Abstract
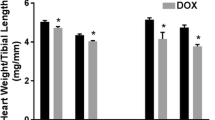
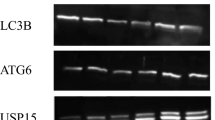
Cancer survivors may experience long-term cardiovascular complications due to chemotherapeutic drugs such as doxorubicin (DOX). The exact mechanism of delayed DOX-induced cardiotoxicity has not been fully elucidated. Sex is an important risk factor for DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. In the current study, we identified sex differences in delayed DOX-induced cardiotoxicity and determined the underlying molecular determinants of the observed sexual dimorphism. Five-week-old male and female mice were administered intraperitoneal injections of DOX (4 mg/kg/week) or saline for 6 weeks. Echocardiography was performed 5 weeks after the last dose of DOX to evaluate cardiac function. Thereafter, mice were sacrificed and gene expression of markers of apoptosis, senescence, and inflammation was measured by PCR in hearts and livers. Proteomic profiling of the heart from both sexes was conducted to determine differentially expressed proteins (DEPs). Only DOX-treated male, but not female, mice demonstrated cardiac dysfunction, cardiac atrophy, and upregulated cardiac expression of Nppb and Myh7. No sex-related differences were observed in DOX-induced expression of most apoptotic, senescence, and pro-inflammatory markers. However, the gene expression of Trp53 was significantly reduced in hearts of DOX-treated female mice only. The anti-inflammatory marker Il-10 was significantly reduced in hearts of DOX-treated male mice only, while the pro-inflammatory marker Il-1α was significantly reduced in livers of DOX-treated female mice only. Gene expression of Tnf-α was reduced in hearts of both DOX-treated male and female mice. Proteomic analysis identified several DEPs after DOX treatment in a sex-specific manner, including anti-inflammatory acute phase proteins. This is the first study to assess sex-specific proteomic changes in a mouse model of delayed DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. Our proteomic analysis identified several sexually dimorphic DEPs, many of which are associated with the anti-inflammatory marker Il-10.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
References
Abdelgawad IY, Grant MKO, Popescu FE, Largaespada DA, Zordoky BN (2021a) Doxorubicin paradoxically ameliorates tumor-induced inflammation in young mice. Int J Mol Sci 22:9023
Abdelgawad IY, Sadak KT, Lone DW, Dabour MS, Niedernhofer LJ, Zordoky BN (2021b) Molecular mechanisms and cardiovascular implications of cancer therapy-induced senescence. Pharmacol Ther 221:107751
Abdelgawad IY, Agostinucci K, Sadaf B, Grant MKO, Zordoky BN (2023) Metformin mitigates SASP secretion and LPS-triggered hyper-inflammation in Doxorubicin-induced senescent endothelial cells. Front Aging 4:1170434
Agostinucci K, Grant MKO, Melaku W, Nair C, Zordoky BN (2023) Exposure to doxorubicin modulates the cardiac response to isoproterenol in male and female mice. Pharmaceuticals 16:391
Al-Amrani S, Al-Jabri Z, Al-Zaabi A, Alshekaili J, Al-Khabori M (2021) Proteomics: concepts and applications in human medicine. World J Biol Chem 12:57
Amara IE, Elshenawy OH, Abdelrady M, El-Kadi AO (2014) Acute mercury toxicity modulates cytochrome P450, soluble epoxide hydrolase and their associated arachidonic acid metabolites in C57Bl/6 mouse heart. Toxicol Lett 226:53–62
Bertaggia E, Scabia G, Dalise S, Lo Verso F, Santini F, Vitti P, Chisari C, Sandri M, Maffei M (2014) Haptoglobin is required to prevent oxidative stress and muscle atrophy. PLoS ONE 9:e100745
