Abstract
Introduction
Cognitive deficits are a core feature of patients with schizophrenia and methamphetamine (METH) psychosis. We have recently found that repeated METH treatment (1 mg/kg, s.c.) in mice, which induces behavioral sensitization, impairs long-term recognition memory in a novel object recognition test (NORT) and that the impairment is ameliorated by clozapine, but not haloperidol. Recent studies indicate that minocycline, a second-generation tetracycline, has potent neuroprotective effects in various animal models of neurological diseases.
Objectives
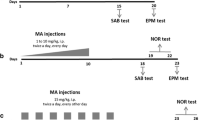
In the present study, we investigated the effect of minocycline on learning and memory in the NORT and behavioral sensitization in mice that had been administered METH for 7 days.
Results
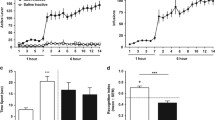
When minocycline (20–40 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally once a day for seven consecutive days to mice that had previously been treated with METH for 7 days, it ameliorated the METH-induced impairment of recognition memory in a dose-dependent manner, although the same treatment with minocycline had no effect on behavioral sensitization to METH. The administration of minocycline, together with METH, inhibited the development of METH-induced behavioral sensitization. The improvement in memory caused by minocycline was associated with an amelioration of the novelty-induced activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in the prefrontal cortex of METH-treated mice.
Conclusions
These results suggest that minocycline is useful for the treatment of cognitive deficits in patients with METH psychosis or schizophrenia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggleton JP, Brown MW (1999) Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal-anterior thalamic axis. Behav Brain Sci 22:425–444
Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD (1998) The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci 1:602–609
Bonelli RM, Kapfhammer HP (2003) Why minocycline is helpful in Huntington’s disease. J Psychopharmacol 17:461
Brown MW, Aggleton JP (2001) Recognition memory: what are the roles of the perirhinal cortex and hippocampus? Nat Rev Neurosci 2:51–61
Chen M, Ona VO, Li M, Ferrante RJ, Fink KB, Zhu S, Bian J, Guo L, Farrell LA, Hersch SM, Hobbs W, Vonsattel JP, Cha JH, Friedlander RM (2000) Minocycline inhibits caspase-1 and caspase-3 expression and delays mortality in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington disease. Nat Med 6:797–801
Choi Y, Kim HS, Shin KY, Kim EM, Kim M, Kim HS, Park CH, Jeong YH, Yoo J, Lee JP, Chang KA, Kim S, Suh YH (2007) Minocycline attenuates neuronal cell death and improves cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease models. Neuropsychopharmacology (in press)
Fan R, Xu F, Previti ML, Davis J, Grande AM, Robinson JK, Van Nostrand WE (2007) Minocycline reduces microglial activation and improves behavioral deficits in a transgenic model of cerebral microvascular amyloid. J Neurosci 27:3057–3063
Flora G, Lee YW, Nath A, Maragos W, Hennig B, Toborek M (2002) Methamphetamine-induced TNF-alpha gene expression and activation of AP-1 in discrete regions of mouse brain: potential role of reactive oxygen intermediates and lipid peroxidation. Neuromolecular Med 2:71–85
Frankin KBJ, Paxinos G (1997) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Hashimoto K, Tsukada H, Nishiyama S, Fukumoto D, Kakiuchi T, Iyo M (2007) Protective effects of minocycline on the reduction of dopamine transporters in the striatum after administration of methamphetamine: a positron emission tomography study in conscious monkeys. Biol Psychiatry 61:577–581
Hunter CL, Quintero EM, Gilstrap L, Bhat NR, Granholm AC (2004) Minocycline protects basal forebrain cholinergic neurons from mu p75-saporin immunotoxic lesioning. Eur J Neurosci 19:3305–3316
Ito Y, Takuma K, Mizoguchi H, Nagai T, Yamada K (2007) A novel azaindolizinone derivative ZSET1446 (spiro[imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3,2-indan]-2(3H)-one) improves methamphetamine-induced impairment of recognition memory in mice by activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:819–827
Kalechstein AD, Newton TF, Green M (2003) Methamphetamine dependence is associated with neurocognitive impairment in the initial phases of abstinence. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 15:215–220
Kamei H, Nagai T, Nakano H, Togan Y, Takayanagi M, Takahashi K, Kobayashi K, Yoshida S, Maeda K, Takuma K, Nabeshima T, Yamada K (2006) Repeated methamphetamine treatment impairs recognition memory through a failure of novelty-induced ERK1/2 activation in the prefrontal cortex of mice. Biol Psychiatry 59:75–84
Kofman O, Klein E, Newman M, Hamburger R, Kimchi O, Nir T, Shimon H, Belmaker RH (1990) Inhibition by antibiotic tetracyclines of rat cortical noradrenergic adenylate cyclase and amphetamine-induced hyperactivity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 37:417–424
Kofman O, van Embden S, Alpert C, Fuchs I (1993) Central and peripheral minocycline suppresses motor activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:397–402
Lai AY, Todd KG (2006) Hypoxia-activated microglial mediators of neuronal survival are differentially regulated by tetracyclines. Glia 53:809–816
Lee MA, Jayathilake K, Meltzer HY (1999) A comparison of the effect of clozapine with typical neuroleptics on cognitive function in neuroleptic-responsive schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 37:1–11
Machado LS, Kozak A, Ergul A, Hess DC, Borlongan CV, Fagan SC (2006) Delayed minocycline inhibits ischemia-activated matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 after experimental stroke. BMC Neurosci 17:1–7
Meltzer HY, McGurk SR (1999) The effects of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine on cognitive function in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 25:233–255
Meunier M, Bachevalier J, Mishkin M (1997) Effects of orbital frontal and anterior cingulate lesions on object and spatial memory in rhesus monkeys. Neuropsychologia 35:999–1015
