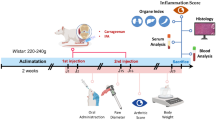
Abstract
An autoimmune disease, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by the onset of inflammation and subsequent damage to the joints. Although several therapies are available for RA, none are effective, and many have undesirable side effects. The roots of Sinomenium acutum produce an alkaloid called Sinomenine (SIN), which has been used for centuries in Chinese medicine to treat arthritis due to its anti-inflammatory properties. This study aimed to explore the potential therapeutic benefits of SIN through oral administration following RA induction using Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA) injections. The study monitored changes in the arthritic index, hind paw volume, inflammation and oxidative stress markers. Results demonstrated that SIN effectively inhibited the activity of NF-κB and IKKβ in knee joint tissues, which led to a decrease in tissue levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and iNOS in RA-induced rats. The production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10, Arg-1, and Fizz1 also increased. In rat knee joints, SIN elevated the expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-3 and decreased the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Additionally, SIN modulated the RANK/RANKL/OPG pathway in RA-induced rat knee joint tissues, reducing RANKL expression and increasing OPG. SIN also effectively decreased MDA, NO, and elevated antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, GPx, and GSH) in RA-induced rats via Nrf2/Keap 1 signaling pathway activation. In conclusion, this study suggests that SIN possesses potential therapeutic benefits for treating RA by modulating the RANK/RANKL/OPG pathway, which may impact osteoclast activity, oxidative stress, and inflammation in knee joint tissues.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdel Jaleel GA, Azab SS, el-Bakly WM, Hassan A (2021) ’Methyl palmitate attenuates adjuvant induced arthritis in rats by decrease of CD68 synovial macrophages. Biomed Pharmacother 137:111347
Alabarse PVG, Lora PS, Silva JMS, Santo RCE, Freitas EC, de Oliveira MS, Almeida AS, Immig M, Teixeira VON, Filippin LI, Xavier RM (2018) Collagen-induced arthritis as an animal model of rheumatoid cachexia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 9:603–612
Azizi G, Boghozian R, Mirshafiey A (2014) The potential role of angiogenic factors in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis 17:369–383
Bi F, Zhang Y, Liu W, Xie K (2021) Sinomenine activation of Nrf2 signaling prevents inflammation and cerebral injury in a mouse model of ischemic stroke. Exp Ther Med 21:1–9
Bullock J, Rizvi SAA, Saleh AM, Ahmed SS, Do DP, Ansari RA, Ahmed J (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis: a brief overview of the treatment. Med Princ Pract 27:501–507
Chadha S, Behl T, Kumar A, Khullar G, Arora S (2020) Role of Nrf2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Res Transl Med 68:171–181
Chang Y-H, Lin IL, Tsay GJ, Yang S-C, Yang T-P, Ho K-T, Hsu T-C, Shiau M-Y (2008) Elevated circulatory MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels and activities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Biochem 41:955–959
Chen Z, Tao ZZ, Zhou XH, Wu TT, Ye LF (2017) Immunosuppressive effect of sinomenine in an allergic rhinitis mouse model. Exp Ther Med 13:2405–2410
Cheng BCY, Yu H, Guo H, Su T, Fu X-Q, Li T, Cao H-H, Tse AK-W, Wu Z-Z, Kwan H-Y, Yu Z-L (2016) A herbal formula comprising Rosae Multiflorae Fructus and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos, attenuates collagen-induced arthritis and inhibits TLR4 signalling in rats. Sci Rep 6:20042
Dogan S, Kimyon G, Ozkan H, Kacmaz F, Camdeviren B, Karaaslan I (2022) TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-10 and fatty acids in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving cDMARD and bDMARD therapy. Clin Rheumatol 41:2341–2349
Elbaz EM, Amin HAA, Kamel AS, Ibrahim SM, Helmy HS (2020) Immunomodulatory effect of diallyl sulfide on experimentally-induced benign prostate hyperplasia via the suppression of CD4+T/IL-17 and TGF-β1/ERK pathways. Inflammopharmacology 28:1407–1420
Fan H, Tu T, Zhang X, Yang Q, Liu G, Zhang T, Bao Y, Lu Y, Dong Z, Dong J (2022) Sinomenine attenuates alcohol-induced acute liver injury via inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 159:112759
Farrow M, Biglands J, Tanner S, Hensor EMA, Buch MH, Emery P, Tan AL (2021) Muscle deterioration due to rheumatoid arthritis: assessment by quantitative MRI and strength testing. Rheumatology 60:1216–1225