Blum S, Asaf R, Guetta J, Miller-Lotan R, Asleh R, Kremer R, Levy Nina S, Berger Franklin G, Aronson D, Fu X, Zhang R, Hazen Stanley L, Levy Andrew P (2007) Haptoglobin genotype determines myocardial infarct size in diabetic mice. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:82–87
Brandão SR, Carvalho F, Amado F, Ferreira R, Costa VM (2022) Insights on the molecular targets of cardiotoxicity induced by anticancer drugs: a systematic review based on proteomic findings. Metabolism 134:155250
Chaanine AH, Higgins L, Markowski T, Harman J, Kachman M, Burant C, Navar LG, Busija D, Delafontaine P (2021) Multi-omics approach profiling metabolic remodeling in early systolic dysfunction and in overt systolic heart failure. Int J Mol Sci 23:1
Chen L, Holder R, Porter C, Shah Z (2021) Vitamin D3 attenuates doxorubicin-induced senescence of human aortic endothelial cells by upregulation of IL-10 via the pAMPKalpha/Sirt1/Foxo3a signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 16:e0252816
Cheng Z, Zheng YZ, Li YQ, Wong CS (2017) Cellular senescence in mouse hippocampus after irradiation and the role of p53 and p21. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 76:260–269
Cheng X, Liu D, Xing R, Song H, Tian X, Yan C, Han Y (2020) Orosomucoid 1 attenuates doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes via Nrf2 signaling. Biomed Res Int 2020:5923572
Chiche A, le Roux I, von Joest M, Sakai H, Aguín SB, Cazin C, Salam R, Fiette L, Alegria O, Flamant P, Tajbakhsh S, Li H (2017) Injury-induced senescence enables in vivo reprogramming in skeletal muscle. Cell Stem Cell 20:407-414.e4
Desai VG, Azevedo-Pouly A, Vijay V, Phanavanh B, Moland CL, Han T, Revollo J, Aryal B, Rao VA, Fuscoe JC (2023) Potential role of the apelin-APJ pathway in sex-related differential cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin in mice. J Appl Toxicol 43:557–576
Falkenham A, de Antueno R, Rosin N, Betsch D, Lee TD, Duncan R, Legare JF (2015) Nonclassical resident macrophages are important determinants in the development of myocardial fibrosis. Am J Pathol 185:927–942
Franco VI, Lipshultz SE (2015) Cardiac complications in childhood cancer survivors treated with anthracyclines. Cardiol Young 25:107–116
García MA, Collado M, Muñoz-Fontela C, Matheu A, Marcos-Villar L, Arroyo J, Esteban M, Serrano M, Rivas C (2006) Antiviral action of the tumor suppressor ARF. Embo j 25:4284–4292
Gonzalez-Gualda E, Baker AG, Fruk L, Munoz-Espin D (2021) A guide to assessing cellular senescence in vitro and in vivo. FEBS J 288:56–80
Grant MK, Seelig DM, Sharkey LC, Zordoky BN (2017) Sex-dependent alteration of cardiac cytochrome P450 gene expression by doxorubicin in C57Bl/6 mice. Biol Sex Differ 8:1
Grant MKO, Seelig DM, Sharkey LC, Choi WSV, Abdelgawad IY, Zordoky BN (2019) Sexual dimorphism of acute doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity in C57Bl/6 mice. PLoS ONE 14:e0212486
Grant MKO, Abdelgawad IY, Lewis CA, Seelig D, Zordoky BN (2020a) Lack of sexual dimorphism in a mouse model of isoproterenol-induced cardiac dysfunction. PLoS ONE 15:e0232507
Grant MKO, Abdelgawad IY, Lewis CA, Zordoky BN (2020b) Sexual dimorphism in doxorubicin-induced systemic inflammation: implications for hepatic cytochrome P450 regulation. Int J Mol Sci 21:1
Henninger C, Huelsenbeck S, Wenzel P, Brand M, Huelsenbeck J, Schad A, Fritz G (2015) Chronic heart damage following doxorubicin treatment is alleviated by lovastatin. Pharmacol Res 91:47–56
Hudgins AD, Tazearslan C, Tare A, Zhu Y, Huffman D, Suh Y (2018) Age- and tissue-specific expression of senescence biomarkers in mice. Front Genet 9:1
