Abstract
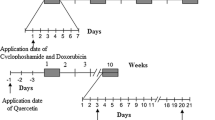
Cytarabine, an anti-metabolite drug, remains the mainstay of treatment for hematological malignancies. It causes various toxic effects including teratogenicity. Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is a natural antioxidant reported to offer protection against hepatotoxicity induced by various pathological conditions, drugs, or chemicals. We investigated the protective effect of ALA against prenatal cytarabine exposure-induced hepatotoxicity in rat female neonates. A total of 30 dams were randomly assigned to five groups and received normal saline, ALA 200 mg/kg, cytarabine 12.5 mg/kg, cytarabine 25 mg/kg, and cytarabine 25 mg/kg + ALA 200 mg/kg, respectively, from gestational day (GD)8 to GD21. Cytarabine and ALA were administered via intraperitoneal and oral (gavage) routes, respectively. On postnatal day (PND)1, all the live female neonates (pups) were collected and weighed. The blood and liver from pups were carefully collected and used for histopathological, and biochemical evaluations. A significant and dose-dependent decrease in maternal food intake and weight gain was observed in the pregnant rats (dams) of the cytarabine groups as compared to the dams of the control group. The pups exposed to cytarabine showed a significant and dose-dependent (a) decrease in body weight, liver weight, hepatosomatic index, catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, serum albumin levels and (b) increase in malondialdehyde, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase, AST/ALT ratio, and histopathological anomalies. Maternal co-administration of ALA ameliorated these biochemical changes and histopathological abnormalities by combating oxidative stress. Future studies are warranted to explore the molecular mechanisms involved in the ALA’s protective effects against prenatal cytarabine-induced hepatotoxicity.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials related to this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdul-Ghani MR, Naser AS (2022) The protective impacts of lipoic acid on diclofenac-induced hepatorenal toxicity in broiler chicks. Iraqi J Vet Sci 36:1023–1027. https://doi.org/10.33899/ijvs.2022.132915.2148
Abdulrazzaq AM, Badr M, Gammoh O et al (2019) Hepatoprotective actions of ascorbic acid, alpha lipoic acid and silymarin or their combination against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Med Kaunas Lith 55:E181. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55050181
Ahamed F (2012) Hepatoprotective effect of lipoic acid in ethanol intoxicated chicks on liver biochemical parameters like LDH, SDH, & glucose-6- phosphatase. Pharm Res Allied Sci 1:12–22
Al Ghafli MHM, Padmanabhan R, Kataya HH, Berg B (2004) Effects of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation on maternal diabetes-induced growth retardation and congenital anomalies in rat fetuses. Mol Cell Biochem 261:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:mcbi.0000028747.92084.42
Ali R, Ozkalemkaş F, Ozçelik T et al (2003) Maternal and fetal outcomes in pregnancy complicated with acute leukemia: a single institutional experience with 10 pregnancies at 16 years. Leuk Res 27:381–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0145-2126(02)00182-0
Al-Qahtani FA, Arafah M, Sharma B, Siddiqi NJ (2017) Effects of alpha lipoic acid on acrylamide-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Cell Mol Biol Noisy--Gd Fr 63:1–6. https://doi.org/10.14715/cmb/2017.63.6.1
Aly HAA, Mansour AM, Hassan MH, Abd-Ellah MF (2016) Lipoic acid attenuates Aroclor 1260-induced hepatotoxicity in adult rats. Environ Toxicol 31:913–922. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22101
Amacher DE (2014) Female gender as a susceptibility factor for drug-induced liver injury. Hum Exp Toxicol 33:928–939. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327113512860
Amadori S, Papa G, Avvisati G et al (1984) Sequential combination of systemic high-dose ara-C and asparaginase for the treatment of central nervous system leukemia and lymphoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 2:98–101. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1984.2.2.98
Anandakumar PP, Malarkodi SP, Sivaprasad TR, Saravanan GD (2007) Antioxidant DL-alpha lipoic acid as an attenuator of adriamycin induced hepatotoxicity in rat model. Indian J Exp Biol 45:1045–1049
Anto SK, Koyada N, Khan S, Jena G (2016) α-Lipoic acid attenuates transplacental nicotine-induced germ cell and oxidative DNA damage in adult mice. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 27:585–593. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2015-0151
Artlich A, Möller J, Kruse K et al (1994) Teratogenic effects in a case of maternal treatment for acute myelocytic leukaemia—neonatal and infantile course. Eur J Pediatr 153:488–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957002
Avci B, Bahadir A, Tuncel OK, Bilgici B (2016) Influence of α-tocopherol and α-lipoic acid on bisphenol-A-induced oxidative damage in liver and ovarian tissue of rats. Toxicol Ind Health 32:1381–1390. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233714563433
