Abstract
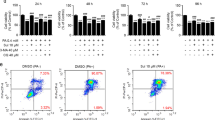
Salvianolic acid (Sal A) is a water-soluble compound extracted from Radix Salvia miltiorrhiza (danshen), which has been widely used to treat acute hepatitis and hepatic damage in traditional Chinese medicine. The aim of the present study was to delineate the antiapoptotic signaling pathways involved in Sal A’s hepato-protective action in hepatocyte LO2 cells and to further elucidate the mechanism by which Sal A elicits the antiapoptotic effects on hepatocytes. Here, the study showed that Sal A had antiapoptotic effects on the TNF-α/d-GalN-treated LO2 cells. Moreover, Western blotting demonstrated that the levels of p-eIF2α, ATF4, GRP78, CHOP and caspase-4 were markedly decreased in Sal A group. Additionally, the decrease of the cell mitochondrial membrane permeability and increase of ΔΨm were detected in Sal A-treated cells by high-content screening (HCS) analysis. And the levels of cleaved-caspase-9, cleaved-caspase-3, apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), Apaf-1, and Cytc (cyto) were downregulated, while Cytc (mito) was upregulated by Sal A via Western blotting. Furthermore, the decreased levels of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and calcium release were measured in Sal A-treated cells. In summary, Sal A attenuates TNF-α- and d-GalN-induced both ER stress and mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis by suppression of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and prevention of calcium release, which support the notion that Sal A could be developed into a novel hepatic protectant.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- d-GalN:
-
d-Galactosamine
- TRAIL:
-
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- GRP78:
-
ER chaperone 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein
- IRE1α:
-
Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α
- PERK:
-
PKR-like ER kinase
- ATF6:
-
Activating transcription factor 6
- eIF2α:
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP homologous protein
- GADD153:
-
Growth-arrest and DNA damage-inducible gene 153
- CCK-8:
-
Cell counting kit-8
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- ΔΨm:
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential
References
Adams JM, Cory S (2007) The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 26:1324–1337
Ando K, Hiroishi K, Kaneko T, Moriyama T, Muto Y, Kayagaki N, Yagita H, Okumura K, Imawari M (1997) Perforin, Fas/Fas ligand, and TNF-alpha pathways as specific and bystander killing mechanisms of hepatitis C virus-specific human CTL. J Immunol 158:5283–5291
Angela K, Christian E, Nikolai S, Kerstin A, Menger MD, Brigitte V (2008) Hepatocellular apoptosis is mediated by TNFalpha-dependent Fas/FasLigand cytotoxicity in a murine model of acute liver failure. Apoptosis 13:1427–1438
Arnaudeau S, Kelley WL, Walsh JV Jr, Demaurex N (2001) Mitochondria recycle Ca (2+) to the endoplasmic reticulum and prevent the depletion of neighboring endoplasmic reticulum regions. Biol Chem 276:29430–29439
Bernd M, Rainer O (2003) Mitochondrial regulation of apoptosis. News Physiol Sci 18:89–94
Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2:326–332
Bouchier HL, Munoz PC, Connell S, Green DR (2008) Measuring apoptosis at the single cell level. Methods 44:222–228
Breckenridge DG, Germain M, Mathai JP, Nguyen M, Shore GC (2003) Regulation of apoptosis by endoplasmic reticulum pathways. Oncogene 22:8608–8618
Brostrom MA, Brostrom CO (2003) Calcium dynamics and endoplasmic reticular function in the regulation of protein syn-thesis: implications for cell growth and adaptability. Cell Calcium 34:345–363
Chen MJ, Du YH, Qui M, Wang MY, Chen KJ, Huang ZZ, Jiang M, Xiong F, Chen JP, Zhou J, Jiang FR, Yin L, Tang YP, Ye LH, Zhan Z, Duan JA, Fu HA, Zhang X (2013) Ophiopogonin B-induced autophage in non-small cell lung cancer cells via inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncol Rep 29:430–436