Miyaoka T, Yasukawa R, Yasuda H, Hayashida M, Inagaki T, Horiguchi J (2007) Possible antipsychotic effects of minocycline in patients with schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:304–307
Mizoguchi H, Yamada K, Mizuno M, Mizuno T, Nitta A, Noda Y, Nabeshima T (2004) Regulations of methamphetamine reward by extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2/ets-like gene-1 signaling pathway via the activation of dopamine receptors. Mol Pharmacol 65:1293–1301
Mizoguchi H, Yamada K, Niwa M, Mouri A, Mizuno T, Noda Y, Nitta A, Itohara S, Banno Y, Nabeshima T (2007a) Reduction of methamphetamine-induced sensitization and reward in matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9-deficient mice. J Neurochem 100:1579–88
Mizoguchi H, Yamada K, Mouri A, Niwa M, Mizuno T, Noda Y, Nitta A, Itohara S, Banno Y, Nabeshima T (2007b) Role of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of MMP in methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization and reward: implications for dopamine receptor down-regulation and dopamine release. J Neurochem 102:1548–1560
Munzar P, Li H, Nicholson KL, Wiley JL, Balster RL (2002) Enhancement of the discriminative stimulus effects of phencyclidine by the tetracycline antibiotics doxycycline and minocycline in rats. Psychopharmacology 160:331–336
Nagai T, Kamei H, Dohniwa M, Takayanagi M, Suzuki M, Matsuya T, Nabeshima T, Takuma K, Yamada K (2006) Involvement of hippocampal extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in spatial working memory in rats. Neuroreport 17:1453–1457
Nagai T, Takuma K, Dohniwa M, Daisuke Ibi D, Mizoguchi M, Kamei M, Nabeshima T, Yamada K (2007a) Repeated methamphetamine treatment impairs spatial working memory in rats: reversal by clozapine but not haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 194:21–32
Nagai T, Takuma K, Kamei H, Ito Y, Nakamichi N, Ibi D, Nakanishi Y, Murai M, Mizoguchi H, Nabeshima T, Yamada K (2007b) Dopamine D1 receptors regulate protein synthesis-dependent long-term recognition memory via extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in the prefrontal cortex. Learn Mem 14:117–125
Nakajima A, Yamada K, Nagai T, Uchiyama T, Miyamoto Y, Mamiya T, He J, Nitta A, Mizuno M, Tran MH, Seto A, Yoshimura M, Kitaichi K, Hasegawa T, Saito K, Yamada Y, Seishima M, Sekikawa K, Kim HC, Nabeshima T (2004) Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in methamphetamine-induced drug dependence and neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 24:2212–2225
Nordahl TE, Salo R, Leamon M (2003) Neuropsychological effects of chronic methamphetamine use on neurotransmitters and cognition. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 15:317–325
Quintero EM, Willis L, Singleton R, Harris N, Huang P, Bhat N, Granholm AC (2006) Behavioral and morphological effects of minocycline in the 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1093:198–207
Ravina BM, Fagan SC, Hart RG, Hovinga CA, Murphy DD, Dawson TM, Marler JR (2003) Neuroprotective agents for clinical trials in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic assessment. Neurology 60:1234–1240
Simon SL, Domier C, Carnell J, Brethen P, Rawson R, Ling W (2000) Cognitive impairment in individuals currently using methamphetamine. Am J Addict 9:222–231
Sriram K, Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP (2006) Minocycline attenuates microglial activation but fails to mitigate striatal dopaminergic neurotoxicity: role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Neurochem 96:706–718
Tamminga CA (2006) The neurobiology of cognition in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 67:9–13
Valjent E, Corvol JC, Pages C, Besson MJ, Maldonado R, Caboche J (2000) Involvement of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade for cocaine-rewarding properties. J Neurosci 20:8701–8709
Van den Steen PE, Dubois B, Nelissen I, Rudd PM, Dwek RA, Opdenakker G (2002) Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 37:375–536
Volkow ND, Chang L, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Leonido-Yee M, Franceschi D, Sedler MJ, Gatley SJ, Hitzemann R, Ding YS, Logan J, Wong C, Miller EN (2001) Association of dopamine transporter reduction with psychomotor impairment in methamphetamine abusers. Am J Psychiatry 158:377–382
Woodward ND, Purdon SE, Meltzer HY, Zald DH (2005) A meta-analysis of neuropsychological change to clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone in schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 8:457–472
Yrjanheikki J, Keinanen R, Pellikka M, Hokfelt T, Koistinaho J (1998) Tetracyclines inhibit microglial activation and are neuroprotective in global brain ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:15769–15774
Zhang L, Kitaichi K, Fujimoto Y, Nakayama H, Shimizu E, Iyo M, Hashimoto K (2006) Protective effects of minocycline on behavioral changes and neurotoxicity in mice after administration of methamphetamine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:1381–1393
Zhu S, Stavrovskaya IG, Drozda M, Kim BY, Ona V, Li M, Sarang S, Liu AS, Hartley DM, Wu DC, Gullans S, Ferrante RJ, Przedborski S, Kristal BS, Friedlander RM (2002) Minocycline inhibits cytochrome c release and delays progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in mice. Nature 417:74–78
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 18790052, 19390062), and the 21st Century COE Program from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and a grant from the Smoking Research Foundation, Japan and by JSPS and KOSEF under the Japan-Korea Basic Scientific Cooperation Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizoguchi, H., Takuma, K., Fukakusa, A. et al. Improvement by minocycline of methamphetamine-induced impairment of recognition memory in mice. Psychopharmacology 196, 233–241 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0955-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0955-0