Jenkins GR, Lee T, Moland CL, Vijay V, Herman EH, Lewis SM, Davis KJ, Muskhelishvili L, Kerr S, Fuscoe JC, Desai VG (2016) Sex-related differential susceptibility to doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 310:159–174
Kienesberger PC, Pulinilkunnil T, Sung MM, Nagendran J, Haemmerle G, Kershaw EE, Young ME, Light PE, Oudit GY, Zechner R, Dyck JR (2012) Myocardial ATGL overexpression decreases the reliance on fatty acid oxidation and protects against pressure overload-induced cardiac dysfunction. Mol Cell Biol 32:740–750
Kobayashi M, Usui F, Karasawa T, Kawashima A, Kimura H, Mizushina Y, Shirasuna K, Mizukami H, Kasahara T, Hasebe N (2016) NLRP3 deficiency reduces macrophage interleukin-10 production and enhances the susceptibility to doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Sci Rep 6:26489
Kurita H, Carreira VS, Fan Y, Jiang M, Naticchioni M, Koch S, Rubinstein J, Puga A (2016) Ah receptor expression in cardiomyocytes protects adult female mice from heart dysfunction induced by TCDD exposure. Toxicology 355–356:9–20
Lamason R, Zhao P, Rawat R, Davis A, Hall JC, Chae JJ, Agarwal R, Cohen P, Rosen A, Hoffman EP, Nagaraju K (2006) Sexual dimorphism in immune response genes as a function of puberty. BMC Immunol 7:2
Lérida-Viso A, Estepa-Fernández A, Morellá-Aucejo Á, Lozano-Torres B, Alfonso M, Blandez JF, Bisbal V, Sepúlveda P, García-Fernández A, Orzáez M, Martínez-Máñez R (2022) Pharmacological senolysis reduces doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and improves cardiac function in mice. Pharmacol Res 2022:106356
Linders AN, Dias IB, Ovchinnikova ES, Vermeer M, Hoes MF, Markousis Mavrogenis G, Deiman FE, Arevalo Gomez KF, Bliley JM, Nehme J, Vink A, Gietema J, De Boer RA, Westenbrink D, Sillje HHW, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, van Laake LW, Feinberg AW, Demaria M, Bomer N, Van Der Meer P (2023) Evaluation of senescence and its prevention in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity using dynamic engineered heart tissues. JACC Cardiooncol 5:298–315
Liu J, Lane S, Lall R, Russo M, Farrell L, Debreli Coskun M, Curtin C, Araujo-Gutierrez R, Scherrer-Crosbie M, Trachtenberg BH, Kim J, Tolosano E, Ghigo A, Gerszten RE, Asnani A (2022) Circulating hemopexin modulates anthracycline cardiac toxicity in patients and in mice. Sci Adv 8:9245
Lotrionte M, Biondi-Zoccai G, Abbate A, Lanzetta G, D’Ascenzo F, Malavasi V, Peruzzi M, Frati G, Palazzoni G (2013) Review and meta-analysis of incidence and clinical predictors of anthracycline cardiotoxicity. Am J Cardiol 112:1980–1984
Lou H, Danelisen I, Singal PK (2004) Cytokines are not upregulated in adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy and heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 36:683–690
Malik A, Bagchi AK, Jassal DS, Singal PK (2022) Interleukin-10 mitigates doxorubicin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress as well as cardiomyopathy. Biomedicines 10:1
Mantawy EM, El-Bakly WM, Esmat A, Badr AM, El-Demerdash E (2014) Chrysin alleviates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol 728:107–118
Matsushita T, Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Fujimoto M, Tedder TF (2008) Regulatory B cells inhibit EAE initiation in mice while other B cells promote disease progression. J Clin Invest 118:3420–3430
Meiners B, Shenoy C, Zordoky BN (2018) Clinical and preclinical evidence of sex-related differences in anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Biol Sex Differ 9:38
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Devasia T, Mariotto AB, Yabroff KR, Jemal A, Kramer J, Siegel RL (2022) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 72:409–436