Gao W-J, Liu J-X, Xie Y, Luo P, Liu Z-Q, Liu L, Zhou H (2021) Suppression of macrophage migration by down-regulating Src/FAK/P130Cas activation contributed to the anti-inflammatory activity of sinomenine. Pharmacol Res 167:105513
Geusens P (2012) The role of RANK ligand/osteoprotegerin in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 4:225–233
Guo Q, Wang Y, Xu D, Nossent J, Pavlos NJ, Xu J (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res 6:15
Hong H, Lu X, Lu Q, Huang C, Cui Z (2022) Potential therapeutic effects and pharmacological evidence of sinomenine in central nervous system disorders. Front Pharmacol 13:1015035
Jiang H, Lu Q, Xu J, Huo G, Cai Y, Geng S, Xu H, Zhang J, Li H, Yuan K, Huang G (2023) Sinomenine ameliorates adjuvant-induced arthritis by inhibiting the autophagy/NETosis/inflammation axis. Sci Rep 13:3933
Jun W, Pei-Gen X, Shi-Ying L, Ping G, Rui-Hai W (1992) The inhibitory effect of Sinomenine on immunological function in mice. Phytother Res 6:117–120
Katsikis PD, Chu CQ, Brennan FM, Maini RN, Feldmann M (1994) Immunoregulatory role of interleukin 10 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med 179:1517–1527
Khalil ASM, Giribabu N, Yelumalai S, Shahzad H, Kilari EK, Salleh N (2021) Myristic acid defends against testicular oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis: restoration of spermatogenesis, steroidogenesis in diabetic rats. Life Sci 278:119605
Kondo N, Kuroda T, Kobayashi D (2021) Cytokine Networks in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci 22:10922
Lai W-D, Wang S, You W-T, Chen S-J, Wen J-J, Yuan C-R, Zheng M-J, Jin Y, Yu J, Wen C-P (2002) Sinomenine regulates immune cell subsets: potential neuro-immune intervene for precise treatment of chronic pain. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:1041006. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.1041006
Lan Z, Wei M, Chen L, Xie G, Liu X, Zhang X (2016) Role of sinomenine on complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. IUBMB Life 68:429–435
Li X, He L, Hu Y, Duan H, Li X, Tan S, Zou M, Gu C, Zeng X, Yu L, Xu J, Liu S (2013) Sinomenine suppresses osteoclast formation and Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra-induced bone loss by modulating RANKL signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 8:e74274
Li RZ, Guan XX, Wang XR, Bao W-Q, Lian L-R, Choi SW, Zhang FY, Yan P-Y, Leung ELH, Pan H-D, Liu L (2023) Sinomenine hydrochloride bidirectionally inhibits progression of tumor and autoimmune diseases by regulating AMPK pathway. Phytomedicine 114:154751
Liao K, Su X, Lei K, Liu Z, Lu L, Wu Q, Pan H, Huang Q, Zhao Y, Wang M, Cai J, Liu L, Li T (2021) Sinomenine protects bone from destruction to ameliorate arthritis via activating p62Thr269/Ser272-Keap1-Nrf2 feedback loop. Biomed Pharmacother 135:111195
Liu X-Y, Xu L, Wang Y, Li J-X, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Wang S-S, Zhang X-M (2017) Protective effects of total flavonoids of Astragalus against adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats by regulating OPG/RANKL/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 44:105–114
Liu W, Zhang Y, Zhu W, Ma C, Ruan J, Long H, Wang Y (2018) Sinomenine inhibits the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by regulating the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and monocyte/macrophage subsets. Front Immunol 9:2228
López-Armada MJ, Fernández-Rodríguez JA, Blanco FJ (2022) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis. Antioxidants (Basel) 11(6):1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11061151
McInnes IB, Schett G (2011) The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365:2205–2219
Nasuti C, Fedeli D, Bordoni L, Piangerelli M, Servili M, Selvaggini R, Gabbianelli R (2019) Anti-inflammatory, anti-arthritic and anti-nociceptive activities of Nigella sativa oil in a rat model of arthritis. Antioxidants (Basel) 8(9):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090342
Ono T, Hayashi M, Sasaki F, Nakashima T (2020) RANKL biology: bone metabolism, the immune system, and beyond. Inflamm Regen 40:2
Papadaki M, Rinotas V, Violitzi F, Thireou T, Panayotou G, Samiotaki M, Douni E (2019) New insights for RANKL as a proinflammatory modulator in modeled inflammatory arthritis. Front Immunol 10:97. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00097
Pathade V, Nene S, Ratnam S, Khatri DK, Raghuvanshi RS, Singh SB, Srivastava S (2022) Emerging insights of peptide-based nanotherapeutics for effective management of rheumatoid arthritis. Life Sci 312:121257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121257
Pope JE, Choy EH (2021) C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities. Semin Arthritis Rheum 51:219–229