Azim HA, Peccatori FA, Pavlidis N (2010) Treatment of the pregnant mother with cancer: a systematic review on the use of cytotoxic, endocrine, targeted agents and immunotherapy during pregnancy. Part I: Solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev 36:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2009.11.007
Babaoglu MO, Karadag O, Saikawa Y et al (2004) Hepatotoxicity due to a possible interaction between cytosine arabinoside and dipyridamole: a case report. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60:455–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-004-0790-8
Bhilare NV, Dhaneshwar SS, Mahadik KR, Dasgupta A (2022) Co-drug of isoniazid and sulfur containing antioxidant for attenuation of hepatotoxicity and treatment of tuberculosis. Drug Chem Toxicol 45:850–860. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2020.1778021
Botha MH, Rajaram S, Karunaratne K (2018) Cancer in pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet Off Organ Int Fed Gynaecol Obstet 143(Suppl 2):137–142. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.12621
Brennan PN, Cartlidge P, Manship T, Dillon JF (2021) Guideline review: EASL clinical practice guidelines: drug-induced liver injury (DILI). Frontline Gastroenterol 13:332–336. https://doi.org/10.1136/flgastro-2021-101886
Buzzetti E, Parikh PM, Gerussi A, Tsochatzis E (2017) Gender differences in liver disease and the drug-dose gender gap. Pharmacol Res 120:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2017.03.014
Chen CB, Hammo B, Barry J, Radhakrishnan K (2021) Overview of albumin physiology and its role in pediatric diseases. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 23:11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-021-00813-6
Chilaka KN, Namoju R (2023) Maternal supplementation of alpha-lipoic acid ameliorates prenatal cytarabine-induced mutilation in reproductive development and function in F1 male adult rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02852-4
Dai Y, Luo J, Xiang E et al (2021) Prenatal exposure to Retrorsine induces developmental toxicity and hepatotoxicity of fetal rats in a sex-dependent manner: the role of pregnane X receptor activation. J Agric Food Chem 69:3219–3231. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06748
de Haan J, Verheecke M, Van Calsteren K et al (2018) Oncological management and obstetric and neonatal outcomes for women diagnosed with cancer during pregnancy: a 20-year international cohort study of 1170 patients. Lancet Oncol 19:337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30059-7
Dhakal P, Soares MJ (2017) Single-step PCR-based genetic sex determination of rat tissues and cells. BioTechniques 62:232–233. https://doi.org/10.2144/000114548
Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR et al (2022) Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood 140:1345–1377. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2022016867
Eastwood-Wilshere N, Turner J, Oliveira N, Morton A (2019) Cancer in pregnancy. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 15:296–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.13235
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
El-Mancy EM, Elsherbini DMA, Al-Serwi RH et al (2022) α-Lipoic acid protects against cyclosporine a-induced hepatic toxicity in rats: effect on oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Toxics 10:442. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080442
El-Yamany MF, Zaki ES, Shaltout SA, Saad MA (2021) Bone marrow mononuclear cells boosts anti-cytogentical aberration effect of N-acetylcysteine and α-lipoic acid in rat’s liver and bone marrow: implication of oxidative and inflammatory pathways. Toxicol Mech Methods 31:437–449. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2021.1906370
European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu, Clinical Practice Guideline Panel: Chair: Panel members, EASL Governing Board representative (2019) EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Drug-induced liver injury. J Hepatol 70:1222–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.014
Farag MM, Ahmed SM, Elhadidy WF, Rashad RM (2019) Superior protective effects of febuxostat plus alpha-lipoic acid on renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced hepatorenal injury in rats. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant Off Publ Saudi Cent Organ Transplant Saudi Arab 30:1364–1374. https://doi.org/10.4103/1319-2442.275480
Fayed MR, El-Naga RN, Akool E-S, El-Demerdash E (2018) The potential antifibrotic impact of apocynin and alpha-lipoic acid in concanavalin A-induced liver fibrosis in rats: Role of NADPH oxidases 1 and 4. Drug Discov Ther 12:58–67. https://doi.org/10.5582/ddt.2017.01065
Fayez AM, Zakaria S, Moustafa D (2018) Alpha lipoic acid exerts antioxidant effect via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation and suppresses hepatic stellate cells activation induced by methotrexate in rats. Biomed Pharmacother Biomedecine Pharmacother 105:428–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.145
Floreani A, Bizzaro D, Shalaby S et al (2023) Sex disparity and drug-induced liver injury. Dig Liver Dis Off J Ital Soc Gastroenterol Ital Assoc Study Liver 55:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2022.06.025
Forman HJ, Zhang H (2021) Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 20:689–709. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-021-00233-1
