Abstract
Rationale
A role of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGlu5) in regulating spontaneous locomotion and psychostimulant-induced hyperactivity has been proposed.
Objectives
This study aims to determine if mGlu5 in GABAergic neurons regulates spontaneous or psychostimulant-induced locomotion.
Methods
We generated mice specifically lacking mGlu5 in forebrain GABAergic neuron by crossing DLX-Cre mice with mGlu5flox/flox mice to generate DLX-mGlu5 KO mice. The locomotion of adult mice was examined in the open-field assay (OFA) and home cage setting. The effects of the mGlu5 antagonist 6-methyl-2-(phenylethynyl)pyridine (MPEP), cocaine, and methylphenidate on acute motor behaviors in DLX-mGlu5 KO and littermate control mice were assessed in OFA. Striatal synaptic plasticity of these mice was examined with field potential electrophysiological recordings.
Results
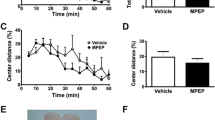
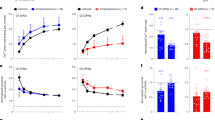
Deleting mGlu5 from forebrain GABAergic neurons results in failure to induce long-term depression (LTD) in the dorsal striatum and absence of habituated locomotion in both novel and familiar settings. In a familiar environment (home cage), DLX-mGlu5 KO mice were hyperactive. In the OFA, DLX-mGlu5 KO mice exhibited initial hypo-activity, and then gradually increased their locomotion with time, resulting in no habituation response. DLX-mGlu5 KO mice exhibited almost no locomotor response to MPEP (40 mg/kg), while the same dose elicited hyperlocomotion in control mice. The DLX-mGlu5 KO mice also showed reduced hyperactivity response to cocaine, while they retained normal hyperactivity response to methylphenidate, albeit with delayed onset.
Conclusion
mGlu5 in forebrain GABAergic neurons is critical to trigger habituation upon the initiation of locomotion as well as to mediate MPEP-induced hyperlocomotion and modulate psychostimulant-induced hyperactivity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JJ, Rao SP, Rowe B, Giracello DR, Holtz G, Chapman DF, Tehrani L, Bradbury MJ, Cosford ND, Varney MA (2002) [3H]Methoxymethyl-3-[(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl]pyridine binding to metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 in rodent brain: in vitro and in vivo characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:1044–1051
Areal LB, Hamilton A, Martins-Silva C, Pires RGW, Ferguson SSG (2019) Neuronal scaffolding protein spinophilin is integral for cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization and ERK1/2 activation. Mol Brain 12:15
Avale ME, Falzone TL, Gelman DM, Low MJ, Grandy DK, Rubinstein M (2004) The dopamine D4 receptor is essential for hyperactivity and impaired behavioral inhibition in a mouse model of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry 9:718–726
Ballard TM, Woolley ML, Prinssen E, Huwyler J, Porter R, Spooren W (2005) The effect of the mGlu5 receptor antagonist MPEP in rodent tests of anxiety and cognition: a comparison. Psychopharmacology 179:218–229
Ballester-Rosado CJ, Albright MJ, Wu CS, Liao CC, Zhu J, Xu J, Lee LJ, Lu HC (2010) mGluR5 in cortical excitatory neurons exerts both cell-autonomous and -nonautonomous influences on cortical somatosensory circuit formation. J Neurosci 30:16896–16909
Ballester-Rosado CJ, Sun H, Huang JY, Lu HC (2016) mGluR5 exerts cell-autonomous influences on the functional and anatomical development of layer IV cortical neurons in the mouse primary somatosensory cortex. J Neurosci 36:8802–8814
Balschun D, Zuschratter W, Wetzel W (2006) Allosteric enhancement of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 function promotes spatial memory. Neuroscience 142:691–702
Barker GR, Bashir ZI, Brown MW, Warburton EC (2006) A temporally distinct role for group I and group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in object recognition memory. Learn Mem 13:178–186
