Abstract
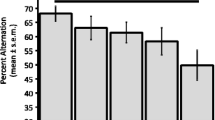
To provide a more specific test of memory impairments following lesions to central cholinergic systems, rats were trained on an operant delayed matching task. Ibotenic acid lesions of the nucleus basalis produced a disruption of performance at all delay intervals (a parallel downward shift in the delay-performance curve). By contrast, fimbriafornix transections had no effects at short delays, but produced a progressively greater impairment as the delays lengthened (an increased downward slope of the delay-performance curve). Scopolamine produced a dose-dependent disruption of performance, apparent at the shortest delays but greater at longer delays, that was similar to the two lesion deficits combined, whereas physostigmine induced a mild but significant enhancement of performance. The results support the hypothesis that disruption of hippocampal circuitries, including cholinergic afferents via the fimbria-fornix, produces short-term or working memory impairments, whereas disruption of the cortical cholinergic system implicates more stable long-term aspects of task performance. Peripherally administered cholinergic drugs produce both types of effect and thus may influence both systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpern HP, Marriott JG (1973) Short-term memory: facilitation and disruption with cholinergic agents. Physiol Behav 11:571–575
Bartus RT, Johnson HR (1976) Short-term memory in the rhesus monkey: disruption from the anti-cholinergic scopolamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 5:39–46
Bartus RT, Dean RL, Beer B, Lippa AS (1982) The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 217:408–417
Cohen JS, Escott M, Ricciardi P (1984) The role of reinforcement symmetry and stimulus modality in successive delayed matching to sample in the rat. Can J Psychol 38:63–79
Coyle JT, Price DL, DeLong MR (1983) Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science 19:1184–1190
Drachman DA, Sahakian BJ (1980) Memory, aging and pharmacosystems. In: Stein D (ed) The psychobiology of aging: Problems and perspectives. Elsevier North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 347–368
Dunnett SB, Low WC, Iversen SD, Stenevi U, Björklund A (1982) Septal transplants restore maze learning in rats with fornix-fimbria lesions. Brain Res 251:335–348
Dunnett SB, Toniolo G, Fine A, Ryan CN, Björklund A, Iversen SD (1985) Transplantation of embryonic ventral forebrain neurons to the neocortex of rats with lesions of nucleus basalis magnocellularis. II Sensorimotor and learning impairments. Neuroscience (in press)
Gaffan D (1974) Recognition memory impaired and association intact in the memory of monkeys after transection of the fornix. J Comp Physiol Psychol 29:577–588
Gage FH, Björklund A, Stenevi U, Dunnett SB (1983) Functional correlates of compensatory collateral sprouting by aminergic and cholinergic afferents in the hippocampal formation. Brain Res 268:39–47
Gage FH, Björklund A, Stenevi U, Dunnett SB, Kelly PA (1984) Intrahippocampal septal grafts ameliorate learning impairments in aged rats. Science 225:533–536
Heise GA, Hrabrich B, Lilie NL, Martin RA (1975) Scopolamine effects on delayed spatial alternation in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 3:993–1002
Heise GA, Connor R, Martin RA (1976) Effects of scopolamine on variable intertrial interval spatial alternation and memory in the rat. Pschopharmacology 49:131–137
Kesner RP, Bierley RA, Pepples P (1981) Short-term memory: role of d-amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:673–676
Ksir C (1974) Scopolamine effects on two-trial delayed-response performance in the rat. Psychopharmacology 34:127–134
Ksir C (1975) Scopolamine and amphetamine effects on discrimination: interaction with stimulus control. Pschopharmacology 43:37–41
Kubanis P, Zornetzer SF (1981) Age-related behavioral and neurobiological changes: a review with an emphasis on memory. Behav Neural Biol 31:115–172
Low WC, Lewis PR, Bunch ST, Dunnett SB, Thomas SR, Iversen SD, Björklund A, Stenevi U (1982) Functional recovery following neural transplantation of embryonic septal nuclei in adult rats with septohippocampal lesions. Nature 300:260–262
Lyon M, Robbins TW (1975) The action of central nervous system stimulant drugs: a general theory concerning amphetamine effects. In: Essman W, Valzelli L (eds), Developments in psychopharmacology, Vol 2. Spectrum Press, New York, pp 81–163
Milar KS, Halgren CR, Heise GA (1978) A reappraisal of scopolamine effects on inhibition. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 9:307–313
Murray CL, Fibiger HC (1985) Learning and memory deficits after lesions of the nucleus basalis magnocellularis: reversal by physostigmine. Neuroscience 14:1025–1032
Olton DS, Feustle W (1981) Hippocampal function and nonspatial memory. Exp Brain Res 41:380–389
Olton DS, Papas BC (1979) Spatial memory and hippocampal function. Neuropsychologia 17:669–682
Olton DS, Becker JT, Handelmann GE (1979) Hippocampus, space, and memory, Behav Brain Sci 2:353–359
Perry EK, Tomlinson BE, Blessed G, Bergmann K, Gibson PH, Perry RH (1978) Correlation of cholinergic abnormalities with senile plaques and mental test scores in senile dementia. Br Med J 2:1457–1459
Pontecorvo MJ (1983) Effects of proactive interference on rats' continuous nonmatching-to-sample performance. Anim Learn Behav 11:356–366
Rawlins JNP, Tsaltas E (1983) The hippocampus, time and working memory. Behav Brain Res 10:233–262
Walker DW, Messer LG, Freund G, Means LW (1972) Effect of hippocampal lesions and intertrial interval on single alternation performance in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol 80:469–477
Wallace J, Steinert PA, Scobie SR, Spear NE (1980) Stimulus modality and short-term memory in rats. Anim Learn Behav 8:10–16
Warburton D (1972) The cholinergic control of internal inhibition. In: Boakes RA, Halliday MS (eds), Inhibition and learning. Academic Press, New York, pp 431–460
Whishaw IQ, O'Connor WT, Dunnett SB (1985) Effects of atropine and basal forebrain lesions on spatial navigation in the rat. Behav Brain Res (in press)
White SR (1974) Atropine, scopolamine and hippocampal lesion effects on alternation performance of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:297–307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunnett, S.B. Comparative effects of cholinergic drugs and lesions of nucleus basalis or fimbria-fornix on delayed matching in rats. Psychopharmacology 87, 357–363 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432721
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432721