Cheng J, Neil K (2010) ER stress signaling in hepatic injury. Signal Pathways Liver Dis 19:287–304
Chung D, Kim YS, Phillips JN, Ulloa A, Ku CY, Galan HL, Sanborn BM (2010) Attenuation of canonical transient receptor potential-like channel 6 expression specifically reduces the diacylglycerol-mediated increase in intracellular calcium in human myometrial cells. Endocrinology 151:406–416
Dambach DM, Andrews BA, Moulin F (2005) New technologies and screening strategies for hepatotoxicity: use of in vitro methods. Toxicol Pathol 33:17–26
Ferri KF, Kroemer G (2001) Organelle-specific initiation of cell death pathways. Nat Cell Biol 3:E255–E263
Gao M, Zhang WC, Liu QS, Hu JJ, Liu GT, Du GH (2008) Pinocembrin prevents glutamate-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y neuronal cells via decrease of bax/bcl-2 ratio. Eur J Pharmacol 591:73–79
Giuliano KA, Haskins JR, Taylor DL (2003) Advances in high content screening for drug discovery. Assay Drug Dev Technol 1:565–577
Gorlach A, Klappa P, Kietzmann T (2006) The endoplasmic reticulum: folding, calcium homeostasis, signaling, and redox control. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1391–1418
Green D, Kroemer G (1998) The central executioners of apoptosis: caspases or mitochondria trends. Cell Biol 8:267–271
Guan LY, Han BS, Li ZS, Hua FY, Huang F, Wei W, Yang Y, Xu C (2009) Sodium selenite induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in human acute promyelocytic leukemia NB4 cells. Apoptosis 14:218–225
Gulbins E, Dreschers S, Bock J (2003) Role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Exp Physiol 88:85–90
Hajnoczky G, Robb-Gaspers LD, Seitz MB, Thomas AP (1995) Decoding of cytosolic calcium oscillations in the mitochondria. Cell 82:415–424
Hayashi N, Mita E (1999) Involvement of Fas system-mediated apoptosis in pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. J Viral Hepat 6:357–365
Herr I, Debatin KM (2001) Cellular stress response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood 98:2603–2614
Hiramatsu N, Hayashi N, Katayama K, Mochizuki K, Kawanishi Y, Kasahara A, Fusamoto H, Kamada T (1994) Immunohistochemical detection of Fas antigen in liver tissue of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 19:1354–1359
Hsu TC, Wu WJ, Chen MC, Tsay GJ (2004) Human parvovirus B19 non-structural protein (NS1) induces apoptosis through mitochondria cell death pathway in COS-7 cells. Scand J Infect Dis 36:570–577
Janicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR, Porter AG (1998) Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem 273:9357–9360
Jedrusik A, Ajduk A, Pomorski P, Maleszewski M (2007) Mouse oocytes fertilised by ICSI during in vitro maturation retain the ability to be activated after refertilisation in metaphase II and can generate Ca2+ oscillations. BMC Dev Biol 7:72
Jiang X, Wang X (2000) Cytochrome c promotes caspase-9 activation by inducing nucleotide binding to Apaf-1. J Biol Chem 275:31199–31203
Jiang ZQ, Yan XX, Bi L, Chen JP, Zhou Q, Chen WP (2013) Mechanism for hepato-protective action of Liangxue Huayu Recipe (LHR): blockade of mitochondrial cytochrome c release and caspase activation. J Ethnopharmacol 148:851–860
Jouaville LS, Ichas F, Holmuhamedov EL, Camacho P, Lechleiter JD (1995) Synchronization of calcium waves by mitochondrial substrates in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nature 377:438–441
Kadowaki H, Nishitoh H, Ichijo H (2004) Survival and apoptosis signals in ER stress: the role of protein kinases. J Chem Neuroanat 28:93–100
Kaestner L, Tabellion W, Weiss E, Bernhardt I, Lipp P (2006) Calcium imaging of individual erythrocytes: problems and approaches. Cell Calcium 39:13–19
Kei T, Shuuji M, Shin Y, Tadayoshi S, Nobuhiko T, Michihiko I (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand 1 (TRAIL1) enhances the transition of red blood cells from the larval to adult type during metamorphosis in Xenopus. Blood 115:850–859
Kroemer G, Petit P, Zamzami N, Vayssiere JL, Mignotte B (1995) The biochemistry of programmed cell death. FASEB J 9:1277–1287