Prasad P, Verma S, Surbhi, Ganguly NK, Chaturvedi V, Mittal SA (2023) Rheumatoid arthritis: advances in treatment strategies. Mol Cell Biochem 478:69–88
Qian X, Zhao Z, Shang W, Xu Z, Zhang B, Cai H (2018) Serum proteomic analysis of the anti-arthritic effects of sinomenine on rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Mol Med Rep 18:49–58
Shaker OG, Elbaz EM (2020) Possible prognostic potential of RANKL and OPG in metastatic breast cancer egyptian females. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 21:355–361
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, Kavanaugh A, McInnes IB, Solomon DH, Strand V, Yamamoto K (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Prim 4:18001
Sun Y, Liu J, Xin L, Wen J, Zhou Q, Chen X, Ding X, Zhang X (2023) Xinfeng capsule inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis by up-regulating LINC00638 and activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 301:115839
Tian Z, Zhang H, Shang C (2021) Farrerol ameliorate adjuvant-induced ankle injury via alteration of PPAR-γ signal pathway. J Food Biochem 45:e13585
Vasdev N, Pawar B, Gupta T, Mhatre M, Tekade RK (2023) A bird’s eye view of various cell-based biomimetic nanomedicines for the treatment of arthritis. Pharmaceutics 15:1150
Wahab NAA, Giribabu N, Kilari EK, Salleh N (2022) Abietic acid ameliorates nephropathy progression via mitigating renal oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis in high fat diet and low dose streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 107:154464
Wang Q, Li XK (2011) Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory activities of sinomenine. Int Immunopharmacol 11:373–376
Wei ST, Sun YH, Zong SH, Xiang YB (2015) Serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-α may correlate with activity and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Med Sci Monit 21:4030–4038
Xiao-Qing Z, Ke-Wu Z (2021) Advances in anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory mechanisms of sinomenine. Tradit Med Res 6:6
Yamamoto K, Wilkinson D, Bou-Gharios G (2021) Targeting dysregulation of metalloproteinase activity in osteoarthritis. Calcif Tissue Int 109:277–290
Yao R-B, Zhao Z-M, Zhao L-J, Cai H (2017) Sinomenine inhibits the inflammatory responses of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Die Pharmazie-An Int J Pharm Sci 72:355–360
Yap HY, Tee SZ, Wong MM, Chow SK, Peh SC, Teow SY (2018) Pathogenic role of immune cells in rheumatoid arthritis: implications in clinical treatment and biomarker development. Cells 7(10):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100161
Yong W, Yongfei F, Xin Z, Bing Z (2003) Effect of different concentration sinomenine on cytokines mRNA expression of synoviocytes in rats. Chin J Inf Tradit Chin Med 10:25–27
Zampeli E, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG, Tzioufas AG (2015) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: unraveling the conundrum. J Autoimmun 65:1–18
Zeng L, Yu G, Yang K, Li J, Hao W, Chen H (2021) The efficacy of antioxidative stress therapy on oxidative stress levels in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:3302886
Zhang L, Zhang W, Zheng B, Tian N (2019) Sinomenine attenuates traumatic spinal cord injury by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via Nrf2 pathway. Neurochem Res 44:763–775
Zhang MW, Wang XH, Shi J, Yu JG (2021) Sinomenine in cardio-cerebrovascular diseases: potential therapeutic effects and pharmacological evidences. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:749113
Zhao X-X, Peng C, Zhang H, Qin L-P (2012) Sinomenium acutum: a review of chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. Pharm Biol 50:1053–1061
Funding
Shaanxi Provincial Key Research and Development Program (No. 2021SF-259); Xi’an Science and Technology Bureau Innovation Ability Strong Foundation Program Project (No. 21YXYJ0003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL and RL conceived the idea and designed the study. JC and QC performed the experiments. JL helped in statistical analysis. JL and RL wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by The First Ward of Rheumatology and Immunology, Xi'an No.5 Hospital, Xi'an, China in compliance with the institutional committee's rules for animal care and authorized procedures (Ethics No. 2022-1667).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Cao, J., Chen, Q. et al. Investigating the therapeutic potential of sinomenine in rheumatoid arthritis: anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory mechanisms. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02810-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02810-0