Abstract
Rationale
3-((2-Methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl)pyridine hydrochloride (MTEP) is a metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) antagonist that may alter drug sensitivity in differentially reared rats due to its involvement in the psychostimulant reward pathway and plasticity.
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to assess the effects of MTEP on acute amphetamine-induced hyperactivity, conditioned hyperactivity, and sensitization.
Methods
Rats were reared in an enriched (EC), isolated (IC), or standard (SC) condition after which rats were either administered MTEP (1.0 mg/kg, ip) or saline prior to an acute (0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg, sc) or repeated (0.3 mg/kg, sc) amphetamine exposure. Rats undergoing repeated amphetamine exposure were administered MTEP prior to conditioned hyperactivity and sensitization tests.
Results
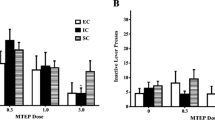
EC and SC rats administered with MTEP prior to acute amphetamine demonstrated attenuated amphetamine-induced locomotor activity compared to controls, while IC rats administered MTEP following repeated amphetamine exposure demonstrated attenuated amphetamine-induced locomotor activity. Interestingly, MTEP treatment only altered conditioned hyperactivity in EC rats, as MTEP pretreatment resulted in conditioned hyperactivity in EC rats while conditioned hyperactivity was not observed in EC rats pretreated with saline.
Conclusions
Glutamatergic pathways are altered during differential rearing, which differentially alters the role of mGluR5 in EC, IC, and SC rats when administered psychostimulant acutely versus repeatedly. These findings suggest that differential rearing alters glutamatergic function, which reduces sensitivity to psychostimulants.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler RA (1979) Morphometry of the effect of increased experience and training on synaptic density in area CA3 of the rat hippocampus. J Histochem Cytochem 27:1548–50
Bäckström P, Hyytiä P (2007) Involvement of AMPA/kainate, NMDA, and mGlu5 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core in cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 192:571–80
Barbelivien A, Herbeaux K, Oberling P, Kelche C, Galani R, Majchrzak M (2006) Environmental enrichment increases responding to contextual cues but decreases overall conditioned fear in the rat. Behavioural Brain Research 169:231–8
Bardo MT, Dwoskin LP (2004) Biological connection between novelty- and drug-seeking motivational systems. Nebr Symp Motiv 50:127–58
Bardo MT, Bowling SL, Rowlett JK, Manderscheid P, Buxton ST, Dwoskin LP (1995) Environmental enrichment attenuates locomotor sensitization, but not in vitro dopamine release, induced by amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 51:397–405
Bowling SL, Bardo MT (1994) Locomotor and rewarding effects of amphetamine in enriched, social, and isolate reared rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 48:459–64
Cosford ND, Tehrani L, Roppe J, Schweiger E, Smith ND, Anderson J, Bristow L, Brodkin J, Jiang X, McDonald I, Rao S, Washburn M, Varney MA (2003) 3-[(2-Methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl]-pyridine: a potent and highly selective metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptor antagonist with anxiolytic activity. J Med Chem 46:204–6
Dravolina OA, Danysz W, Bespalov AY (2006) Effects of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists on the behavioral sensitization to motor effects of cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology 187:397–404
Duffy SN, Craddock KJ, Abel T, Nguyen PV (2001) Environmental enrichment modifies the PKA-dependence of hippocampal LTP and improves hippocampus-dependent memory. Learn Mem 8:26–34
Gass JT, Osborne MP, Watson NL, Brown JL, Olive MF (2009) mGluR5 antagonism attenuates methamphetamine reinforcement and prevents reinstatement of methamphetamine-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:820–33
Gill M, Weiss M, Cain M (2011) Effects of differential rearing on amphetamine-induced c-fos expression in rats
Giorgetti M, Hotsenpiller G, Ward P, Teppen T, Wolf ME (2001) Amphetamine-induced plasticity of AMPA receptors in the ventral tegmental area: effects on extracellular levels of dopamine and glutamate in freely moving rats. J Neurosci 21:6362–9
Gormley S, Rompre PP (2010) Blockade of mGLUR5 receptors differentially alters amphetamine-induced enhancement of locomotor activity and of brain stimulation reward. J Psychopharmacol 25(3):393–401
Green EJ, Greenough WT (1986) Altered synaptic transmission in dentate gyrus of rats reared in complex environments: evidence from hippocampal slices maintained in vitro. J Neurophysiol 55:739–50
Hao Y, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2010) Behavioral and functional evidence of metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 and metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 dysregulation in cocaine-escalated rats: factor in the transition to dependence. Biol Psychiatry 68:240–248
Herzig V, Schmidt WJ (2004) Effects of MPEP on locomotion, sensitization and conditioned reward induced by cocaine or morphine. Neuropharmacology 47:973–84
