Abstract
Rationale
Repeated methamphetamine (MA) use leads to increases in the incentive motivational properties of the drug as well as cognitive impairments. These behavioral alterations persist for some time following abstinence, and neuroadaptations in the structure and function of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) are particularly important for their expression. However, there is a weak understanding of the changes in neural firing and oscillatory activity in the PFC evoked by repeated drug use, thus complicating the development of novel treatment strategies for addiction.
Objectives
The purpose of the current study was to assess changes in cognitive and brain function following MA sensitization.
Methods
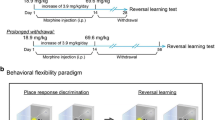
Sensitization was induced in rats, then temporal and recognition memory were assessed after 1 or 30 days of abstinence. Electrophysiological recordings from the medial PFC were also acquired from rats whereupon simultaneous measures of oscillatory and spiking activity were examined.
Results
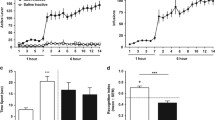
Impaired temporal memory was observed after 1 and 30 days of abstinence. However, recognition memory was only impaired after 1 day of abstinence. An injection of MA profoundly decreased neuronal firing rate and the anesthesia-induced slow oscillation (SO) in both sensitized (SENS) and control (CTRL) rats. Strong correlations were observed between the SO and gamma band power, which was altered in SENS animals. A decrease in the number of neurons phase-locked to the gamma oscillation was also observed in SENS animals.
Conclusions
The changes observed in PFC function may play an integral role in the expression of the altered behavioral phenotype evoked by MA sensitization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balleine BW, O’Doherty JP (2009) Human and rodent homologies in action control: corticostriatal determinants of goal-directed and habitual action. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:48–69
Bartos M, Vida I, Jonas P (2007) Synaptic mechanisms of synchronized gamma oscillations in inhibitory interneuron networks. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:45–56
Bechara A (2005) Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: a neurocognitive perspective. Nat Neurosci 8:1458–1463
Belcher AM, O’Dell SJ, Marshall JF (2006) A sensitizing regimen of methamphetamine causes impairments in a novelty preference task of object recognition. Behav Brain Res 170:167–172
Broadbent NJ, Gaskin S, Squire LR, Clark RE (2010) Object recognition memory and the rodent hippocampus. Learn Mem 17:5–11
Buzsaki G, Chrobak JJ (1995) Temporal structure in spatially organized neuronal ensembles: a role for interneuronal networks. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5:504–510
Camarasa J, Rodrigo T, Pubill D, Escubedo E (2010) Memantine is a useful drug to prevent the spatial and non-spatial memory deficits induced by methamphetamine in rats. Pharmacol Res 62:450–456
Carr MF, Karlsson MP, Frank LM (2012) Transient slow gamma synchrony underlies hippocampal memory replay. Neuron 75:700–713
Chang EH-Y, Huerta PT (2012) Neurophysiological correlates of object recognition in the dorsal subiculum. Front Behav Neurosci 6
Cheng RK, Etchegaray M, Meck WH (2007) Impairments in timing, temporal memory, and reversal learning linked to neurotoxic regimens of methamphetamine intoxication. Brain Res 1186:255–266
Clark RE, Kuczenski R, Segal DS (2007) Escalating dose, multiple binge methamphetamine regimen does not impair recognition memory in rats. Synapse 61(7):515–522
Colgin LL (2011) Oscillations and hippocampal-prefrontal synchrony. Curr Opin Neurobiol 21:467–474
Dalley JW, Theobald DE, Berry D, Milstein JA, Lääne K, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2005) Cognitive sequelae of intravenous amphetamine self-administration in rats: evidence for selective effects on attentional performance. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:525–537