Mitry MA, Laurent D, Keith BL, Sira E, Eisenberg CA, Eisenberg LM, Joshi S, Gupte S, Edwards JG (2020) Accelerated cardiomyocyte senescence contributes to late-onset doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 318:C380–C391
Morimoto M, Nakano T, Egashira S, Irie K, Matsuyama K, Wada M, Nakamura Y, Shigemori Y, Ishikura H, Yamashita Y, Hayakawa K, Sano K, Mishima K (2022) Haptoglobin regulates macrophage/microglia-induced inflammation and prevents ischemic brain damage via binding to HMGB1. J Am Heart Assoc 11:e024424
Moulin M, Piquereau J, Mateo P, Fortin D, Rucker-Martin C, Gressette M, Lefebvre F, Gresikova M, Solgadi A, Veksler V, Garnier A, Ventura-Clapier R (2015) Sexual dimorphism of doxorubicin-mediated cardiotoxicity: potential role of energy metabolism remodeling. Circ Heart Fail 8:98–108
Myrehaug S, Pintilie M, Tsang R, Mackenzie R, Crump M, Chen Z, Sun A, Hodgson DC (2008) Cardiac morbidity following modern treatment for Hodgkin lymphoma: supra-additive cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin and radiation therapy. Leuk Lymphoma 49:1486–1493
Norton N, Bruno KA, di Florio DN, Whelan ER, Hill AR, Morales-Lara AC, Mease AA, Sousou JM, Malavet JA, Dorn LE, Salomon GR, Macomb LP, Khatib S, Anastasiadis ZP, Necela BM, McGuire MM, Giresi PG, Kotha A, Beetler DJ, Weil RM, Landolfo CK, Fairweather D (2021) Trpc6 promotes doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in male mice with pleiotropic differences between males and females. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:757784
Nteeba J, Ortinau LC, Perfield JW II, Keating AF (2013) Diet-induced obesity alters immune cell infiltration and expression of inflammatory cytokine genes in mouse ovarian and peri-ovarian adipose depot tissues. Mol Reprod Dev 80:948–958
Patel A, Zhang S, Paramahamsa M, Jiang W, Wang L, Moorthy B, Shivanna B (2015) Leflunomide induces pulmonary and hepatic CYP1A enzymes via aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Drug Metab Dispos 43:1966–1970
Pecoraro M, del Pizzo M, Marzocco S, Sorrentino R, Ciccarelli M, Iaccarino G, Pinto A, Popolo A (2016) Inflammatory mediators in a short-time mouse model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 293:44–52
Postmus AC, Kruit JK, Eilers RE, Havinga R, Koster MH, Johmura Y, Nakanishi M, van de Sluis B, Jonker JW (2023) The chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin does not exacerbate p16Ink4a-positive senescent cell accumulation and cardiometabolic disease development in young adult female LDLR-deficient mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 468:116531
Quagliariello V, Vecchione R, Coppola C, di Cicco C, de Capua A, Piscopo G, Paciello R, Narciso V, Formisano C, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Iaffaioli RV, Botti G, Netti PA, Maurea N (2018) Cardioprotective effects of nanoemulsions loaded with anti-inflammatory nutraceuticals against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nutrients 10:1
Rappsilber J, Ishihama Y, Mann M (2003) Stop and go extraction tips for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization, nanoelectrospray, and LC/MS sample pretreatment in proteomics. Anal Chem 75:663–670
Scoumanne A, Cho SJ, Zhang J, Chen X (2011) The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 is regulated by RNA-binding protein PCBP4 via mRNA stability. Nucl Acids Res 39:213–224
Shi W, Sheng X, Dorr KM, Hutton JE, Emerson JI, Davies HA, Andrade TD, Wasson LK, Greco TM, Hashimoto Y, Federspiel JD, Robbe ZL, Chen X, Arnold AP, Cristea IM, Conlon FL (2021) Cardiac proteomics reveals sex chromosome-dependent differences between males and females that arise prior to gonad formation. Dev Cell 56:3019-3034 e7