Kim W, Vezina P, Kim J (2008) Blockade of group II, but not group I, mGluRs in the rat nucleus accumbens inhibits the expression of conditioned hyperactivity in an amphetamine-associated environment. Behavioural Brain Research 191:62–66
Kumaresan V, Yuan M, Yee J, Famous KR, Anderson SM, Schmidt HD, Pierce RC (2009) Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) antagonists attenuate cocaine priming- and cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking. Behavioral Brain Research 202:238–44
Martin-Fardon R, Baptista MAS, Dayas CV, Weiss F (2009) Dissociation of the effects of MTEP [3-[(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl]piperidine] on conditioned reinstatement and reinforcement: comparison between cocaine and a conventional reinforcer. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329:1084–1090
Mathiesen J, Svendsen N, Bruner-Osborne H, Thomsen C, Ramirez MT (2003) Positive allosteric modulation of the human metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 (hmGluR4) by SIB-1893 and MPEP. Br J Pharmacol 138:1026–30
McGeehan AJ, Olive MF (2003) The mGluR5 antagonist MPEP reduces the conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine but not other drugs of abuse. Synapse 47:240–2
Melendez RI, Gregory ML, Bardo MT, Kalivas PW (2004) Impoverished rearing environment alters metabotropic glutamate receptor expression and function in the prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1980–7
National Research Council (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory rats. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C.
Palmatier MI, Liu X, Donny EC, Caggiula AR, Sved AF (2008) Metabotropic glutamate 5 receptor (mGluR5) antagonists decrease nicotine seeking, but do not affect the reinforcement enhancing effects of nicotine. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2139–47
Rahman S, Bardo MT (2008) Environmental enrichment increases amphetamine-induced glutamate neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens: a neurochemical study. Brain Research 1197:40–46
Renner MJ, Rosenzweig MR (1987) Enriched and impoverished environments: effects on brain and behavior. Springer, New York
Rutten K, Van der Kam E, De Vry J, Bruckmann W, Tzschentke T (2010) The mGluR5 antagonist 2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine (MPEP) potentiates conditioned place preference induced by various addictive and non-addictive drugs in rats. Addictive Biology 16:108–115
Schenk S, Hunt T, Malovechko R, Robertson A, Klukowski G, Amit Z (1986) Differential effects of isolation housing on the conditioned place preference produced by cocaine and amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:1793–6
Schwendt M, McGinty JF (2007) Regulator of G-protein signaling 4 interacts with metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 in rat striatum: relevance to amphetamine behavioral sensitization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:650–7
Simpson J, Kelly JP (2011) The impact of environmental enrichment in laboratory rats—behavioural and neurochemical aspects. Behavioural Brain Research 222:246–64
Solinas M, Chauvet C, Thiriet N, El Rawas R, Jaber M (2008) Reversal of cocaine addiction by environmental enrichment. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:17145–50
Stairs DJ, Bardo MT (2009) Neurobehavioral effects of environmental enrichment and drug abuse vulnerability. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:377–82
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage F (2001) Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci 1:191–198
Veeneman M, Boleig H, Broekhoven M, Snoeren E, Guitart Masip M, Cousign J, Spooren W, Vanderschuren L (2011) Dissociable roles of mGlu5 and dopamine receptors in the rewarding and sensitizating properties of morphine and cocaine. Psychopharmacology 214:863–876
Wolf ME (1998) The role of excitatory amino acids in behavioral sensitization to psychomotor stimulants. Prog Neurobiol 54:679–720
Wolf ME, Xue CJ (1999) Amphetamine-induced glutamate efflux in the rat ventral tegmental area is prevented by MK-801, SCH 23390, and ibotenic acid lesions of the prefrontal cortex. J Neurochem 73:1529–38
Wood DA, Buse JE, Wellman CL, Rebec GV (2005) Differential environmental exposure alters NMDA but not AMPA receptor subunit expression in nucleus accumbens core and shell. Brain Research 1042:176–83
Woodcock E, Richardson R (2000) Effects of environmental enrichment on rate of contextual processing and discriminative ability in adult rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 73:1–10
Wooters TE, Bardo MT, Dwoskin LP, Midde NM, Gomez AM, Mactutus CF, Booze RM, Zhu J (2011) Effect of environmental enrichment on methylphenidate-induced locomotion and dopamine transporter dynamics. Behav Brain Res 219(1):98–107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gill, M.J., Arnold, J.C. & Cain, M.E. Impact of mGluR5 during amphetamine-induced hyperactivity and conditioned hyperactivity in differentially reared rats. Psychopharmacology 221, 227–237 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2565-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2565-0