Barnes SA, Pinto-Duarte A, Kappe A, Zembrzycki A, Metzler A, Mukamel EA, Lucero J, Wang X, Sejnowski TJ, Markou A, Behrens MM (2015) Disruption of mGluR5 in parvalbumin-positive interneurons induces core features of neurodevelopmental disorders. Mol Psychiatry 20:1161–1172
Bateup HS, Santini E, Shen W, Birnbaum S, Valjent E, Surmeier DJ, Fisone G, Nestler EJ, Greengard P (2010) Distinct subclasses of medium spiny neurons differentially regulate striatal motor behaviors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:14845–14850
Beninger RJ (1983) The role of dopamine in locomotor activity and learning. Brain Res 287:173–196
Bertran-Gonzalez J, Bosch C, Maroteaux M, Matamales M, Herve D, Valjent E, Girault JA (2008) Opposing patterns of signaling activation in dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-expressing striatal neurons in response to cocaine and haloperidol. J Neurosci 28:5671–5685
Bespalov AY, Dravolina OA, Sukhanov I, Zakharova E, Blokhina E, Zvartau E, Danysz W, van Heeke G, Markou A (2005) Metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR5) antagonist MPEP attenuated cue- and schedule-induced reinstatement of nicotine self-administration behavior in rats. Neuropharmacology 49(Suppl 1):167–178
Bird MK, Reid CA, Chen F, Tan HO, Petrou S, Lawrence AJ (2010) Cocaine-mediated synaptic potentiation is absent in VTA neurons from mGlu5-deficient mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13:133–141
Bordi F, Marcon C, Chiamulera C, Reggiani A (1996) Effects of the metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist MCPG on spatial and context-specific learning. Neuropharmacology 35:1557–1565
Brody SA, Dulawa SC, Conquet F, Geyer MA (2004) Assessment of a prepulse inhibition deficit in a mutant mouse lacking mGlu5 receptors. Mol Psychiatry 9:35–41
Centonze D, Picconi B, Gubellini P, Bernardi G, Calabresi P (2001) Dopaminergic control of synaptic plasticity in the dorsal striatum. Eur J Neurosci 13:1071–1077
Chao HT, Chen H, Samaco RC, Xue M, Chahrour M, Yoo J, Neul JL, Gong S, Lu HC, Heintz N, Ekker M, Rubenstein JL, Noebels JL, Rosenmund C, Zoghbi HY (2010) Dysfunction in GABA signalling mediates autism-like stereotypies and Rett syndrome phenotypes. Nature 468:263–269
Chen R, Han DD, Gu HH (2005) A triple mutation in the second transmembrane domain of mouse dopamine transporter markedly decreases sensitivity to cocaine and methylphenidate. J Neurochem 94:352–359
Chiamulera C, Epping-Jordan MP, Zocchi A, Marcon C, Cottiny C, Tacconi S, Corsi M, Orzi F, Conquet F (2001) Reinforcing and locomotor stimulant effects of cocaine are absent in mGluR5 null mutant mice. Nat Neurosci 4:873–874
Chuhma N, Tanaka KF, Hen R, Rayport S (2011) Functional connectome of the striatal medium spiny neuron. J Neurosci 31:1183–1192
Conn PJ, Pin JP (1997) Pharmacology and functions of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37:205–237
Conn PJ, Battaglia G, Marino MJ, Nicoletti F (2005) Metabotropic glutamate receptors in the basal ganglia motor circuit. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:787–798
Conn PJ, Lindsley CW, Jones CK (2009) Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors as a novel approach for the treatment of schizophrenia. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:25–31
Crawley JN, Paylor R (1997) A proposed test battery and constellations of specific behavioral paradigms to investigate the behavioral phenotypes of transgenic and knockout mice. Horm Behav 31:197–211
Cui G, Jun SB, Jin X, Pham MD, Vogel SS, Lovinger DM, Costa RM (2013) Concurrent activation of striatal direct and indirect pathways during action initiation. Nature 494:238–242
