Abstract
Rationale
We previously reported that the NR2B subunit-selective N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist Ro 63-1908 produced a marked deficit in response control in the five-choice serial reaction time task (5-CSRTT).
Objectives
The present studies were designed to investigate this further by studying the NR2B NMDA antagonists, ifenprodil, traxoprodil (CP101,606), Ro 25-6981 as well as Ro 63-1908 in this test.
Methods
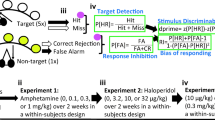
Following training in the 5-CSRTT, separate groups of rats were either tested under (1) standard test conditions [5 s inter-trial interval (ITI), 0.5 s stimulus duration, 100 trials], (2) high (3 s ITI) and low (10 s ITI) event rate of stimulus presentation and (3) a 250-trial protocol in aged 2-year-old rats. In a final study, the effects of traxoprodil were investigated in an operant delayed match to position (DMTP) task, a test of working memory, and compared to dizocilpine and Ro 63-1908.
Results
Similar to Ro 63-1908, both traxoprodil (1–10 mg/kg) and Ro 25-6981 (3–30 mg/kg) increased premature responding but also increased response speed with no error trade-off. Conversely, ifenprodil (1–10 mg/kg) slowed response speed and increased omissions with no effect on premature responding. Tested under a variable ITI, Ro 63-1908 (1 mg/kg) increased premature responding at all ITIs, but this change was proportional to controls. At short ITI (3 s), Ro 63-1908 reliably improved performance both in terms of response speed and accuracy (percent correct). In a 250-trial protocol in aged rats, both Ro 63-1908 (0.1–0.3 mg/kg) and, particularly, traxoprodil (1–3 mg/kg) improved performance—increasing response speed and increasing the number of rewards earned during test. Finally, traxoprodil (1–10 mg/kg) improved accuracy and increased response speed in the DMTP task.
Conclusions
The present studies support the view that selective NR2B NMDA antagonists promote impulsive-type responding in the 5-CSRTT; however, under certain test conditions, drugs of this class—notably traxoprodil—may also improve task performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anson LC, Chen PE, Wyllie DJ, Colquhoun D, Schoepfer R (1998) Identification of amino acid residues of the NR2A subunit that control glutamate potency in recombinant NR1/NR2A NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 18:581–589
Auberson YP, Allgeier H, Bischoff S, Lingenhoehl K, Moretti R, Schmutz M (2002) 5-Phosphonomethylquinoxalinediones as competitive NMDA receptor antagonists with a preference for the human 1A/2A, rather than 1A/2B receptor composition. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12:1099–1102
Blondel A, Sanger DJ, Moser PC (2000) Characterisation of the effects of nicotine in the five-choice serial reaction time task in rats: antagonist studies. Psychopharmacology 149:293–305
Boyce S, Wyatt A, Webb JK, O’Donnell R, Mason G, Rigby M, Sirinathsinghji D, Hill RG, Rupniak NM (1999) Selective NMDA NR2B antagonists induce antinociception without motor dysfunction: correlation with restricted localisation of NR2B subunit in dorsal horn. Neuropharmacology 38:611–623
Brimecombe JC, Gallagher MJ, Lynch DR, Aizenman E (1998) An NR2B point mutation affecting haloperidol and CP101,606 sensitivity of single recombinant N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. J Pharm Exp Ther 286:627–634
Carli M, Robbins TW, Evenden JL, Everitt BJ (1983) Effects of lesions to ascending noradrenergic neurones on performance of a 5-choice serial reaction time task in rats: implications for theories of dorsal noradrenergic bundle function based on selective attention and arousal. Behav Brain Res 9:361–380
Carli M, Baviera M, Invernizzi RW, Balducci C (2004) The serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonist M100907 prevents impairment in attentional performance by NMDA receptor blockade in the rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1637–1647
Carter C, Rivy JP, Scatton B (1989) Ifenprodil and SL 82.0715 are antagonists at the polyamine site of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 164:611–612
Chaperon F, Muller W, Auberson YP, Tricklebank MD, Neijt HC (2003) Substitution for PCP, disruption of PPI induced by N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists: preferential involvement of the NR2B rather than NR2A subunit. Behav Pharmacol 14:477–487
Chazot PL, Lawrence S, Thompson CL (2002) Studies on the subtype selectivity of CP-101,606: evidence for two classes of NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 42:319–324