Fu SH, Flannery AH, Thompson Bastin ML (2019) Acute hepatotoxicity after high-dose cytarabine for the treatment of relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: a case report. Hosp Pharm 54:160–164. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018578718779763
Ganesan TS, Barnett MJ, Amos RJ et al (1987) Cytosine arabinoside in the management of recurrent leukaemia. Hematol Oncol 5:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/hon.2900050108
Gomes MB, Negrato CA (2014) Alpha-lipoic acid as a pleiotropic compound with potential therapeutic use in diabetes and other chronic diseases. Diabetol Metab Syndr 6:80. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-5996-6-80
Grümayer ER, Schmidmeier W, Panzer S, Gadner H (1986) Toxicity of sequential high-dose ARA-C asparaginase treatment in childhood poor risk leukemia. Blut 53:309–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00320890
Gruppuso PA, Sanders JA (2016) Regulation of liver development: implications for liver biology across the lifespan. J Mol Endocrinol 56:R115-125. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-15-0313
Guo Y, Xiao D, Yang X et al (2019) Prenatal exposure to pyrrolizidine alkaloids induced hepatotoxicity and pulmonary injury in fetal rats. Reprod Toxicol Elmsford N 85:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2019.02.006
Horowitz NA, Henig I, Henig O et al (2018) Acute myeloid leukemia during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Leuk Lymphoma 59:610–616. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428194.2017.1347651
Iimuro Y, Frankenberg MV, Arteel GE et al (1997) Female rats exhibit greater susceptibility to early alcohol-induced liver injury than males. Am J Physiol 272:G1186-1194. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.1997.272.5.G1186
Javitt MC (2022) Cancer in pregnancy: overview and epidemiology. Abdom Radiol N Y. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03633-y
Karagiannis P, Alsdorf W, Tallarek A-C et al (2021) Treatment of refractory acute myeloid leukaemia during pregnancy with venetoclax, high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone. Br J Haematol 192:e60–e63. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17220
Khalaf AA, Zaki AR, Galal MK et al (2017) The potential protective effect of α-lipoic acid against nanocopper particle-induced hepatotoxicity in male rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 36:881–891. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327116674526
Koblihová E, Mrázová I, Vaňourková Z et al (2020) Sex-linked differences in the course of thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure in Lewis rats. Physiol Res 69:835–845. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.934499
Kono Y (1978) Generation of superoxide radical during autoxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys 186:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(78)90479-4
Kurrle E, Ehninger G, Freund M et al (1986) Age adapted induction and intensified consolidation therapy in acute myelogenous leukemia. Onkologie 9:141–143. https://doi.org/10.1159/000215987
Li M, Wu X, Zou J et al (2022) Dietary α-lipoic acid alleviates deltamethrin-induced immunosuppression and oxidative stress in northern snakehead (Channa argus) via Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathway. Fish Shellfish Immunol 127:228–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2022.06.029
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lu M, Bai J, Xu B et al (2017) Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on relieving ammonia stress and hepatic proteomic analyses of broilers. Poult Sci 96:88–97. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pew285
Luo J, Yang X, Qiu S et al (2019) Sex difference in monocrotaline-induced developmental toxicity and fetal hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicology 418:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2019.02.014
Magina KN, Pregartner G, Zebisch A et al (2017) Cytarabine dose in the consolidation treatment of AML: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood 130:946–948. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-04-777722
Makeeva AV, Popova TN, Matasova LV (2007) Thioctic acid action on glutathione-dependent antioxidant system functioning at toxic hepatitis of rats. Biomeditsinskaia Khimiia 53:181–189
Marley R, Holt S, Fernando B et al (1999) Lipoic acid prevents development of the hyperdynamic circulation in anesthetized rats with biliary cirrhosis. Hepatol Baltim Md 29:1358–1363. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.510290519
McCarthy MM (2015) Incorporating sex as a variable in preclinical neuropsychiatric research. Schizophrenia bulletin 41:1016–1020. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbv077
Mennecozzi M, Landesmann B, Palosaari T et al (2015) Sex differences in liver toxicity—do female and male human primary hepatocytes react differently to toxicants in vitro? PLoS ONE 10:e0122786. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122786
Micili SC, Goker A, Kuscu K et al (2019) α-Lipoic acid vaginal administration contrasts inflammation and preterm delivery in rats. Reprod Sci Thousand Oaks Calif 26:128–138. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719118766266