Del Arco A, Mora F (2009) Neurotransmitters and prefrontal cortex-limbic system interactions: implications for plasticity and psychiatric disorders. J Neural Transm 116:941–952
Durieux PF, Schiffmann SN, de Kerchove d’Exaerde A (2011) Targeting neuronal populations of the striatum. Front Neuroanat 5:40
Elia J, Gai X, Xie HM, Perin JC, Geiger E, Glessner JT, D'Arcy M, deBerardinis R, Frackelton E, Kim C, Lantieri F, Muganga BM, Wang L, Takeda T, Rappaport EF, Grant SF, Berrettini W, Devoto M, Shaikh TH, Hakonarson H, White PS (2010) Rare structural variants found in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder are preferentially associated with neurodevelopmental genes. Mol Psychiatry 15:637–646
Elia J, Glessner JT, Wang K, Takahashi N, Shtir CJ, Hadley D, Sleiman PM, Zhang H, Kim CE, Robison R, Lyon GJ, Flory JH, Bradfield JP, Imielinski M, Hou C, Frackelton EC, Chiavacci RM, Sakurai T, Rabin C, Middleton FA, Thomas KA, Garris M, Mentch F, Freitag CM, Steinhausen HC, Todorov AA, Reif A, Rothenberger A, Franke B, Mick EO, Roeyers H, Buitelaar J, Lesch KP, Banaschewski T, Ebstein RP, Mulas F, Oades RD, Sergeant J, Sonuga-Barke E, Renner TJ, Romanos M, Romanos J, Warnke A, Walitza S, Meyer J, Palmason H, Seitz C, Loo SK, Smalley SL, Biederman J, Kent L, Asherson P, Anney RJ, Gaynor JW, Shaw P, Devoto M, White PS, Grant SF, Buxbaum JD, Rapoport JL, Williams NM, Nelson SF, Faraone SV, Hakonarson H (2012a) Genome-wide copy number variation study associates metabotropic glutamate receptor gene networks with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Nat Genet 44:78–84
Elia J, Sackett J, Turner T, Schardt M, Tang SC, Kurtz N, Dunfey M, McFarlane NA, Susi A, Danish D, Li A, Nissley-Tsiopinis J, Borgmann-Winter K (2012b) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder genomics: update for clinicians. Curr Psychiatry Rep 14:579–589
Faraone SV (2018) The pharmacology of amphetamine and methylphenidate: relevance to the neurobiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and other psychiatric comorbidities. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 87:255–270
Ferrada C, Sotomayor-Zarate R, Abarca J, Gysling K (2017) The activation of metabotropic glutamate 5 receptors in the rat ventral tegmental area increases dopamine extracellular levels. Neuroreport 28:28–34
Foster DJ, Conn PJ (2017) Allosteric modulation of GPCRs: new insights and potential utility for treatment of schizophrenia and other CNS disorders. Neuron 94:431–446
Gerdeman GL, Ronesi J, Lovinger DM (2002) Postsynaptic endocannabinoid release is critical to long-term depression in the striatum. Nat Neurosci 5:446–451
Gerfen CR, Surmeier DJ (2011) Modulation of striatal projection systems by dopamine. Annu Rev Neurosci 34:441–466
Ghanem N, Yu M, Poitras L, Rubenstein JL, Ekker M (2008) Characterization of a distinct subpopulation of striatal projection neurons expressing the Dlx genes in the basal ganglia through the activity of the I56ii enhancer. Dev Biol 322:415–424
Gittis AH, Kreitzer AC (2012) Striatal microcircuitry and movement disorders. Trends Neurosci 35:557–564
Gray L, van den Buuse M, Scarr E, Dean B, Hannan AJ (2009) Clozapine reverses schizophrenia-related behaviours in the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 knockout mouse: association with N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor up-regulation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:45–60
Graybiel AM (2005) The basal ganglia: learning new tricks and loving it. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:638–644
Graybiel AM, Aosaki T, Flaherty AW, Kimura M (1994) The basal ganglia and adaptive motor control. Science 265:1826–1831