Dalley JW, Laane K, Theobald DE, Pena Y, Bruce CC, Huszar AC, Wojcieszek M, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2007) Enduring deficits in sustained visual attention during withdrawal of intravenous methylenedioxymethamphetamine self-administration in rats: results from a comparative study with d-amphetamine and methamphetamine. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1195–1206
Dayan P, Abbott LF (2001) Theoretical neuroscience. MIT Press, Cambridge
Durstewitz D, Seamans JK (2008) The dual-state theory of prefrontal cortex dopamine function with relevance to catechol-O-methyltransferase genotypes and schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 64:739–749
Ellinwood EH Jr, Balster RL (1974) Rating the behavioral effects of amphetamine. Eur J Pharmacol 28:35–41
Euston DR, Gruber AJ, McNaughton BL (2012) The role of medial prefrontal cortex in memory and decision making. Neuron 76:1057–1070
Futamura T, Akiyama S, Sugino H, Forbes A, McQuade RD, Kikuchi T (2010) Aripiprazole attenuates established behavioral sensitization induced by methamphetamine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:1115–1119
George O, Koob GF (2010) Individual differences in prefrontal cortex function and the transition from drug use to drug dependence. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:232–247
Gruber T, Müller MM (2005) Oscillatory brain activity dissociates between associative stimulus content in a repetition priming task in the human EEG. Cereb Cortex 15:109–116
Gulley JM, Stanis JJ (2010) Adaptations in medial prefrontal cortex function associated with amphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization. Neuroscience 166:615–624
Hannesson DK, Howland JG, Phillips AG (2004) Interaction between perirhinal and medial prefrontal cortex is required for temporal order but not recognition memory for objects in rats. J Neurosci 24:4596–4604
Herring NR, Schaefer TL, Gudelsky GA, Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2008) Effect of (+)-methamphetamine on path integration learning, novel object recognition, and neurotoxicity in rats. Psychopharmacology 199:637–650
Hoffman WF, Moore M, Templin R, McFarland B, Hitzemann RJ, Mitchell SH (2006) Neuropsychological function and delay discounting in methamphetamine-dependent individuals. Psychopharmacology 188:162–170
Hoffman KL, Battaglia FP, Harris K, MacLean JN, Marshall L, Mehta MR (2007) The upshot of up states in the neocortex: from slow oscillations to memory formation. J Neurosci 27:11838–11841
Homayoun H, Moghaddam B (2006) Progression of cellular adaptations in medial prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortex in response to repeated amphetamine. J Neurosci 26:8025–8039
Isomura Y, Sirota A, Ozen S, Montgomery S, Mizuseki K, Henze DA, Buzsaki G (2006) Integration and segregation of activity in entorhinal-hippocampal subregions by neocortical slow oscillations. Neuron 52:871–882
Iudicello JE, Weber E, Grant I, Weinborn M, Woods SP, Group HNRC (2011) Misremembering future intentions in methamphetamine-dependent individuals. Clin Neuropsychol 25:269–286
Jang J, Ha HJ, Kim YB, Chung YK, Jung MW (2007) Effects of methamphetamine on single unit activity in rat medial prefrontal cortex in vivo. Neural Plast 2007:29821
Kosheleff AR, Rodriguez D, O’Dell SJ, Marshall JF, Izquierdo A (2012) Comparison of single-dose and extended methamphetamine administration on reversal learning in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 224:459–467
Kurti A, Swanton D, Matell M (2013) The potential link between temporal averaging and drug-taking behavior. Subjective Time. MIT Press
Lapish CC, Chiang J, Wang JZ, Phillips AG (2012) Oscillatory power and synchrony in the rat forebrain are altered by a sensitizing regime of D-amphetamine. Neuroscience 203:108–121
Lee H, Simpson GV, Logothetis NK, Rainer G (2005) Phase locking of single neuron activity to theta oscillations during working memory in monkey extrastriate visual cortex. Neuron 45:147–156
Lisman JE, Idiart M (1995) Storage of 7+/−2 short-term memories in oscillatory subcycles. Science 267:1512–1515
