Abstract
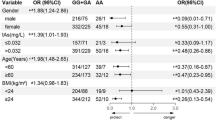
Arsenic is a toxic metal-like element. The toxic reaction of the body to arsenic is related to the ability of arsenic methylation metabolism. As the rate-limiting enzyme of arsenic methylation metabolism, the genetic single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of arsenic (+ 3 oxidation state) methyltransferase (AS3MT) gene are related to capacity of arsenic methylation. In this paper, we investigated the association of five SNPs (rs7085104, rs3740390, 3740393, rs10748835, and rs1046778) in AS3MT with arsenic methylation metabolizing using the data and samples from a cross-sectional case–control study of arsenic and Type 2 diabetes mellitus conducted in Shanxi, China. A total of 340 individuals were included in the study. Urinary total arsenic (tAs, μg/L) was detected by liquid chromatography–atomic fluorescence spectrometry (LC–AFS). According to “safety guidance value of urinary arsenic for population” as specified in WS/T665-2019 (China), participants were divided into the control group (tAs ≤ 32 μg/L, n = 172) and arsenic-exposed group (tAs > 32 μg/L, n = 168). iAs%, MMA%, and DMA% are as the indicator of arsenic methylation capacity. The genotypes of AS3MT SNPs were examined by Multiple PCR combined sequencing. Linear regression analysis showed that AG + GG genotype in rs7085104 was associated with decreased iAs% and increased DMA%. Moreover, AG + AA genotype in rs10748835 and TC + CC genotype in rs1046778 were associated with decreased iAs% and MMA% and increased DMA%. The interaction between rs7085104 and arsenic is associated with iAs% and DMA%. The interaction of rs3740390 and rs10748835 with arsenic is associated with iAs%. Haplotype CTAC (rs3740393-rs3740390-rs10748835-rs1046778) was associated with lower iAs% and higher DMA%, but this association disappeared after adjusting for age, gender, drink, smoking, BMI and tAs. Haplotype GCAC was associated with decreased MMA%. Our study provides additional support for revealing the factors influencing the metabolic capacity of arsenic methylation and might be helpful to identify the population susceptible to arsenic exposure through individualized screening in the future.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [Yanmei Yang], upon reasonable request.
References
Akey J, Jin L, Xiong M (2001) Haplotypes vs single marker linkage disequilibrium tests: what do we gain. Eur J Hum Genet 9(4):291–300. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200619
Argos M, Ahsan H, Graziano JH (2012) Arsenic and human health: epidemiologic progress and public health implications. Rev Environ Health 27(4):191–195. https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh-2012-0021
Bahrami A, Sathyapalan T, Moallem SA, Sahebkar A (2020) Counteracting arsenic toxicity: curcumin to the rescue. J Hazard Mater 400:123160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123160
Bustaffa E, Gorini F, Bianchi F, Minichilli F (2020) Factors affecting arsenic methylation in contaminated italian areas. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145226
Chen QY, Costa M (2021) Arsenic: a global environmental challenge. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 61:47–63. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-030220-013418
Chen YC, Su HJ, Guo YL et al (2003) Arsenic methylation and bladder cancer risk in Taiwan. Cancer Causes Control 14(4):303–310. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1023905900171
Chen JW, Wang SL, Wang YH et al (2012) Arsenic methylation, GSTO1 polymorphisms, and metabolic syndrome in an arseniasis endemic area of southwestern Taiwan. Chemosphere 88(4):432–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.059
Chen Y, Wu F, Liu M et al (2013) A prospective study of arsenic exposure, arsenic methylation capacity, and risk of cardiovascular disease in Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 121(7):832–838. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1205797
de la Rosa R, Steinmaus C, Akers NK et al (2017) Associations between arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase (AS3MT) and N-6 adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase 1 (N6AMT1) polymorphisms, arsenic metabolism, and cancer risk in a chilean population. Environ Mol Mutagen 58(6):411–422. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.22104
Drobná Z, Waters SB, Devesa V, Harmon AW, Thomas DJ, Stýblo M (2005) Metabolism and toxicity of arsenic in human urothelial cells expressing rat arsenic (+3 oxidation state)-methyltransferase. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207(2):147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.12.007