Greenhill L, Kollins S, Abikoff H, McCracken J, Riddle M, Swanson J, McGough J, Wigal S, Wigal T, Vitiello B, Skrobala A, Posner K, Ghuman J, Cunningham C, Davies M, Chuang S, Cooper T (2006) Efficacy and safety of immediate-release methylphenidate treatment for preschoolers with ADHD. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 45:1284–1293
Gubellini P, Pisani A, Centonze D, Bernardi G, Calabresi P (2004) Metabotropic glutamate receptors and striatal synaptic plasticity: implications for neurological diseases. Prog Neurobiol 74:271–300
Guimaraes IM, Carvalho TG, Ferguson SS, Pereira GS, Ribeiro FM (2015) The metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 role on motor behavior involves specific neural substrates. Mol Brain 8:24
Hanson JE, Smith Y (2002) Subcellular distribution of high-voltage-activated calcium channel subtypes in rat globus pallidus neurons. J Comp Neurol 442:89–98
Hinney A, Scherag A, Jarick I, Albayrak O, Putter C, Pechlivanis S, Dauvermann MR, Beck S, Weber H, Scherag S, Nguyen TT, Volckmar AL, Knoll N, Faraone SV, Neale BM, Franke B, Cichon S, Hoffmann P, Nothen MM, Schreiber S, Jockel KH, Wichmann HE, Freitag C, Lempp T, Meyer J, Gilsbach S, Herpertz-Dahlmann B, Sinzig J, Lehmkuhl G, Renner TJ, Warnke A, Romanos M, Lesch KP, Reif A, Schimmelmann BG, Hebebrand J (2011) Genome-wide association study in German patients with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 156B:888–897
Hippenmeyer S, Vrieseling E, Sigrist M, Portmann T, Laengle C, Ladle DR, Arber S (2005) A developmental switch in the response of DRG neurons to ETS transcription factor signaling. PLoS Biol 3:e159
Howes OD, McCutcheon R, Owen MJ, Murray RM (2017) The role of genes, stress, and dopamine in the development of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 81:9–20
Ishisaka M, Kakefuda K, Oyagi A, Ono Y, Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M, Kitaichi K, Hara H (2012) Diacylglycerol kinase beta knockout mice exhibit attention-deficit behavior and an abnormal response on methylphenidate-induced hyperactivity. PLoS One 7:e37058
Jew CP, Wu CS, Sun H, Zhu J, Huang JY, Yu D, Justice NJ, Lu HC (2013) mGluR5 ablation in cortical glutamatergic neurons increases novelty-induced locomotion. PLoS One 8:e70415
Johanson CE, Fischman MW (1989) The pharmacology of cocaine related to its abuse. Pharmacol Rev 41:3–52
Kachroo A, Orlando LR, Grandy DK, Chen JF, Young AB, Schwarzschild MA (2005) Interactions between metabotropic glutamate 5 and adenosine A2A receptors in normal and parkinsonian mice. J Neurosci 25:10414–10419
Kenny PJ, Boutrel B, Gasparini F, Koob GF, Markou A (2005) Metabotropic glutamate 5 receptor blockade may attenuate cocaine self-administration by decreasing brain reward function in rats. Psychopharmacology 179:247–254
Kinney GG, Burno M, Campbell UC, Hernandez LM, Rodriguez D, Bristow LJ, Conn PJ (2003) Metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptors modulate locomotor activity and sensorimotor gating in rodents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:116–123
Kirov G, Pocklington AJ, Holmans P, Ivanov D, Ikeda M, Ruderfer D, Moran J, Chambert K, Toncheva D, Georgieva L, Grozeva D, Fjodorova M, Wollerton R, Rees E, Nikolov I, van de Lagemaat LN, Bayes A, Fernandez E, Olason PI, Bottcher Y, Komiyama NH, Collins MO, Choudhary J, Stefansson K, Stefansson H, Grant SG, Purcell S, Sklar P, O'Donovan MC, Owen MJ (2012) De novo CNV analysis implicates specific abnormalities of postsynaptic signalling complexes in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 17:142–153
Knackstedt LA, Trantham-Davidson HL, Schwendt M (2014) The role of ventral and dorsal striatum mGluR5 in relapse to cocaine-seeking and extinction learning. Addict Biol 19:87–101
Kratochvil CJ, Heiligenstein JH, Dittmann R, Spencer TJ, Biederman J, Wernicke J, Newcorn JH, Casat C, Milton D, Michelson D (2002) Atomoxetine and methylphenidate treatment in children with ADHD: a prospective, randomized, open-label trial. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41:776–784
