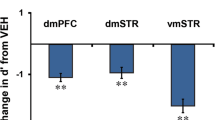
Abstract
Rationale
N-methyl-d-Aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonists such as ketamine induce cognitive symptoms in man similar to those of schizophrenia and therefore might be useful as models of the disease in animals. However, it is unclear which NMDAR antagonist(s) offer the best means to produce cognitive deficits in attention and working memory and to what extent those deficits can be measured selectively in rats.
Objectives
The present study systematically compared the effects of eight different NMDAR antagonists—MK-801, phencyclidine, (S)-(+)-ketamine, memantine, SDZ-220,581, Ro 25-6981, CP 101-606 and NVP-AAM077—in rats using standard tests of visual attention, the five-choice serial reaction time task (5CSRT), and working memory, the delayed matching to position task (DMTP).
Results
Drug-induced responses varied qualitatively and quantitatively in both a compound- and a task-dependent manner. Effects were generally confounded by concomitant motor and motivational disruption, although individual doses of phencyclidine for example appeared to impair selectively cognitive functions. Interestingly, GluN2B selective antagonists were unique in their effects; inducing potential performance benefit in the 5CSRT.
Conclusions
Overall, the opportunity to induce a selective cognitive deficit in attention (5CSRT) or working memory (DMTP) in the rat is limited by both the NMDAR antagonist and the dose range used. The importance of a preclinical focus on ketamine, which is used more frequently in clinical settings, is limited by the extent to which cognitive effects can be both detected and quantified using this exposure regimen within these two operant assays.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NMDAR:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor
- DMTP:
-
Delayed matching to position
- 5CSRT:
-
Five-choice serial reaction time task
References
Alexander SP, Mathie A, Peters JA (2008) Guide to receptors and channels (GRAC), 3rd edn. Br J Pharmacol 153(suppl 2):S1–S209
Amitai N, Markou A (2009a) Chronic nicotine improves cognitive performance in a test of attention but does not attenuate cognitive disruption induced by repeated phencyclidine administration. Psychopharmacology 202(1–3):275–286
Amitai N, Markou A (2009b) Increased impulsivity and disrupted attention induced by repeated phencyclidine are not attenuated by chronic quetiapine treatment. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 93(3):248–257
Amitai N, Markou A (2010) Disruption of performance in the five-choice serial reaction time task induced by administration of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists: relevance to cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 68(1):5–16
Amitai N, Semenova S, Markou A (2007) Cognitive-disruptive effects of the psychotomimetic phencyclidine and attenuation by atypical antipsychotic medications in rats. Psychopharmacology 193(4):521–537
Auberson YP, Allgeier H, Bischoff S, Lingenhoehl K, Moretti R, Schmutz M (2002) 5-Phosphonomethylquinoxalinediones as competitive NMDA receptor antagonists with a preference for the human 1A/2A, rather than 1A/2B receptor composition. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12:1099–1102
Bakshi VP, Tricklebank M, Neijt HC, Lehmann-Masten V, Geyer MA (1999) Disruption of prepulse inhibition and increases in locomotor activity by competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:643–652
Barch DM, Berman MG, Engle R, Jones JH, Jonides J, Macdonald A III, Nee DE, Redick TS, Sponheim SR (2009a) CNTRICS final task selection: working memory. Schizophr Bull 35:136–152
Barch DM, Carter CS, Arnsten A, Buchanan RW, Cohen JD, Geyer M, Green MF, Krystal JH, Nuechterlein K, Robbins T, Silverstein S, Smith EE, Strauss M, Wykes T, Heinssen R (2009b) Selecting paradigms from cognitive neuroscience for translation into use in clinical trials: proceedings of the Third CNTRICS Meeting. Schizophr Bull 35:109–114
Carter CS, Barch DM, Buchanan RW, Bullmore E, Krystal JH, Cohen J, Geyer M, Green M, Nuechterlein KH, Robbins T, Silverstein S, Smith EE, Strauss M, Wykes T, Heinssen R (2008) Identifying cognitive mechanisms targeted for treatment development in schizophrenia: an overview of the First Meeting of the Cognitive Neuroscience Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia Initiative. Biol Psychiatry 64:4–10