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, Yuan J (1998) Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94:491–501
Li F, Zhou X, Zhu J, Xia W, Ma J, Wong ST (2008) Workflow and methods of high-content time-lapse analysis for quantifying intracellular calcium signals. Neuroinformatics 6:97–108
Lin YL, Lee TF, Huang YJ, Huang YT (2006) Antiproliferative effect of salvianolic acid A on rat hepatic stellate cells. J Pharm Pharmacol 58:933
Liu LM, Zhang JX, Luo J, Guo HX, Deng H, Chen JY, Sun SL (2008) A role of cell apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nonlethal liver injury in D-galactosamine (D-GalN)-sensitized rats. Dig Dis Sci 53:1316–1324
Liu XA, Song J, Jiang Q, Wang Q, Tian Q, Wang JZ (2012) Expression of the hyperphosphorylated tau attenuates ER stress-induced apoptosis with upregulation of unfolded protein response. Apoptosis 17:1039–1049
Lu JW, Wang H, Yan-Li J, Zhang C, Ning H, Li XY, Zhang H, Duan ZH, Zhao L, Wei W, Xu DX (2008) Differential effects of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on TNF-α-mediated liver injury in two different models of fulminant hepatitis. J Hepatol 48:442–452
Luo KX, Zhu YF, Zhang LX, He HT, Wang XS, Zhang L (1997) In situ investigation of Fas/FasL expression in chronic hepatitis B infection and related liver diseases. J Viral Hepat 4:303–307
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X (1998) Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 94:481–490
Lv L, Zhou ZX, Huang XZ, Zhao YP, Zhang L, Shi Y, Sun M, Zhang J (2010) Inhibition of peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase Pin1 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Apoptosis 15:41–54
Nakagawa T, Yuan J (2006) Cross-talk between two cysteine protease families. Activation of caspase-12 by calpain in apoptosis. J Cell Biol 150:887–894
Nicolas D, Clark D (2003) Apoptosis—the calcium connection. Science 300:65–67
Ow YP, Green DR, Hao Z, Mark TW (2008) Cytochrome c: functions beyond respiration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:532–542
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11:381–389
Pacher P, Hajnoczky G (2001) Propagation of the apoptotic signal by mitochondrial waves. EMBO J 20:4107
Palacios C, Yerbes R, Lopez-Rivas A (2006) Flavopiridol induces cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein degradation by the proteasome and promotes TRAIL-induced early signaling and apoptosis in breast tumor cells. Cancer Res 66:8858–8869
Park IJ, Kim MJ, Park OJ, Choe W, Kang I, Kim SS, Ha J (2012) Cryptotanshinone induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF7 cells. Apoptosis 17:248–257
Patel T, Gores GJ (1995) Apoptosis and hepatobiliary disease. Hepatology 21:1725–1741
Qu FN, Qi LW, Wei YJ, Wen XD, Yi L, Luo HW, Li P (2008) Multiple target cell extraction and LC-MS analysis for predicting bioactive components in Radix Salviae miltiorrhizae. Biol Pharm Bull 31:501–506
Raj PV, Nitesg K, Prateek J, Sankhe MN, Rao JV, Rao CM, Udupa N (2011) Effect of lecithin on D-galactosamine induced hepatotoxicity through mitochondrial pathway involving Bcl-2 and Bax. Indian J Clin Biochem 26:378–384
Rizzuto R, Brini M, Murgia M, Pozzan T (1993) Microdomains with high Ca2+ close to IP3-sensitive channels that are sensed by neighboring mitochondria. Science 262:744–747
Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:519–529
Rosa MP, Maho N, Abelardo L (2012) ER stress sensitizes cells to TRAIL through down-regulation of FLIP and Mcl-1 and PERK-dependent up-regulation of TRAIL-R2. Apoptosis 17:349–363
Sanges D, Marigo V (2006) Cross-talk between two apoptotic pathways activated by endoplasmic reticulum stress: differential contribution of caspase-12 and AIF. Apoptosis 11:1629–1641
Schroder M, Kaufman RJ (2005) The mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Biochem 74:739–789
Scorrano L, Korsmeyer SJ (2003) Mechanisms of cytochrome c release by proapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304:437–444