Chenard BL, Menniti FS (1999) Antagonists selective for NMDA receptors containing the NR2B subunit. Curr Pharm Des 5:381–404
Chenard BL, Shalaby IA, Koe BK, Ronau RT, Butler TW, Prochniak MA, Schmidt AW, Fox CB (1991) Separation of α1 adrenergic and N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist activity in a series of ifenprodil compounds. J Med Chem 34:3085–3090
Chenard BL, Bordner J, Butler TW, Chambers LK, Collins MA, De Costa DL, Ducat MF, Dumont ML, Fox CB, Mena EE (1995) (1S,2S)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-4-phenylpiperidino)-1-propanol: a potent new neuroprotectant which blocks N-methyl-d-aspartate responses. J Med Chem 38:3138–3145
Chudasama Y, Passetti F, Rhodes SEV, Lopian D, Desai A, Robbins TW (2003) Dissociable aspects of performance on the 5-choice serial reaction time task following lesions of the dorsal anterior cingulate, infralimbic and orbitofrontal cortex in the rat: differential effects on selectivity, impulsivity and compulsivity. Behav Brain Res 146:105–119
Cole BJ, Klewer M, Jones GH, Stephens DN (1993) Contrasting the effects of the competitive NMDA antagonist CPP and the non-competitive NMDA antagonist MK801 on performance of an operant delayed matching to position task in rats. Psychopharmacology 111:465–471
Deacon RMJ (1991) Pharmacological studies of a rat spatial delayed nonmatch-to-sample task as an animal model of dementia. Drug Dev Res 24:67–79
Doyle KM, Feerick S, Kirkby DL, Eddleston A, Higgins GA (1998) Comparison of various N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists in a model of short-term memory and on overt behaviour. Behav Pharmacol 9:671–681
Dunnet SB (1985) Comparative effects of cholinergic drugs and lesions of nucleus basalis or fimbria–fornix on delayed matching in rats. Psychopharmacology 87:357–363
Fischer G, Mutel V, Trube G, Malherbe P, Kew JNC, Mohacsi E, Heitz MP, Kemp JA (1997) Ro 25-6981, a highly potent and selective blocker of N-methyl-d- aspartate receptors containing the NR2B subunit. Characterization in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:1285–1292
Gill R, Kemp JA, Richards JG, Kew JNC (1999) NMDA receptor antagonists: past disappointments and future prospects as neuroprotective agents. Curr Opin Cardiovasc Pulm Ren Investig Drugs 1:576–591
Gill R, Alanine A, Bourson A, Buttelman B, Fischer G, Heitz M-P, Kew JNC, Levet-Trafit B, Lorez H-P, Malherbe P, Miss M-T, Mutel V, Pinard E, Roever S, Schmitt M, Trube G, Wybrecht R, Wyler R, Kemp JA (2002) Pharmacological characterisation of Ro 63-1908, a novel sub-type selective NMDA antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:940–948
Grimwood S, Gilbert E, Ragan CI, Hutson PH (1996) Modulation of 45Ca2+ influx into cells stably expressing recombinant human NMDA receptors by ligands acting at distinct recognition sites. J Neurochem 66:2589–2595
Grottick AJ, Higgins GA (2000) Effect of subtype selective nicotinic compounds on attention as assessed by the five-choice serial reaction time task. Behav Brain Res 117:197–208
Grottick AJ, Higgins GA (2002) Assessing a vigilance decrement in aged rats: effects of pre-feeding, task manipulation, and psychostimulants. Psychopharmacology 164:33–41
Grottick AJ, Haman M, Wyler R, Higgins GA (2003) Reversal of a vigilance decrement in the 5-choice serial reaction time task by subtype-selective nicotinic ligands. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:880–887
Guscott MR, Clarke HF, Murray F, Grimwood S, Bristow LJ, Hutson PH (2003) The effect of (+)-CP-101,606, an NMDA receptor 2B subunit selective antagonist, in the Morris watermaze. Eur J Pharmacol 476:193–199
Hargreaves EL, Cain DP (1992) Hyperactivity, hyper-reactivity, and sensorimotor deficits induced by low doses of the N-methyl-d-aspartate non-competitive channel blocker MK801. Behav Brain Res 47:23–33
Harrison AA, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1997) Central 5-HT depletion enhances impulsive responding without affecting the accuracy of attentional performance: interactions with dopaminergic mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 133:329–342
Higgins GA, Ballard TM, Huwyler J, Kemp JA, Gill R (2003a) Evaluation of the NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonist Ro 63-1908 on rodent behaviour: evidence for an involvement of NR2B NMDA receptors in response inhibition. Neuropharmacology 44:324–341
