Abstract
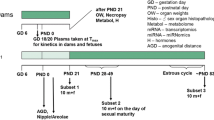
A multigeneration study on the reproductive toxicity of TCDD in rats was conducted. In this paper, the results of extensive pharmacokinetic evaluations are presented. The time course of tissue concentrations within the framework of a multigeneration study was investigated, using radioactive labeled 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a substance with a long elimination half-life. So far, long term exposure to TCDD has generally been conducted by administering the same daily doses via the feed. Since the half-life of TCDD in rats is several weeks, the concentration of the test substance can be predicted to change continuously during such a study. Therefore we intended to expose the animals to a constant tissue concentration by using a loading dose/maintenance dose approach. To achieve this, the animals were treated with initial loading doses of 50, 120 or 250 ng TCDD/kg body wt. Based on the elimination half-life of 3 weeks and a planned dosing interval of 7 days, the weekly maintenance doses were calculated to be 20% of the loading dose. During the postnatal phase of rapid growth, this dosing schedule was insufficient to keep the tissue concentration of TCDD constant. It was necessary to administer a second loading dose and to increase the weekly maintenance dose to 40% of the loading dose. While it was possible to control the tissue concentrations in the F0 generation, a considerably larger variation was observed during the different developmental stages of the F1 generation. The fluctuations could be reduced by using a complex dosing schedule, but even with that it was impossible to achieve completely steady levels in liver and adipose tissue. This was mainly due to the fact that levels in liver and adipose tissue did not change together. In the case of a lipophilic substance with a long elimination half-life, attempts at a risk assessment on the basis of a multigeneration test cannot rest on the assumption of defined tissue levels during the study while pharmacokinetic variables are difficult to control in such a study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham K, Krowke R, Neubert D (1988) Pharmacokinetics and biological activity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: 1. Dose-dependent tissue distribution and induction of hepatic ethoxyresorufin 0-deethylase in rats following a single injection. Arch Toxicol 62: 359–368
Dost FH (1968) Grundlagen der Pharmakokinetik. Georg Thieme, Stuttgart
Glatke E, Hattingberg HM (1973) Pharmakokinetik. Springer, Berlin
Kociba RJ, Keyes DG, Beyes JE, Carreon RM, Wade CE, Dittenber DA, Kalnins RP, Frauson LE, Park CN, Barnard SD, Hummel RA, Humiston CH (1978) Results of a twoear chronic toxicity and oncogenicity study of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 26: 279–303
Korte M, Thiel R, Koch E, Stahlmann R, Neubert D (1992) Tissue concentrations of 2,3,7,8-TCDD in rats and offspring after continuous exposure during the late fetal and postnatal period. Chemosphere 25: 1183–1188
Krowke R (1986) Studies on distribution and embryotoxicity of different PCDDs and PCDFs in mice and marmosets. Chemosphere 15: 2011–2022
Krowke R, Chahoud I, Baumann-Wilschke I, Neubert D (1989) Pharmacokinetics and biological activity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. 2. Pharmacokinetics in rats using a loading-dose/maintenance-dose regime with high doses. Arch Toxicol 63: 356–360
Lamb JC, Marks TA, Gladen BC, Allen JW, Moore JA (1981a) Male fertility, sister chromatid exchange, and germ cell toxicity following exposure to mixtures of chlorinated phenoxy acids containing 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Toxicol Environ Health 8: 825–834
Lamb JC, Moore JA, Marks TA, Haseman JK (1981b) Development and viability of offspring of male mice treated with chlorinated phenoxy acids and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Toxicol Environ Health 8: 835–844
Murray FJ, Smith FA, Nitschke KD, Humiston CG, Kociba RJ, Schwetz BA (1979) Three-generation reproduction study of rats given 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in the diet. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 50: 241–252
Neubert D, Abraham K, Golor G, Krowke R, Krüger N, Nagao T, Neubert R, Schulz-Schalge T, Stahlmann R, Wiesmüller T, Hagenmaier H (1991) Comparison of the effects of PCDDs and PCDFs on different species taking kinetic variables into account. In: Gallo M, Scheuplein RJ, Van Heijden KA (eds) Banbury Report 35, Biological basis for risk assessment of dioxins and related compounds. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, pp 27–44
Rose JQ, Ramsey JC, Wentzler TH, Hummel RA, Gehring PJ (1976) The fate of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin following single and repeated oral doses to the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 36: 209–226
Takagi Y, Otake T, Katoaka M, Murata Y, Aburada S, Akasaka S, Hashimoto K, Uda H, Kitaura T (1976) Studies on the transfer and distribution of 14C polychlorinated biphenyls from maternal to fetal and suckling rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 38: 549–558
Van den Berg M, Heeremans C, Veenhoven E, Oliem K (1987) Transfer of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans to fetal and neonatal rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol 9: 635–644
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koch, E., Thiel, E., Chahoud, E. et al. Four generation reproductive toxicity study with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-P-dioxin (TCDD) in rats. Arch Toxicol 69, 271–279 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050170
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050170