Smith A, McCulloh R (2015) Hemopexin and haptoglobin: allies against heme toxicity from hemoglobin not contenders. Front Physiol 6:1
Song P, Zhao Q, Zou M-H (2020) Targeting senescent cells to attenuate cardiovascular disease progression. Ageing Res Rev 60:101072
Sun Y, Cui D, Zhang Z, Zhang T, Shi J, Jin H, Ge Z, Ji L, Ding S (2016) Attenuated oxidative stress following acute exhaustive swimming exercise was accompanied with modified gene expression profiles of apoptosis in the skeletal muscle of mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:8381242
Sun T, Zhang L, Feng J, Bao L, Wang J, Song Z, Mao Z, Li J, Hu Z (2022) Characterization of cellular senescence in doxorubicin-induced aging mice. Exp Gerontol 163:111800
Tanaka I, Chakraborty A, Saulnier O, Benoit-Pilven C, Vacher S, Labiod D, Lam EWF, Bièche I, Delattre O, Pouzoulet F, Auboeuf D, Vagner S, Dutertre M (2020) ZRANB2 and SYF2-mediated splicing programs converging on ECT2 are involved in breast cancer cell resistance to doxorubicin. Nucl Acids Res 48:2676–2693
Todorova VK, Beggs ML, Delongchamp RR, Dhakal I, Makhoul I, Wei JY, Klimberg VS (2012) Transcriptome profiling of peripheral blood cells identifies potential biomarkers for doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in a rat model. PLoS ONE 7:e48398
van Almen GC, Swinnen M, Carai P, Verhesen W, Cleutjens JP, D’Hooge J, Verheyen FK, Pinto YM, Schroen B, Carmeliet P, Heymans S (2011) Absence of thrombospondin-2 increases cardiomyocyte damage and matrix disruption in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 51:318–328
Volkova M, Russell R III (2011) Anthracycline cardiotoxicity: prevalence, pathogenesis and treatment. Curr Cardiol Rev 7:214–220
Wagner EF, Nebreda AR (2009) Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 9:537–549
Wang L, Chen Q, Qi H, Wang C, Wang C, Zhang J, Dong L (2016) Doxorubicin-induced systemic inflammation is driven by upregulation of toll-like receptor TLR4 and endotoxin leakage. Cancer Res 76:6631–6642
Wilcox NS, Rotz SJ, Mullen M, Song EJ, Hamilton BK, Moslehi J, Armenian SH, Wu JC, Rhee J-W, Ky B (2022) Sex-specific cardiovascular risks of cancer and its therapies. Circ Res 130:632–651
Wong-Siegel JR, Hayashi RJ, Foraker R, Mitchell JD (2023) Cardiovascular toxicities after anthracycline and VEGF-targeted therapies in adolescent and young adult cancer survivors. Cardiooncology 9:30
Xu Z, Lin S, Wu W, Tan H, Wang Z, Cheng C, Lu L, Zhang X (2008) Ghrelin prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB pathways and mitochondrial protective mechanisms. Toxicology 247:133–138
Xu S, Zhang J, Liu J, Ye J, Xu Y, Wang Z, Yu J, Ye D, Zhao M, Feng Y (2021) The role of interleukin-10 family members in cardiovascular diseases. Int Immunopharmacol 94:107475
Yousefzadeh MJ, Zhao J, Bukata C, Wade EA, McGowan SJ, Angelini LA, Bank MP, Gurkar AU, McGuckian CA, Calubag MF, Kato JI, Burd CE, Robbins PD, Niedernhofer LJ (2020) Tissue specificity of senescent cell accumulation during physiologic and accelerated aging of mice. Aging Cell 19:e13094
Yu LR, Cao Z, Makhoul I, Daniels JR, Klimberg S, Wei JY, Bai JP, Li J, Lathrop JT, Beger RD, Todorova VK (2018) Immune response proteins as predictive biomarkers of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Exp Biol Med (maywood) 243:248–255
Zhang QL, Yang JJ, Zhang HS (2019) Carvedilol (CAR) combined with carnosic acid (CAA) attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by suppressing excessive oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother 109:71–83
Zhang K, Li M, Yin L, Fu G, Liu Z (2020a) Role of thrombospondin-1 and thrombospondin-2 in cardiovascular diseases (review). Int J Mol Med 45:1275–1293