Higgins GA, Enderlin M, Haman M, Fletcher PJ (2003b) The 5-HT2A receptor antagonist M100,907 attenuates motor and ‘impulsive-type’ behaviours produced by NMDA receptor antagonism. Psychopharmacology 170:309–319
Jones DNC, Barnes JC, Kirkby DL, Higgins GA (1995) Age-associated impairments in a test of attention: evidence for involvement of cholinergic systems. J Neurosci 15:7282–7292
Kemp JA, Kew JNC (1998) NMDA receptor antagonists. In: Leff P (ed) Receptor-based drug design. Marcel Decker Inc., New York, pp. 297–321
Kemp JA, McKernan RM (2002) NMDA receptor pathways as drug targets. Nat Neurosci 5:1039–1042
Kentros CG, Agnihotri NT, Streater S, Hawkins RD, Kandel ER (2004) Increased attention to spatial context increases both place field stability and spatial memory. Neuron 42:283–295
Kiyama Y, Manabe T, Sakimura K, Kawakami F, Mori H, Mishini M (1998) Increased thresholds for long-term potentiation and contextual learning in mice lacking the NMDA-type glutamate receptor ɛ1 subunit. J Neurosci 18:6704–6712
Kutsuwada T, Sakimura K, Manabe T, Takayama C, Katakura N, Kushiya E, Natsume R, Watanabe M, Inoue Y, Yagi T, Aizawa S, Arakawa M, Takahashi T, Nakamura Y, Mori H, Mishina M (1996) Impairment of suckling response, trigeminal neuronal pattern formation, and hippocampal LTD in NMDA receptor ɛ2 subunit mutant mice. Neuron 16:333–344
Laube B, Hirai H, Sturgess M, Betz H, Kuhse J (1997) Molecular determinants of agonist discrimination by NMDA receptor subunits: analysis of the glutamate binding site on the NR2B subunit. Neuron 18:493–503
Laurie DJ, Bartke I, Schoepfer R, Naujoks K, Seeburg PH (1997) Regional, developmental and interspecies expression of the four NMDAR2 subunits, examined using monoclonal antibodies. Mol Brain Res 51:23–32
Lynch DR, Shim SS, Seifert KM, Kurapathi S, Mutel V, Gallagher MJ, Guttmann RP (2001) Pharmacological characterization of interactions of Ro 25-6981 with the NR2B (ɛ2) subunit. Eur J Pharmacol 416:185–195
Mathe JM, Nomikos GG, Hildebrand BE, Hertel P, Svensson TH (1996) Prazosin inhibits MK-801-induced hyperlocomotion and dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Eur J Pharmacol 309:1–11
McBain CJ, Mayer ML (1994) N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor structure and function. Physiol Rev 74:723–760
Menniti FS, Chenard B, Collins M, Ducat M, Shalaby I, White F (1997) CP-101,606, a potent neuroprotectant selective for forebrain neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 331:117–126
Mirza NR, Stolerman IP (1998) Nicotine enhances sustained attention in the rat under specific task conditions. Psychopharmacology 138:266–274
Mondadori C, Weiskrantz L, Buerki H, Petschke F, Fagg GE (1989) NMDA receptor antagonists can enhance or impair learning performance in animals. Exp Brain Res 75:449–456
Monyer H, Burnashev N, Laurie DJ, Sakmann B, Seeburg PH (1994) Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors. Neuron 12:529–540
Morris RGM, Anderson E, Lynch GS, Baudry M (1986) Selective impairment of learning and blockade of long-term potentiation by an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, AP5. Nature 319:774–776
Muir KW, Lees KR (1995) Clinical experience with excitatory amino acid antagonist drugs. Stroke 26:503–513
Muir JL, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1996) The cerebral cortex of the rat and visual attentional function: dissociable effects of mediofrontal, cingulate, anterior dorsolateral, and parietal cortex lesions on a five-choice serial reaction time task. Cereb Cortex 6:470–481
Muir JL, Fischer W, Bjorklund A (1999) Decline in visual attention and spatial memory in aged rats. Neurobiol Aging 20:605–615
Murphy ER, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2005) Local glutamate receptor antagonism in the rat prefrontal cortex disrupts response inhibition in a visuospatial attentional task. Psychopharmacology (DOI 10.1007/s00213-004-2068-3)
Murray TK, Ridley RM, Snape MF, Cross AJ (1995) The effect of dizocilpine (MK801) on spatial and visual discrimination tasks in the rat. Behav Pharmacol 6:540–549
Mutel V, Buchy D, Klingelschmidt A, Messer J, Bluel Z, Kemp JA, Richards JG (1998) In vitro binding properties in rat brain of [3H] Ro 25-6981, a potent and selective antagonist of NMDA receptors containing NR2B subunits. J Neurochem 70:2147–2155
Okiyama K, Smith DH, White WF, Richter K, McIntosh TK (1997) Effects of the novel NMDA antagonists CP-98,113, CP-101,581 and CP-101,606 on cognitive function and regional cerebral edema following experimental brain injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 14:211–222