Kreitzer AC, Malenka RC (2007) Endocannabinoid-mediated rescue of striatal LTD and motor deficits in Parkinson’s disease models. Nature 445:643–647
Kreitzer AC, Malenka RC (2008) Striatal plasticity and basal ganglia circuit function. Neuron 60:543–554
Li X, Peng XQ, Jordan CJ, Li J, Bi GH, He Y, Yang HJ, Zhang HY, Gardner EL, Xi ZX (2018) mGluR5 antagonism inhibits cocaine reinforcement and relapse by elevation of extracellular glutamate in the nucleus accumbens via a CB1 receptor mechanism. Sci Rep 8:3686
Lobo MK, Covington HE 3rd, Chaudhury D, Friedman AK, Sun H, Damez-Werno D, Dietz DM, Zaman S, Koo JW, Kennedy PJ, Mouzon E, Mogri M, Neve RL, Deisseroth K, Han MH, Nestler EJ (2010) Cell type-specific loss of BDNF signaling mimics optogenetic control of cocaine reward. Science 330:385–390
Lovinger DM (2010) Neurotransmitter roles in synaptic modulation, plasticity and learning in the dorsal striatum. Neuropharmacology 58:951–961
Lu YM, Jia Z, Janus C, Henderson JT, Gerlai R, Wojtowicz JM, Roder JC (1997) Mice lacking metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 show impaired learning and reduced CA1 long-term potentiation (LTP) but normal CA3 LTP. J Neurosci 17:5196–5205
Luo Z, Volkow ND, Heintz N, Pan Y, Du C (2011) Acute cocaine induces fast activation of D1 receptor and progressive deactivation of D2 receptor striatal neurons: in vivo optical microprobe [Ca2+]i imaging. J Neurosci 31:13180–13190
Malvaez M, Wassum KM (2018) Regulation of habit formation in the dorsal striatum. Curr Opin Behav Sci 20:67–74
Mathur BN, Lovinger DM (2012) Endocannabinoid-dopamine interactions in striatal synaptic plasticity. Front Pharmacol 3:66
Matosin N, Newell KA (2012) Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in the pathology and treatment of schizophrenia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:256–268
McGeehan AJ, Olive MF (2003) The mGluR5 antagonist MPEP reduces the conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine but not other drugs of abuse. Synapse 47:240–242
McIlwain KL, Merriweather MY, Yuva-Paylor LA, Paylor R (2001) The use of behavioral test batteries: effects of training history. Physiol Behav 73:705–717
Monory K, Massa F, Egertova M, Eder M, Blaudzun H, Westenbroek R, Kelsch W, Jacob W, Marsch R, Ekker M, Long J, Rubenstein JL, Goebbels S, Nave KA, During M, Klugmann M, Wolfel B, Dodt HU, Zieglgansberger W, Wotjak CT, Mackie K, Elphick MR, Marsicano G, Lutz B (2006) The endocannabinoid system controls key epileptogenic circuits in the hippocampus. Neuron 51:455–466
Moretti P, Bouwknecht JA, Teague R, Paylor R, Zoghbi HY (2005) Abnormalities of social interactions and home-cage behavior in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 14:205–220
Muzumdar MD, Tasic B, Miyamichi K, Li L, Luo L (2007) A global double-fluorescent Cre reporter mouse. Genesis 45:593–605
Nicoletti F, Bruno V, Ngomba RT, Gradini R, Battaglia G (2015) Metabotropic glutamate receptors as drug targets: what’s new? Curr Opin Pharmacol 20:89–94
Niswender CM, Conn PJ (2010) Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:295–322
O'Leary DM, Movsesyan V, Vicini S, Faden AI (2000) Selective mGluR5 antagonists MPEP and SIB-1893 decrease NMDA or glutamate-mediated neuronal toxicity through actions that reflect NMDA receptor antagonism. Br J Pharmacol 131:1429–1437
Olsen CM, Childs DS, Stanwood GD, Winder DG (2010) Operant sensation seeking requires metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5). PLoS One 5:e15085
Ossowska K, Konieczny J, Wolfarth S, Wieronska J, Pilc A (2001) Blockade of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGluR5) produces antiparkinsonian-like effects in rats. Neuropharmacology 41:413–420