Liu N, Liu Y, Fan Y, Yu H, Wilson FA, Ma Y, Hu X (2005) EEG activities in the orbitofrontal cortex and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex during the development of morphine dependence, tolerance and withdrawal in rhesus monkeys. Brain Res 1053:137–145
Lu P, Mamiya T, Lu L, Mouri A, Niwa M, Kim H-C, Zou L-B, Nagai T, Yamada K, Ikejima T (2010) Silibinin attenuates cognitive deficits and decreases of dopamine and serotonin induced by repeated methamphetamine treatment. Behav Brain Res 207:387–393
Martinovic J, Gruber T, Muller MM (2007) Induced gamma band responses predict recognition delays during object identification. J Cogn Neurosci 19:921–934
Masquelier T, Hugues E, Deco G, Thorpe SJ (2009) Oscillations, phase-of-firing coding, and spike timing-dependent plasticity: an efficient learning scheme. J Neurosci 29:13484–13493
McGuire BA, Baladi MG, France CP (2011) Eating high-fat chow enhances sensitization to the effects of methamphetamine on locomotion in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 658:156–159
Mizoguchi H, Takuma K, Fukakusa A, Ito Y, Nakatani A, Ibi D, Kim H-C, Yamada K (2008) Improvement by minocycline of methamphetamine-induced impairment of recognition memory in mice. Psychopharmacology 196:233–241
Newton TF, Kalechstein AD, Hardy DJ, Cook IA, Nestor L, Ling W, Leuchter AF (2004) Association between quantitative EEG and neurocognition in methamphetamine-dependent volunteers. Clin Neurophysiol 115:194–198
O’Keefe J, Recce ML (1993) Phase relationship between hippocampal place units and the EEG theta rhythm. Hippocampus 3:317–330
Parsegian A, Glen WB Jr, Lavin A, See RE (2011) Methamphetamine self-administration produces attentional set-shifting deficits and alters prefrontal cortical neurophysiology in rats. Biol Psychiatry 69:253–259
Paulus MP, Hozack N, Frank L, Brown GG, Schuckit MA (2003) Decision making by methamphetamine-dependent subjects is associated with error-rate-independent decrease in prefrontal and parietal activation. Biol Psychiatry 53:65–74
Petrides M (1991) Functional specialization within the dorsolateral frontal cortex for serial order memory. Proc R Soc London, Ser B 246:299–306
Pierce RC, Kalivas PW (1997) A circuitry model of the expression of behavioral sensitization to amphetamine-like psychostimulants. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 25:192–216
Pirch J, Corbus M, Ebenezer I (1985) Conditioned cortical slow potential responses in urethane anesthetized rats. Int J Neurosci 25:207–218
Pitel AL, Witkowski T, Vabret F, Guillery-Girard B, Desgranges B, Eustache F, Beaunieux H (2007) Effect of episodic and working memory impairments on semantic and cognitive procedural learning at alcohol treatment entry. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:238–248
Reichel CM, Schwendt M, McGinty JF, Olive MF, See RE (2010) Loss of object recognition memory produced by extended access to methamphetamine self-administration is reversed by positive allosteric modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:782–792
Reichel CM, Chan CH, Ghee SM, See RE (2012) Sex differences in escalation of methamphetamine self-administration: cognitive and motivational consequences in rats. Psychopharmacology 223:371–380
Rømer Thomsen K, Joensson M, Lou HC, Møller A, Gross J, Kringelbach ML, Changeux J-P (2013) Altered paralimbic interaction in behavioral addiction. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:4744–4749
Rose JE, Woolsey CN (1947) The orbitofrontal cortex and its connections with the mediodorsal nucleus in rabbit, sheep and cat. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis 27:210–232
Salo R, Nordahl TE, Galloway GP, Moore CD, Waters C, Leamon MH (2009) Drug abstinence and cognitive control in methamphetamine-dependent individuals. J Subst Abuse Treat 37:292–297
Salo R, Gabay S, Fassbender C, Henik A (2011) Distributed attentional deficits in chronic methamphetamine abusers: evidence from the Attentional Network Task (ANT). Brain Cogn 77:446–452
Sax KW, Strakowski SM (2001) Behavioral sensitization in humans. J Addict Dis 20:55–65