Drobná Z, Martin E, Kim KS et al (2016) Analysis of maternal polymorphisms in arsenic (+3 oxidation state)-methyltransferase AS3MT and fetal sex in relation to arsenic metabolism and infant birth outcomes: Implications for risk analysis. Reprod Toxicol 61:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.02.017
Drobna Z, Xing W, Thomas DJ, Stýblo M (2006) shRNA silencing of AS3MT expression minimizes arsenic methylation capacity of HepG2 cells. Chem Res Toxicol 19(7):894–898. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx060076u
Drobna Z, Naranmandura H, Kubachka KM et al (2009) Disruption of the arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase gene in the mouse alters the phenotype for methylation of arsenic and affects distribution and retention of orally administered arsenate. Chem Res Toxicol 22(10):1713–1720. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx900179r
Engström K, Vahter M, Mlakar SJ et al (2011) Polymorphisms in arsenic(+III oxidation state) methyltransferase (AS3MT) predict gene expression of AS3MT as well as arsenic metabolism. Environ Health Perspect 119(2):182–188. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1002471
Fan C, Zhan Z, Zhang X et al (2022) Research for type 2 diabetes mellitus in endemic arsenism areas in central China: role of low level of arsenic exposure and KEAP1 rs11545829 polymorphism. Arch Toxicol 96(6):1673–1683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03279-1
Gao S, Mostofa MG, Quamruzzaman Q et al (2019) Gene-environment interaction and maternal arsenic methylation efficiency during pregnancy. Environ Int 125:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.042
Gao Yanhui DS, al LZe (2020) Safety guidance value of urinary arsenic for population. National Health Commission PRC
González-Martínez F, Sánchez-Rodas D, Varela NM, Sandoval CA, Quiñones LA, Johnson-Restrepo B (2020) As3MT and GST polymorphisms influencing arsenic metabolism in human exposure to drinking groundwater. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144832
Hernández A, Paiva L, Creus A, Quinteros D, Marcos R (2014) Micronucleus frequency in copper-mine workers exposed to arsenic is modulated by the AS3MT Met287Thr polymorphism. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 759:51–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.09.010
Huang YK, Tseng CH, Huang YL, Yang MH, Chen CJ, Hsueh YM (2007) Arsenic methylation capability and hypertension risk in subjects living in arseniasis-hyperendemic areas in southwestern Taiwan. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 218(2):135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2006.10.022
Huang MC, Douillet C, Su M et al (2017) Metabolomic profiles of arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase knockout mice: effect of sex and arsenic exposure. Arch Toxicol 91(1):189–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1676-0
Kile ML, Hoffman E, Hsueh YM et al (2009) Variability in biomarkers of arsenic exposure and metabolism in adults over time. Environ Health Perspect 117(3):455–460. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.11251
Kuo CC, Howard BV, Umans JG et al (2015) Arsenic exposure, arsenic metabolism, and incident diabetes in the strong heart study. Diabetes Care 38(4):620–627. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-1641
Kuo CC, Moon KA, Wang SL, Silbergeld E, Navas-Acien A (2017) The association of arsenic metabolism with cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes: a systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. Environ Health Perspect 125(8):087001. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP577
Lin S, Shi Q, Nix FB et al (2002) A novel S-adenosyl-L-methionine:arsenic(III) methyltransferase from rat liver cytosol. J Biol Chem 277(13):10795–10803. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110246200
Lin YC, Chen WJ, Huang CY et al (2018) Polymorphisms of arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase and arsenic methylation capacity affect the risk of bladder cancer. Toxicol Sci 164(1):328–338. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfy087
Lindberg AL, Ekström EC, Nermell B et al (2008) Gender and age differences in the metabolism of inorganic arsenic in a highly exposed population in Bangladesh. Environ Res 106(1):110–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2007.08.011
Lis M, Walther D (2016) The orientation of transcription factor binding site motifs in gene promoter regions: does it matter. BMC Genomics 17:185. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2549-x