Page G, Peeters M, Najimi M, Maloteaux JM, Hermans E (2001) Modulation of the neuronal dopamine transporter activity by the metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 in rat striatal synaptosomes through phosphorylation mediated processes. J Neurochem 76:1282–1290
Parkitna JR, Sikora M, Golda S, Golembiowska K, Bystrowska B, Engblom D, Bilbao A, Przewlocki R (2013) Novelty-seeking behaviors and the escalation of alcohol drinking after abstinence in mice are controlled by metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 on neurons expressing dopamine d1 receptors. Biol Psychiatry 73:263–270
Partridge JG, Tang KC, Lovinger DM (2000) Regional and postnatal heterogeneity of activity-dependent long-term changes in synaptic efficacy in the dorsal striatum. J Neurophysiol 84:1422–1429
Paylor R, Spencer CM, Yuva-Paylor LA, Pieke-Dahl S (2006) The use of behavioral test batteries, II: effect of test interval. Physiol Behav 87:95–102
Phillips PE, Stuber GD, Heien ML, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2003) Subsecond dopamine release promotes cocaine seeking. Nature 422:614–618
Pietraszek M, Sukhanov I, Maciejak P, Szyndler J, Gravius A, Wislowska A, Plaznik A, Bespalov AY, Danysz W (2005) Anxiolytic-like effects of mGlu1 and mGlu5 receptor antagonists in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 514:25–34
Schwendt M, Sigmon SA, McGinty JF (2012) RGS4 overexpression in the rat dorsal striatum modulates mGluR5- and amphetamine-mediated behavior and signaling. Psychopharmacology 221:621–635
Sethna F, Wang H (2016) Acute inhibition of mGluR5 disrupts behavioral flexibility. Neurobiol Learn Mem 130:1–6
Shen W, Flajolet M, Greengard P, Surmeier DJ (2008) Dichotomous dopaminergic control of striatal synaptic plasticity. Science 321:848–851
Spencer CM, Serysheva E, Yuva-Paylor LA, Oostra BA, Nelson DL, Paylor R (2006) Exaggerated behavioral phenotypes in Fmr1/Fxr2 double knockout mice reveal a functional genetic interaction between fragile X-related proteins. Hum Mol Genet 15:1984–1994
Spencer CM, Alekseyenko O, Hamilton SM, Thomas AM, Serysheva E, Yuva-Paylor LA, Paylor R (2011) Modifying behavioral phenotypes in Fmr1KO mice: genetic background differences reveal autistic-like responses. Autism Res 4:40–56
Spooren WP, Gasparini F, Bergmann R, Kuhn R (2000) Effects of the prototypical mGlu(5) receptor antagonist 2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine on rotarod, locomotor activity and rotational responses in unilateral 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Eur J Pharmacol 406:403–410
Sung KW, Choi S, Lovinger DM (2001) Activation of group I mGluRs is necessary for induction of long-term depression at striatal synapses. J Neurophysiol 86:2405–2412
Sunohara GA, Malone MA, Rovet J, Humphries T, Roberts W, Taylor MJ (1999) Effect of methylphenidate on attention in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): ERP evidence. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:218–228
Swanson JM, Lerner M, Williams L (1995) More frequent diagnosis of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. N Engl J Med 333:944
Tallaksen-Greene SJ, Kaatz KW, Romano C, Albin RL (1998) Localization of mGluR1a-like immunoreactivity and mGluR5-like immunoreactivity in identified populations of striatal neurons. Brain Res 780:210–217
Taniguchi H, He M, Wu P, Kim S, Paik R, Sugino K, Kvitsiani D, Fu Y, Lu J, Lin Y, Miyoshi G, Shima Y, Fishell G, Nelson SB, Huang ZJ (2011) A resource of Cre driver lines for genetic targeting of GABAergic neurons in cerebral cortex. Neuron 71:995–1013
Tepper JM, Tecuapetla F, Koos T, Ibanez-Sandoval O (2010) Heterogeneity and diversity of striatal GABAergic interneurons. Front Neuroanat 4:150