Seamans JK, Lapish CC, Durstewitz D (2008) Comparing the prefrontal cortex of rats and primates: insights from electrophysiology. Neurotox Res 14:249–262
Senior TJ, Huxter JR, Allen K, O’Neill J, Csicsvari J (2008) Gamma oscillatory firing reveals distinct populations of pyramidal cells in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. J Neurosci 28:2274–2286
Shinomoto S, Shima K, Tanji J (2003) Differences in spiking patterns among cortical neurons. Neural Comput 15:2823–2842
Simon SL, Domier C, Carnell J, Brethen P, Rawson R, Ling W (2000) Cognitive impairment in individuals currently using methamphetamine. Am J Addict 9:222–231
Simon SL, Dacey J, Glynn S, Rawson R, Ling W (2004) The effect of relapse on cognition in abstinent methamphetamine abusers. J Subst Abuse Treat 27:59–66
Sirota A, Montgomery S, Fujisawa S, Isomura Y, Zugaro M, Buzsaki G (2008) Entrainment of neocortical neurons and gamma oscillations by the hippocampal theta rhythm. Neuron 60:683–697
Slamberova R, Mikulecka A, Pometlova M, Schutova B, Hruba L, Deykun K (2011) Sex differences in social interaction of methamphetamine-treated rats. Behav Pharmacol 22:617–623
Sohal VS, Zhang F, Yizhar O, Deisseroth K (2009) Parvalbumin neurons and gamma rhythms enhance cortical circuit performance. Nature 459:698–702
Staff NRC (2003) Guidelines for the care and use of mammals in neuroscience and behavioral research. National Academies Press
Steketee JD, Kalivas PW (2011) Drug wanting: behavioral sensitization and relapse to drug-seeking behavior. Pharmacol Rev 63:348–365
Steriade M (1997) Synchronized activities of coupled oscillators in the cerebral cortex and thalamus at different levels of vigilance. Cereb Cortex 7:583–604
Steriade M (2006) Grouping of brain rhythms in corticothalamic systems. Neuroscience 137:1087–1106
Steriade M, Nuñez A, Amzica F (1993) Intracellular analysis of relations between the slow (<1 Hz) neocortical oscillation and other sleep rhythms of the electroencephalogram. J Neurosci 13:3266–3283
Tolliver BK, McRae-Clark AL, Saladin M, Price KL, Simpson AN, DeSantis SM, Baker NL, Brady KT (2010) Determinants of cue-elicited craving and physiologic reactivity in methamphetamine-dependent subjects in the laboratory. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 36:106–113
Van Elburg RA, Van Ooyen A (2004) A new measure for bursting. Neurocomputing 58:497–502
van Wingerden M, Vinck M, Lankelma JV, Pennartz CM (2010) Learning-associated gamma-band phase-locking of action-outcome selective neurons in orbitofrontal cortex. J Neurosci 30:10025–10038
Ward LM (2003) Synchronous neural oscillations and cognitive processes. Trends Cogn Sci 7:553–559
Williams S, Boksa P (2010) Gamma oscillations and schizophrenia. J Psychiatry Neurosci 35:75–77
Williamson LL, Cheng R-K, Etchegaray M, Meck WH (2008) “Speed” warps time: methamphetamine’s interactive roles in drug abuse, habit formation, and the biological clocks of circadian and interval timing. Curr Drug Abuse Rev 1:203–212
Winters BD, Bussey TJ (2005) Transient inactivation of perirhinal cortex disrupts encoding, retrieval, and consolidation of object recognition memory. J Neurosci 25:52–61
Wittmann M, Leland DS, Churan J, Paulus MP (2007) Impaired time perception and motor timing in stimulant-dependent subjects. Drug Alcohol Depend 90:183–192
Zakharova E, Leoni G, Kichko I, Izenwasser S (2009) Differential effects of methamphetamine and cocaine on conditioned place preference and locomotor activity in adult and adolescent male rats. Behav Brain Res 198:45–50
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant nos. AA022821 (CCL), AA022268 (DNL), and ABMRF (CCL).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1086 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janetsian, S.S., Linsenbardt, D.N. & Lapish, C.C. Memory impairment and alterations in prefrontal cortex gamma band activity following methamphetamine sensitization. Psychopharmacology 232, 2083–2095 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3840-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3840-7