Loffredo CA, Aposhian HV, Cebrian ME, Yamauchi H, Silbergeld EK (2003) Variability in human metabolism of arsenic. Environ Res 92(2):85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0013-9351(02)00081-6
Lou Q, Guo N, Huang W et al (2022) Association between Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 Gene Polymorphisms and Skeletal Fluorosis of The Brick-tea Type Fluorosis in Tibetans and Kazakhs. China Int J Environ Health Res 32(7):1489–1499. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2021.1892037
Lu R, Gao X, Chen Y et al (2012) Association of an NFKB1 intron SNP (rs4648068) with gastric cancer patients in the Han Chinese population. BMC Gastroenterol 12:87. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-12-87
Melak D, Ferreccio C, Kalman D et al (2014) Arsenic methylation and lung and bladder cancer in a case–control study in northern Chile. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 274(2):225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.11.014
Mendez MA, González-Horta C, Sánchez-Ramírez B et al (2016) Chronic exposure to arsenic and markers of cardiometabolic risk: a cross-sectional study in chihuahua. Mexico Environ Health Perspect 124(1):104–111. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1408742
Ni G, Tan J, Wang M, Ping N, Liu M, He Y (2021) Polymorphisms of the AS3MT gene are associated with arsenic methylation capacity and damage to the P21 gene in arsenic trioxide plant workers. Toxicol Ind Health 37(12):727–736. https://doi.org/10.1177/07482337211013321
Pace C, Smith-Gagen J, Angermann J (2018) Arsenic methylation capacity and metabolic syndrome in the 2013–2014 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010168
Pierce BL, Tong L, Argos M et al (2013) Arsenic metabolism efficiency has a causal role in arsenic toxicity: mendelian randomization and gene-environment interaction. Int J Epidemiol 42(6):1862–1871. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyt182
Revilleza J, Sato M, Irie K, Suda Y, Mizuno T, Irie K (2022) Regulation of CLB6 expression by the cytoplasmic deadenylase Ccr4 through its coding and 3’ UTR regions. PLoS One 17(5):e0268283. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268283
Saintilnord WN, Fondufe-Mittendorf Y (2021) Arsenic-induced epigenetic changes in cancer development. Semin Cancer Biol 76:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.03.019
Schläwicke Engström K, Broberg K, Concha G, Nermell B, Warholm M, Vahter M (2007) Genetic polymorphisms influencing arsenic metabolism: evidence from Argentina. Environ Health Perspect 115(4):599–605. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9734
Stajnko A, Šlejkovec Z, Mazej D et al (2019) Arsenic metabolites; selenium; and AS3MT, MTHFR, AQP4, AQP9, SELENOP, INMT, and MT2A polymorphisms in Croatian–Slovenian population from PHIME-CROME study. Environ Res 170:301–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.11.045
Tseng CH, Huang YK, Huang YL et al (2005) Arsenic exposure, urinary arsenic speciation, and peripheral vascular disease in blackfoot disease-hyperendemic villages in Taiwan. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 206(3):299–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.11.022
Wei B, Yu J, Li H et al (2016) Arsenic metabolites and methylation capacity among individuals living in a rural area with endemic Arseniasis in inner Mongolia. China Biol Trace Elem Res 170(2):300–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0490-5
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the HMU Marshal Initiative Funding (Grant number HMUMIF-21014) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.81830099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MZ:conceptualization, methodology, visualization, writing-original draft. HX: visualization and formal analysis. QL: investigation and formal analysis. ZZ: investigation. FY: investigation. ML: formal analysis. YZ: formal analysis. YY: formal analysis. YG: project administration, funding acquisition. XL: writing review & editing, supervision. YY: writing review & editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
The study was proved by the Harbin Medical University, Center for Endemic Disease Control Ethics Committee (HRBMUECDC 20200317).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Xu, H., Lou, Q. et al. Association between arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase gene polymorphisms and arsenic methylation capacity in rural residents of northern China: a cross-sectional study. Arch Toxicol 97, 2919–2928 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03590-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03590-5