Milojkovic D, Apperley JF (2014) How I treat leukemia during pregnancy. Blood 123:974–984. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-08-283580
Mishra P, Singh U, Pandey CM et al (2019) Application of Student’s t-test, analysis of variance, and covariance. Ann Card Anaesth 22:407–411. https://doi.org/10.4103/aca.ACA_94_19
Mohammed MA, Gharib DM, Reyad HR et al (2021) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of alpha-lipoic acid protect against valproic acid-induced liver injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 99:499–505. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2019-0456
Monastra G, De Grazia S, Cilaker Micili S et al (2016) Immunomodulatory activities of alpha lipoic acid with a special focus on its efficacy in preventing miscarriage. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 13:1695–1708. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425247.2016.1200556
Moura FA, de Andrade KQ, dos Santos JCF, Goulart MOF (2015) Lipoic acid: its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory role and clinical applications. Curr Top Med Chem 15:458–483. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026615666150114161358
Mozaffarian F, Dehghani MA, Vanani AR, Mahdavinia M (2022) Protective effects of alpha lipoic acid against arsenic induced oxidative stress in isolated rat liver mitochondria. Biol Trace Elem Res 200:1190–1200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02712-3
Namoju R, Chilaka NK (2021) Alpha-lipoic acid ameliorates cytarabine-induced developmental anomalies in rat fetus. Hum Exp Toxicol 40:851–868. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120975114
Namoju R, Chilaka NK (2022) Maternal supplementation of α-lipoic acid attenuates prenatal cytarabine exposure-induced oxidative stress, steroidogenesis suppression and testicular damage in F1 male rat fetus. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 11:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-022-00240-0
Namoju RC, Khan S, Patel RS et al (2014) Pre-pubertal exposure of cytarabine-induced testicular atrophy, impaired spermatogenesis and germ cell DNA damage in SD rats. Toxicol Mech Methods 24:703–712. https://doi.org/10.3109/15376516.2014.970679
Newcomb M, Balducci L, Thigpen JT, Morrison FS (1978) Acute leukemia in pregnancy: successful delivery after cytarabine and doxorubicin. JAMA 239:2691–2692. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1978.03280520063023
Nguyen H, Gupta V (2024) Alpha-lipoic acid. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564301/
Niedermeier DM, Frei-Lahr DA, Hall PD (2005) Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Pharmacotherapy 25:1134–1140. https://doi.org/10.1592/phco.2005.25.8.1134
Nowik CM, Gerrie AS, Wong J (2021) Conservative management of presumed fetal anemia secondary to maternal chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. AJP Rep 11:e137–e141. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1740561
Oh RC, Hustead TR, Ali SM, Pantsari MW (2017) Mildly elevated liver transaminase levels: causes and evaluation. Am Fam Physician 96:709–715
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Oosten LEM, Chamuleau MED, Thielen FW et al (2018) Treatment of sporadic Burkitt lymphoma in adults, a retrospective comparison of four treatment regimens. Ann Hematol 97:255–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3167-7
Para O, Crispino P, Barone N et al (2018) Sex differences in adverse drug reaction and liver disease. Ital J Med 12:15. https://doi.org/10.4081/itjm.2018.893
Park S, Karunakaran U, Jeoung NH et al (2014) Physiological effect and therapeutic application of alpha lipoic acid. Curr Med Chem 21:3636–3645. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867321666140706141806
Parrott J, Holland M (2017) Undetected severe fetal myelosuppression following administration of high-dose cytarabine for acute myeloid leukemia: is more frequent surveillance necessary? Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2017:e5175629. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5175629
Perri RT, Weisdorf DJ, Oken MM (1985) Low-dose ARA-C fails to enhance differentiation of leukaemic cells. Br J Haematol 59:697–701. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07365.x
Pınar N, Çakırca G, Hakverdi S, Kaplan M (2020) Protective effect of alpha lipoic acid on cisplatin induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Biotech Histochem Off Publ Biol Stain Comm 95:219–224. https://doi.org/10.1080/10520295.2019.1667025
Pizzuto J, Avilés A, Ramos E et al (1983) Cytosine arabinoside induced liver damage: histopathologic demonstration. Med Pediatr Oncol 11:287–290. https://doi.org/10.1002/mpo.2950110416
Popov I, Jelić S, Radulović S, Tomasević Z (1996) Pilot study of enhancement of cisplatin activity by high dose cytarabine in advanced gastric and colorectal (G3/G4) cancer. Neoplasma 43:221–224
Prati D, Taioli E, Zanella A et al (2002) Updated definitions of healthy ranges for serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Ann Intern Med 137:1–10. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-137-1-200207020-00006