Tessari M, Pilla M, Andreoli M, Hutcheson DM, Heidbreder CA (2004) Antagonism at metabotropic glutamate 5 receptors inhibits nicotine- and cocaine-taking behaviours and prevents nicotine-triggered relapse to nicotine-seeking. Eur J Pharmacol 499:121–133
Testa CM, Standaert DG, Young AB, Penney JB Jr (1994) Metabotropic glutamate receptor mRNA expression in the basal ganglia of the rat. J Neurosci 14:3005–3018
Thomas AM, Bui N, Perkins JR, Yuva-Paylor LA, Paylor R (2011) Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists alter select behaviors in a mouse model for fragile X syndrome. Psychopharmacology (Berl)
Tsai G, Coyle JT (2002) Glutamatergic mechanisms in schizophrenia. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42:165–179
Uchigashima M, Narushima M, Fukaya M, Katona I, Kano M, Watanabe M (2007) Subcellular arrangement of molecules for 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol-mediated retrograde signaling and its physiological contribution to synaptic modulation in the striatum. J Neurosci 27:3663–3676
Vanderschuren LJ, Kalivas PW (2000) Alterations in dopaminergic and glutamatergic transmission in the induction and expression of behavioral sensitization: a critical review of preclinical studies. Psychopharmacology 151:99–120
Verma A, Moghaddam B (1998) Regulation of striatal dopamine release by metabotropic glutamate receptors. Synapse 28:220–226
Vezina P, Kim JH (1999) Metabotropic glutamate receptors and the generation of locomotor activity: interactions with midbrain dopamine. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:577–589
Vinson PN, Conn PJ (2012) Metabotropic glutamate receptors as therapeutic targets for schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 62:1461–1472
Volkow ND, Ding YS, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Logan J, Gatley JS, Dewey S, Ashby C, Liebermann J, Hitzemann R et al (1995) Is methylphenidate like cocaine? Studies on their pharmacokinetics and distribution in the human brain. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:456–463
Wang X, Moussawi K, Knackstedt L, Shen H, Kalivas PW (2013) Role of mGluR5 neurotransmission in reinstated cocaine-seeking. Addict Biol 18:40–49
Wu CS, Zhu J, Wager-Miller J, Wang S, O'Leary D, Monory K, Lutz B, Mackie K, Lu HC (2010) Requirement of cannabinoid CB(1) receptors in cortical pyramidal neurons for appropriate development of corticothalamic and thalamocortical projections. Eur J Neurosci 32:693–706
Xu J, Zhu Y, Contractor A, Heinemann SF (2009) mGluR5 has a critical role in inhibitory learning. J Neurosci 29:3676–3684
Yin HH, Knowlton BJ (2006) The role of the basal ganglia in habit formation. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:464–476
Yin HH, Knowlton BJ, Balleine BW (2004) Lesions of dorsolateral striatum preserve outcome expectancy but disrupt habit formation in instrumental learning. Eur J Neurosci 19:181–189
Zhu J, Zhang X, Xu Y, Spencer TJ, Biederman J, Bhide PG (2012) Prenatal nicotine exposure mouse model showing hyperactivity, reduced cingulate cortex volume, reduced dopamine turnover, and responsiveness to oral methylphenidate treatment. J Neurosci 32:9410–9418
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the helpful comments from Dr. Corinne Marie Spencer and the contributions of the Confocal Imaging and Mouse Neurobehavior cores located in Baylor and TCH supported by BCM IDDRC 5P30HD024064 from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development or the National Institutes of Health.
Funding
This work was supported by the NIH NS048884 to HCL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, CS., Jew, C.P., Sun, H. et al. mGlu5 in GABAergic neurons modulates spontaneous and psychostimulant-induced locomotor activity. Psychopharmacology 237, 345–361 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05367-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05367-0