Parsons CG, Danysz W, Quack G (1999a) Memantine is a clinically well tolerated N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist—a review of the preclinical data. Neuropharmacology 38:735–767
Parsons CG, Danysz W, Bartmann A, Spielmanns P, Frankiewicz T, Hesselink M, Eilbacher B, Quack G (1999b) Amino-alkyl-cyclohexanes are novel uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists with strong voltage-dependency and fast blocking kinetics: in vitro and in vivo characterization. Neuropharmacology 38:85–108
Reisberg B, Doody R, Stoffler A, Schmitt F, Ferris S, Modius HJ (2003) Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N Eng J Med 348:1333–1341
Rigby M, Le Bourdelles B, Heavens RP, Kelly S, Smith D, Butler A, Hammans R, Hills R, Xuereb JH, Hill RG, Whiting PJ, Sirinathsinghji DJ (1996) The messenger RNAs for the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits show region-specific expression of different subunit composition in the human brain. Neuroscience 73:429–447
Robbins TW (2002) The 5-choice serial reaction time task: behavioural pharmacology and functional neurochemistry. Psychopharmacology 163:362–380
Sakimura K, Kutsuwada T, Ito I, Manabe T, Takayama C, Kushiya E, Yagi T, Alzawa S, Inoue Y, Sugiyama H, Mishina M (1995) Reduced hippocampal LTP and spatial learning in mice lacking NMDA receptor ɛ1 subunit. Nature 373:151–155
Sanger DJ (1992) NMDA antagonists disrupt timing behaviour in rats. Behav Pharmacol 3:593–600
Sanger DJ, Joly D (1991) Effects of NMDA antagonists and sigma ligands on the acquisition of conditioned fear in mice. Psychopharmacology 104:27–34
Schorge S, Colquhoun D (2003) Studies of NMDA receptor function and stoichiometry with truncated and tandem subunits. J Neurosci 23:1151–1158
Spooren WPJM, Mombereau C, Maco M, Gill R, Kemp JA, Ozmen L, Nakanishi S, Higgins GA (2004) Pharmacological and genetic evidence indicates that combined inhibition of NR2A and NR2B subunit containing NMDA receptors is required to disrupt prepulse inhibition. Psychopharmacology 175:99–105
Stanhope KJ, McLenachan AP, Dourish CT (1995) Dissociation between cognitive and motor/motivational deficits in the delayed matching to position test: effects of scopolamine, 8-OH DPAT and EAA antagonists. Psychopharmacology 122:268–280
Steece-Collier K, Chambers LK, Jaw-Tsai SS, Menniti FS, Greenamyre JT (2000) Antiparkinsonian actions of CP101,606, an antagonist of NR2B subunit-containing N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Exp Neurol 163:239–243
Tan S, Kirk RC, Abraham WC, McNaughton N (1989) Effects of the NMDA antagonists CPP and MK-801 on delayed conditional discrimination. Psychopharmacology 98:556–560
Tariot PN, Farlow MR, Grossberg GT, Graham SM, McDonald S, Gergel I (2004) Memantine treatment in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease already receiving donepezil: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 291:317–324
Tricklebank MD, Singh L, Oles RJ, Preston C, Iversen SD (1989) The behavioural effects of MK801: a comparison with antagonists acting non-competitively and competitively at the NMDA receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 167:127–135
Venable N, Kelly PH (1990) Effect of NMDA antagonists on passive avoidance learning and retrieval in rats and mice. Psychopharmacology 100:215–221
Watanabe M, Inoue Y, Sakimura K, Mishina M (1993) Distinct spatio-temporal distributions of the NMDA receptor channel subunit mRNAs in the brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 707:463–466
Wenzel A, Fritschy JM, Mohler H, Benke D (1997) NMDA receptor heterogeneity during postnatal development of the rat brain: differential expression of the NR2A, NR2B, and NR2C subunit proteins. J Neurochem 68:469–478
Williams K (1993) Ifenprodil discriminates subtypes of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor—selectivity and mechanisms at recombinant heteromeric receptors. Mol Pharmacol 44:851–859
Witt A, Macdonald N, Kirkpatrick P (2004) Memantine hydrochloride. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:109–110
Wong EHF, Kemp JA, Priestley T, Knight AR, Woodruff GN, Iversen LL (1986) The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:7104–7108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Higgins, G.A., Ballard, T.M., Enderlin, M. et al. Evidence for improved performance in cognitive tasks following selective NR2B NMDA receptor antagonist pre-treatment in the rat. Psychopharmacology 179, 85–98 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2203-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2203-9