Radtke H, Pees HW, Schwamborn J et al (1988) Sequential high-dose cytarabine therapy in combination with asparaginase in acute myeloid leukemia. Onkologie 11:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1159/000216557
Ramachandran A, Jaeschke H (2018) Oxidative stress and acute hepatic injury. Curr Opin Toxicol 7:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2017.10.011
Rapisarda LM (1957) Experimental research on liver damage induced by anesthetics & under the protective effect of thioctic acid. Minerva Anestesiol 23:162–169
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE et al (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 179:588–590. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.179.4073.588
Rumbaugh RC, Colby HD (1980) Is growth hormone the pituitary feminizing factor mediating the actions of estradiol on hepatic drug and steroid metabolism? Endocrinology 107:719–724. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-107-3-719
Salehi B, Berkay Yılmaz Y, Antika G et al (2019) Insights on the use of α-lipoic acid for therapeutic purposes. Biomolecules 9:E356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080356
Seo M-N, Eom S-Y, Lim J-A et al (2023) Effects of environmental cadmium exposure on the liver in Korean adults: cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 84:237–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-023-00982-7
Shi J, Chang X, Zou H et al (2021) Protective effects of α-lipoic acid and chlorogenic acid on cadmium-induced liver injury in three-yellow chickens. Anim Open Access J MDPI 11:1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061606
Sinha AK (1972) Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem 47:389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(72)90132-7
Stentoft J (1990) The toxicity of cytarabine. Drug Saf 5:7–27. https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199005010-00003
Summanen M, Bäck S, Voipio J, Kaila K (2018) Surge of peripheral arginine vasopressin in a rat model of birth asphyxia. Front Cell Neurosci 12:2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00002
Tanaka Y, Kaibori M, Miki H et al (2015) Alpha-lipoic acid exerts a liver-protective effect in acute liver injury rats. J Surg Res 193:675–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2014.08.057
Tashiro H, Umezawa K, Shirota M et al (2011) Acute myelogenous leukemia developed at the 26th week of gestation. Rinsho Ketsueki 52:18–22
Tong TC, Hernandez M, Richardson WH et al (2007) Comparative treatment of alpha-amanitin poisoning with N-acetylcysteine, benzylpenicillin, cimetidine, thioctic acid, and silybin in a murine model. Ann Emerg Med 50:282–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.12.015
Tong W, Shi Q, Salminen W, et al (2011) Unravelling sex differences in drug-induced liver injury. In: General, applied and systems toxicology. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470744307.gat226
Verma J, Gorard DA (2012) Persistently elevated alkaline phosphatase. BMJ Case Rep 2012:bcr2012006768. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2012-006768
Wang WS, Tzeng CH, Chiou TJ et al (1996) High-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone as salvage therapy for refractory non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi Chin Med J Free China Ed 57:100–105
Wang WS, Tzeng CH, Chiou TJ et al (1997) High-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone as salvage therapy for refractory non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol 27:154–157. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/27.3.154
Yamauchi H, Katayama K, Ueno M et al (2004) Involvement of p53 in 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine-induced trophoblastic cell apoptosis and impaired proliferation in rat placenta. Biol Reprod 70:1762–1767. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.103.026252
Yang YM, Cho YE, Hwang S (2022) Crosstalk between oxidative stress and inflammatory liver injury in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Int J Mol Sci 23:774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020774
Yucebilgin MS, Cagirgan S, Donmez A et al (2004) Acute myeloblastic leukemia in pregnancy: a case report and review of the literature. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 25:126–128
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Bhaskar Medical College, Hyderabad, and Bhaskar Pharmacy College, Hyderabad, for providing facilities and Vivo Bio Tech Ltd., Pregnapur, Telangana, for the support in technological aspects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RN and KNC were involved in conceiving the concept and designing the study; analyzing and interpreting data; reviewing and editing of manuscript; and approval of the manuscript. RN contributed to the literature search, carried out the experiment, and wrote the manuscript. KNC supervised the study. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) has approved the protocol (Approval Number: MLRIP/IAEC/2018/02).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Namoju, R., Chilaka, K.N. Protective effect of alpha‑lipoic acid against in utero cytarabine exposure-induced hepatotoxicity in rat female neonates. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03036-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03036-4