double dissociation between hippocampal and prefrontal lesions on an operant delayed matching task and a water maze reference memory task. Behav Brain Res 171:116–126
Steckler T, Lavreysen H, Oliveira AM, Aerts N, Van Craenendonck H, Prickaerts J, Megens A, Lesage AS (2005a) Effects of mGlu1 receptor blockade on anxiety-related behaviour in the rat lick suppression test. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:198–206
Steckler T, Oliveira AF, Van Dyck C, Van Craenendonck H, Mateus AM, Langlois X, Lesage AS, Prickaerts J (2005b) Metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 blockade impairs acquisition and retention in a spatial Water maze task. Behav Brain Res 164:52–60
Sukhanov IM, Zakharova ES, Danysz W, Bespalov AY (2004) Effects of NMDA receptor channel blockers, MK-801 and memantine, on locomotor activity and tolerance to delay of reward in Wistar–Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Behav Pharmacol 15:263–271
van Gaalen MM, Brueggeman RJ, Bronius PF, Schoffelmeer AN, Vanderschuren LJ (2006a) Behavioral disinhibition requires dopamine receptor activation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 187:73–85
van Gaalen MM, van Koten R, Schoffelmeer AN, Vanderschuren LJ (2006b) Critical involvement of dopaminergic neurotransmission in impulsive decision making. Biol Psychiatry 60:66–73
Varty GB, Grilli M, Forlani A, Fredduzzi S, Grzelak ME, Guthrie DH, Hodgson RA, Lu SX, Nicolussi E, Pond AJ, Parker EM, Hunter JC, Higgins GA, Reggiani A, Bertorelli R (2005) The antinociceptive and anxiolytic-like effects of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) antagonists, MPEP and MTEP, and the mGluR1 antagonist, LY456236, in rodents: a comparison of efficacy and side-effect profiles. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:207–217
Wade TR, de Wit H, Richards JB (2000) Effects of dopaminergic drugs on delayed reward as a measure of impulsive behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 150:90–101
Willmore CB, Bespalov AY, Beardsley PM (2001) Competitive and noncompetitive NMDA antagonist effects in rats trained to discriminate lever-press counts. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 69:493–502
Winstanley CA, Dalley JW, Theobald DE, Robbins TW (2003) Global 5-HT depletion attenuates the ability of amphetamine to decrease impulsive choice on a delay-discounting task in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 170:320–331
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by Merz Pharmaceuticals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Irina A. Sukhotina and Olga A. Dravolina contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukhotina, I.A., Dravolina, O.A., Novitskaya, Y. et al. Effects of mGlu1 receptor blockade on working memory, time estimation, and impulsivity in rats. Psychopharmacology 196, 211–220 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0953-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0953-2