Chaperon F, Muller W, Auberson YP, Tricklebank MD, Neijt HC (2003) Substitution for PCP, disruption of prepulse inhibition and hyperactivity induced by N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists: preferential involvement of the NR2B rather than NR2A subunit. Behav Pharmacol 14:477–487
Chenard BL, Bordner J, Butler TW, Chambers LK, Collins MA, De Costa DL, Ducat MF, Dumont ML, Fox CB, Mena EE (1995) (1S,2S)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-4-phenylpiperidino)-1-propanol: a potent new neuroprotectant which blocks N-methyl-d-aspartate responses. J Med Chem 38:3138–3145
Chudasama Y, Muir JL (1997) A behavioural analysis of the delayed non matching to position task: the effects of scopolamine, lesions of the fornix and of the prelimbic region on mediating behaviours by rats. Psychopharmacology 134(1):73–82
Creeley C, Wozniak DF, Labruyere J, Taylor GT, Olney JW (2006) Low doses of memantine disrupt memory in adult rats. J Neurosci 26:3923–3932
Day M, Pan JB, Buckley MJ, Cronin E, Hollingsworth PR, Hirst WD, Navarra R, Sullivan JP, Decker MW, Fox GB (2007) Differential effects of ciproxifan and nicotine on impulsivity and attention measures in the 5-choice serial reaction time test. Biochem Pharmacol 73:1123–1134
Dix SL, Gilmour G, Potts S, Smith JW, Tricklebank MD (2010) A within-subject cognitive battery in the rat: differential effects of NMDA antagonists. Psychopharmacology 212:227–242
Dunnett SB (1985) Comparative effects of cholinergic drugs and lesions of nucleus basalis or fimbria-fornix on delayed matching in rats. Psychopharmacology 87:357–363
Fischer G, Mutel V, Trube G, Malherbe P, Kew JN, Mohacsi E, Heitz MP, Kemp JA (1997) Ro 25-6981, a highly potent and selective blocker of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors containing the NR2B subunit. Characterization in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:1285–1292
Frizelle PA, Chen PE, Wyllie DJ (2006) Equilibrium constants for (R)-[(S)-1-(4-bromo-phenyl)- ethylamino]-(2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxalin-5-yl)-methyl]-phosphonic acid (NVPAAM077) acting at recombinant NR1/NR2A and NR1/NR2B N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors: Implications for studies of synaptic transmission. Mol Pharmacol. 70(3):1022–32
Gilmour G, Pioli EY, Dix SL, Smith JW, Conway MW, Jones WT, Loomis S, Mason R, Shahabi S, Tricklebank MD (2009) Diverse and often opposite behavioural effects of NMDA receptor antagonists in rats: implications for “NMDA antagonist modelling” of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 205(2):203–216
Green MF, Nuechterlein KH, Kern RS, Baade LE, Fenton WS, Gold JM, Keefe RS, Mesholam-Gately R, Seidman LJ, Stover E, Marder SR (2008) Functional co-primary measures for clinical trials in schizophrenia: results from the MATRICS Psychometric and Standardization Study. Am J Psychiatry 165:221–228 (see comment)
Higgins GA, Ballard TM, Enderlin M, Haman M, Kemp JA (2005) Evidence for improved performance in cognitive tasks following selective NR2B NMDA receptor antagonist pre-treatment in the rat. Psychopharmacology 179:85–98
Hill SK, Ragland JD, Gur RC, Gur RE (2002) Neuropsychological profiles delineate distinct profiles of schizophrenia, an interaction between memory and executive function, and uneven distribution of clinical subtypes. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol Off J Int Neuropsychol Soc 24:765–780
Hill SK, Beers SR, Kmiec JA, Keshavan MS, Sweeney JA (2004a) Impairment of verbal memory and learning in antipsychotic-naive patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 68:127–136
Hill SK, Schuepbach D, Herbener ES, Keshavan MS, Sweeney JA (2004b) Pretreatment and longitudinal studies of neuropsychological deficits in antipsychotic-naive patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 68:49–63
Hill SK, Harris MS, Herbener ES, Pavuluri M, Sweeney JA (2008) Neurocognitive allied phenotypes for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Bull 34:743–759
Johnson JW, Kotermanski SE (2006) Mechanism of action of memantine. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:61–67
Kern RS, Nuechterlein KH, Green MF, Baade LE, Fenton WS, Gold JM, Keefe RS, Mesholam-Gately R, Mintz J, Seidman LJ, Stover E, Marder SR (2008) The MATRICS consensus cognitive battery, part 2: co-norming and standardization. Am J Psychiatry 165:214–220
Kotermanski SE, Johnson JW (2009) Mg2+ imparts NMDA receptor subtype selectivity to the Alzheimer’s drug memantine. J Neurosci 29:2774–2779