Scorrano L, Oakes SA, Opferman JT, Cheng EH, Sorcinelli MD, Pozzan T, Korsmeyer SJ (2003) BAX and BAK regulation of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+: a control point for apoptosis. Science 300:135–139
Szalai G, Krishnamurthy R, Hajnoczky G (1999) Apoptosis driven by IP(3)-linked mitochondrial calcium signals. EMBO J 18:6349–6361
Tsai MK, Lin YL, Huang YT (2010) Effects of salvianolic acids oxidative stress and hepatic fibrosis in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 242:155
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2007) Role of the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition in cell death. Apoptosis 12:835–840
Ulloa A, Gonzales AL, Zhong M, Kim YS, Cantlon J, Clay C, Ku CY, Earley S, Sanborn BM (2009) Reduction in TRPC4 expression specifically attenuates G-protein coupled receptor-stimulated increases in intracellular calcium in human myometrial cells. Cell Calcium 46:73–84
Valdimir J, Tatijana SR, Gordana K, Gordana B, Mija C (2011) TNF-α induced apoptosis is accompanied with rapid CD30 and slower CD45 shedding from K-562 cells. J Membr Biol 239:115–122
Vladimir J, Gordana B, Vesna K, Dimitar J, Tatjana S (2006) Effect of TNF-α on Raji cells at different cellular levels estimated by various methods. Ann Hematol 85:86–94
Wang XZ, Lawson B, Brewer JW, Zinszner H, Sanjay A, Mi LJ, Boorstein R, Kreibich G, Hendershot LM, Ron D (1996) Signals from the stressed endoplasmic reticulum induce C/EBP-homologous protein CHOP/GADD153). Mol Cell Biol 16:4273–4280
Wang CY, Ma FL, Liu JT, Tian JW, Fu FH (2007) Protective effect of salvianic acid A on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 30:44
Woo M, Hakem R, Soengas MS, Duncan GS, Shahinian A, Kȁgi D, Hakem A, McCurrach M, Kaufman SA, Senaldi G, Howard T, Lowe SW, Mak TW (1998) Essential contribution of caspase 3/CPP32 to apoptosis and its associated nuclear changes. Genes Dev 12:806–819
Wu ZM, Wen T, Tan YF, Liu Y, Ren F, Wu H (2007) Effects of salvianolic acid A on oxidative stress and liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 100:115
Xu JJ, Diaz D, O Brien PJ (2004) Applications of cytotoxicity assays and pre-lethal mechanistic assays for assessment of human hepatotoxicity potential. Chem Biol Interact 150:115–128
Xue X, Piao JH, Nakajima A, Sakon-Komazawa S, Kojima Y, Mori K, Yagita H, Okumura K, Harding H, Nakano H (2005) Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) induces the unfolded protein response (UPR) in a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent fashion, and the UPR counteracts ROS accumulation by TNF alpha. J Biol Chem 280:33917–33925
Zamzani N, Kroemer G (2001) The mitochondrion in apoptosis: how Pandora’s box opens. Nat Rev 2:67–71
Zhou X, Wong S (2006) High content cellular imaging for drug development. IEEE Signal Process Mag 23:170–174
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (81072777, 81273638). This work was also financially supported in part by the grants from a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). In addition, this program was granted for scientific innovation research of college graduate in Jiangsu province (CXZZ13_0624).
Author contributions
Xiao-jing Yan, Ze-qun Jiang, and Wei-ping Chen designed research; Xiao-jing Yan, Ze-qun Jiang, Lei Bi, and Ye Yang performed research; Xiao-jing Yan wrote this manuscript; Ze-qun Jiang and Wei-ping Chen reviewed and edited this manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiaojing Yan and Zequn Jiang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, X., Jiang, Z., Bi, L. et al. Salvianolic acid A attenuates TNF-α- and d-GalN-induced ER stress-mediated and mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis by modulating Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and calcium release in hepatocyte LO2 cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388, 817–830 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1116-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1116-3