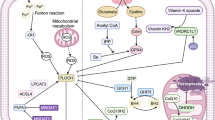
Abstract
Introduction
In this study, we delineated the apoptotic signaling pathways activated by sodium selenite in NB4 cells.
Materials and methods
NB4 cells were treated with 20 μM sodium selenite for different times. The activation of caspases and ER stress markers, ROS levels, mitochondrial membrane potential and cell apoptosis induced by sodium selenite were analyzed by immunoblotting analysis, DCF fluorescence and flow cytometric respectively. siRNA was used to detect the effect of GADD153 on selenite-induced cell apoptosis.
Conclusions
Sodium selenite-induced reactive oxygen species generation is an early event that triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in NB4 cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- MnTMPyp:
-
Mn(III) tetrakis(1-methyl-4-pyridyl) porphyrin pentachloride
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
References
Lavrik IN, Golks A, Krammer PH (2005) Caspases: pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J Clin Invest 115:2665–2672. doi:10.1172/JCI26252
Rutkowski DT, Kaufman RJ (2004) A trip to the ER: coping with stress. Trends Cell Biol 14:20–28. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2003.11.001
Faitova J, Krekac D, Hrstka R, Vojtesek B (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett 11:488–505. doi:10.2478/s11658-006-0040-4
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM et al (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7:880–885. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400779
Zhang KZ, Kaufman RJ (2004) Signaling the unfolded protein response from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 279:25935–25938. doi:10.1074/jbc.R400008200
Kadowaki H, Nishitoh H, Ichijo H (2004) Survival and apoptosis signals in ER stress: the role of protein kinases. J Chem Neuroanat 28:93–100
Wang XZ, Lawson B, Brewer JW et al (1996) Signals from the stressed endoplasmic reticulum induce C/EBP-homologous protein CHOP/GADD153). Mol Cell Biol 16:4273–4280
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11:381–389. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401373
Patrick L (2004) Selenium biochemistry and cancer: a review of the literature. Altern Med Rev 9:239–258
Zeng H, Combs GF Jr (2007) Selenium as an anticancer nutrient: roles in cell proliferation and tumor cell invasion. J Nutr Biochem 19:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2007.02.005
Xiang N, Zhao R, Zhong W (2009) Sodium selenite induces apoptosis by generation of superoxide via the mitochondrial-dependent pathway in human prostate cancer cells. Chemother Pharm 63:351–362
Gopee NV, Johnson VJ, Sharma RP (2004) Sodium selenite-induced apoptosis in murine B-lymphoma cells is associated with inhibition of protein kinase C-δ, nuclear factor-κB, and inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Toxicol Sci 78:204–214. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfh072
Xiao R, Qiao JT, Zhao HF (2006) Sodium selenite induces apoptosis in cultured cortical neurons with special concomitant changes in expression of the apoptosis-related genes. Neurotoxicology 27:478–484. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2006.01.008
Lanotte M, Martin-Thouvenin V, Najman S et al (1991) NB4, a maturation inducible cell line with t(15;17) marker isolated from a human acute promyelocytic leukemia (M3). Blood 77:1080–1086
Chen Z, Chen CG, Shen ZX et al (2001) Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic compounds: in vitro and in vivo studies. Semin Hematol 38:26–36. doi:10.1053/shem.2001.20863
Shen ZX, Shi ZZ, Fang J et al (2004) All-trans retinoic acid/As2O3 combination yields a high quality remission and survival in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:5328–5335. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400053101
Li J, Zuo L, Shen T, Xu CM et al (2003) Induction of apoptosis by sodium selenite in human acute promyelocytic leukemia NB4 cells: involvement of oxidative stress and mitochondria. J Trace Elem Med Biol 17:19–26. doi:10.1016/S0946-672X(03)80041-X
Han BS, Wei W, Hua FY et al (2007) Requirement for ERK activity in sodium selenite-induced apoptosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia-derived NB4 cells. J Biochem Mol Biol 40:196–204
Wu Y, Zhang HT, Dong Y et al (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum stress signal mediators are targets of selenium action. Cancer Res 65:9073–9079. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2016
Hitomi J, Katayama T, Eguchi Y et al (2004) Involvement of caspase-4 in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and Aβ-induced cell death. J Cell Biol 165:347–356. doi:10.1083/jcb.200310015
Fels DR, Koumenis C (2006) The PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 module of the UPR in hypoxia resistance and tumor growth. Cancer Biol Ther 5:723–728. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0164
Jiang HY, Wek RC (2005) Phosphorylation of the α-subunit of the eukaryotic initiation factor-2α (eIF2α) reduces protein dynthesis and enhances apoptosis in response to proteasome inhibition. J Biol Chem 280:14189–14202. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413660200
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A et al (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107:881–891. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00611-0
Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Glimcher LH (2003) XBP-1 regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol 23:7448–7459. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.21.7448-7459.2003
Ruddock LW, Molinari M (2006) N-glycan processing in ER quality control. J Cell Sci 119:4373–4380. doi:10.1242/jcs.03225
Zu K, Bihani T, Lin A et al (2006) Enhanced selenium effect on growth arrest by BiP/GRP78 knockdown in p53-null human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 25:546–554
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon AD, Exton JH (2004) Critical role of endogenous AKT/IAPs and MEK1/ERK pathways in counteracting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 279:49420–49429. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407700200
Shen HM, Yang CF, Ong CN (1999) Sodium selenite-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Int J Cancer 81:820–828. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19990531)81:5<820::AID-IJC25>3.0.CO;2-F
Li GX, Hu H, Jiang C, Schuster T (2007) Differential involvement of reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induced by two classes of selenium compounds in human prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer 120:2034–2043. doi:10.1002/ijc.22480
Karen DM, Jennifer LM, Lars-oliver K et al (2001) Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating bcl2 and perturbing the cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol 21:1249–1259. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.4.1249-1259.2001
Kuo CT, Hsu MJ, Chen BC et al (2008) Denbinobin induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells via Akt inactivation, bad activation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol Lett 177:48–58
Nobumichi O, Satoshi Y, Takayuki H (2005) TRB3, a novel ER stress-inducible gene, is induced via ATF4–CHOP pathway and is involved in cell death. EMBO J 24:1243–1255. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600596
Kato S, Du K (2007) TRB3 modulates C2C12 differentiation by interfering with AKT activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 353:933–938. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.12.161
Xue X, Piao JH, Nakajima A et al (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) induces the unfolded protein response (UPR) in a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent fashion, and the UPR counteracts ROS accumulation by TNF-α. J Biol Chem 280:33917–33925. doi:10.1074/jbc.M505818200
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (no. 30370348 and no. 30770491), Doctoral Point Foundation of National Educational Committee (no. 20010023029), and Natural Sciences Foundation of Beijing (no. 7032034 and no. 5082015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, L., Han, B., Li, Z. et al. Sodium selenite induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in human acute promyelocytic leukemia NB4 cells. Apoptosis 14, 218–225 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0295-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0295-5