Leaver KR, Allbutt HN, Creber NJ, Kassiou M, Henderson JM (2008) Neuroprotective effects of a selective N-methyl-d-aspartate NR2b receptor antagonist in the 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 35(11):1388–1394
Lodge D, Johnson KM (1990) Noncompetitive excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11:81–86
Malhotra AK, Adler CM, Kennison SD, Elman I, Pickar D, Breier A (1997) Clozapine blunts N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist-induced psychosis: a study with ketamine. Biol Psychiatry 42:664–668
Menniti F, Chenard B, Collins M, Ducat M, Shalaby I, White F (1997) CP-101,606, a potent neuroprotectant selective for forebrain neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 331:117–126
Minkeviciene R, Banerjee P, Tanila H (2004) Memantine improves spatial learning in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 311:677–682
Minkeviciene R, Banerjee P, Tanila H (2008) Cognition-enhancing and anxiolytic effects of memantine. Neuropharmacology 54:1079–1085
Miyamoto S, Duncan GE, Marx CE, Lieberman JA (2005) Treatments for schizophrenia: a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs. Mol Psychiatry 10:79–104
More L, Gravius A, Nagel J, Valastro B, Greco S, Danysz W (2008) Therapeutically relevant plasma concentrations of memantine produce significant L-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor occupation and do not impair learning in rats. Behav Pharmacol 19:724–734
Morgan CJ, Curran HV (2006) Acute and chronic effects of ketamine upon human memory: a review. Psychopharmacology 188:408–424
Newcomer JW, Farber NB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Selke G, Melson AK, Hershey T, Craft S, Olney JW (1999) Ketamine-induced NMDA receptor hypofunction as a model of memory impairment and psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:106–118
Nuechterlein KH, Green MF, Kern RS, Baade LE, Barch DM, Cohen JD, Essock S, Fenton WS, Frese FJ III, Gold JM, Goldberg T, Heaton RK, Keefe RS, Kraemer H, Mesholam-Gately R, Seidman LJ, Stover E, Weinberger DR, Young AS, Zalcman S, Marder SR (2008) The MATRICS consensus cognitive battery, part 1: test selection, reliability, and validity. Am J Psychiatry 165:203–213
Parsons CG, Stoffler A, Danysz W (2007) Memantine: a NMDA receptor antagonist that improves memory by restoration of homeostasis in the glutamatergic system—too little activation is bad, too much is even worse. Neuropharmacology 53:699–723
Rammsayer TH (2001) Effects of pharmacologically induced changes in NMDA-receptor activity on long-term memory in humans. Learn Mem 8:20–25
Robbins TW (2002) The 5-choice serial reaction time task: behavioural pharmacology and functional neurochemistry. Psychopharmacology 163:362–380
Schugens MM, Egerter R, Daum I, Schepelmann K, Klockgether T, Loschmann PA (1997) The NMDA antagonist memantine impairs classical eyeblink conditioning in humans. Neurosci Lett 224:57–60
Tzschentke TM (2002) Glutamatergic mechanisms in different disease states: overview and therapeutical implications—an introduction. Amino Acids 23(1–3):147–152
Williams AJ, Dave JR, Lu XM, Ling G, Tortella FC (2002) Selective NR2B NMDA receptor antagonists are protective against staurosporine-induced apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol 452(1):135–136
Witt A, Macdonald N, Kirkpatrick P (2004) Memantine hydrochloride. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:109–110
Wong EH, Kemp JA, Priestley T, Knight AR, Woodruff GN, Iversen LL (1986) The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7104–7108
Young JW, Powell SB, Risbrough V, Marston HM, Geyer MA (2009) Using the MATRICS to guide development of a preclinical cognitive test battery for research in schizophrenia. Pharmacol Ther 122(2):150–202
Yuede CM, Dong H, Csernansky JG (2007) Anti-dementia drugs and hippocampal-dependent memory in rodents. Behav Pharmacol 18:347–363
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
5CSRT Stats_Supplementary Data Tables
(XLS 130 kb)
DMTP Stats_Supplementary Data Tables
(XLS 144 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, J.W., Gastambide, F., Gilmour, G. et al. A comparison of the effects of ketamine and phencyclidine with other antagonists of the NMDA receptor in rodent assays of attention and working memory. Psychopharmacology 217, 255–269 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2277-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2277-5