Zhang N, Shou B, Chen L, Lai X, Luo Y, Meng X, Liu R (2020b) Cardioprotective effects of latifolin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by macrophage polarization in mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 75:564–572
Zordoky BN, Radin MJ, Heller L, Tobias A, Matise I, Apple FS, McCune SA, Sharkey LC (2016) The interplay between genetic background and sexual dimorphism of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cardio-Oncology 2:4
Acknowledgements
We thank LeeAnn Higgins, Todd Markowski, and Cesar Anguaya Velasquez in the Center for Metabolomics and Proteomics at the University of Minnesota for providing services related to the generation of quantitative proteomics data. The Orbitrap Eclipse instrumentation platform used in this work was purchased through High-end Instrumentation Grant S10OD028717 from the NIH. Experiments using the NanoDrop 8000 and QuantStudio 5 were performed with staff support at the University of Minnesota Genomics Center. Experiments using the Vevo2100 and Amersham Imager were supported by the resources and staff at the University of Minnesota University Imaging Centers (UIC). SCR_020997. We thank Ms. Engie S. El-Sawaf for her help with western blotting experiments.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Grant R01HL151740 (B.N.Z) and National Cancer Institute, Grant R01CA229618 (R. S. H). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. R.S. H. also receives support from NIH/NCI Grant R01CA204856, the University of Minnesota (UMN) Office of Academic Clinical Affairs (OACA) Faculty Research Development Grant, UMN College of Pharmacy SURRGE award and the UMN OACA Grant-in-Aid Program (GIA) award. I.Y.A. is supported by the Doctoral Dissertation Fellowship (DDF) offered by the University of Minnesota and the Bighley Graduate Fellowship from the College of Pharmacy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, BNZ and IYA; methodology, IYA and MKOG; formal analysis, IYA, BG, YS, and YH; data curation, IYA, MKOG, BG, YS, and YH; writing-original draft preparation, IYA, BG; writing-review and editing, IYA, BG, YH, YS, MKOG, RSH, and BNZ; supervision, BNZ; project administration, MKOG and BNZ; funding acquisition, BNZ. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflcit of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflcit of interest.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Experimental procedures were conducted according to the ethical guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals. All animal procedures in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at the University of Minnesota (Protocol ID: 1807-36187A).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1. Fig. S1
: Hearts were harvested from male and female mice 6 weeks following the administration of 4 mg/kg/week DOX or an equivalent volume of sterile saline for 6 weeks (n = 5–8 per group). Following the extraction of total RNA, the mRNA expression of inflammatory markers, including a Pai-1, b Mcp-1, and c Mmp-13. (DOCX 144 kb)
Supplementary file 2. Online Resource 1
: Proteomics results spreadsheets. (XLSM 769 kb)
Supplementary file 3. Online Resource 2
: Uncropped western blot images for Fig. 8. (PPTX 12715 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelgawad, I.Y., George, B., Grant, M.K.O. et al. Sex-related differences in delayed doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction in C57BL/6 mice. Arch Toxicol 98, 1191–1208 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03678-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03678-y