Abstract
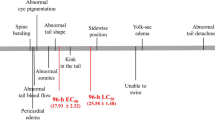
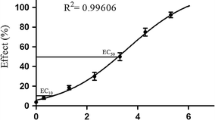
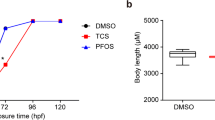
Triclosan (TCS) poses potential risks to reproduction and development due to its endocrine-disrupting properties. However, the mechanism of TCS’s effects on early embryonic development is little known. Embryonic stem cells (ESC) and zebrafish embryos provide valuable models for testing the toxic effects of environmental chemicals on early embryogenesis. In this study, mouse embryonic stem cells (mESC) were acutely exposed to TCS for 24 h, and general cytotoxicity and the effect of TCS on pluripotency were then evaluated. In addition, zebrafish embryos were exposed to TCS from 2- to 24-h post-fertilization (hpf), and their morphology was evaluated. In mESC, alkaline phosphatase staining was significantly decreased after treatment with the highest concentration of TCS (50 μM). Although the expression levels of Sox2 mRNA were not changed, the mRNA levels of Oct4 and Nanog in TCS-treated groups were significantly decreased compared to controls. In addition, the protein levels of Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog were significantly reduced in response to TCS treatment. MicroRNA (miR)-134, an expression inhibitor of pluripotency markers, was significantly increased in TCS-treated mESC. In zebrafish experiments, after 24 hpf of treatment, the controls had developed to the late stage of somitogenesis, while embryos exposed to 300 μg/L of TCS were still at the early stage of somitogenesis, and three genes (Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog) were upregulated in treated groups when compared with the controls. The two models demonstrated that TCS may affect early embryonic development by disturbing the expression of the pluripotency markers (Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog).





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TCS:
-
Triclosan
- mESC:
-
Mouse embryonic stem cells
- hpf:
-
Hour post-fertilization
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5)-Dimethylthiahiazo(-z-y1)-3,5-di-phenytetrazoliumromide
- AP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
References
Adolfsson-Erici M, Pettersson M, Parkkonen J, Sturve J (2002) Triclosan, a commonly used bactericide found in human milk and in the aquatic environment in Sweden. Chemosphere 46(9–10):1485–1489
Allmyr M, Adolfsson-Erici M, McLachlan MS, Sandborgh-Englund G (2006) Triclosan in plasma and milk from Swedish nursing mothers and their exposure via personal care products. Sci Total Environ 372(1):87–93
Aoki T, Takada T (2012) Bisphenol A modulates germ cell differentiation and retinoic acid signaling in mouse ES cells. Reprod Toxicol 34(3):463–470
Balmer NV, Weng MK, Zimmer B, Ivanova VN, Chambers SM, Nikolaeva E, Jagtap S, Sachinidis A, Hescheler J, Waldmann T, Leist M (2012) Epigenetic changes and disturbed neural development in a human embryonic stem cell-based model relating to the fetal valproate syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 21(18):4104–4114
Berry JP, Gantar M, Gibbs PD, Schmale MC (2007) The zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo as a model system for identification and characterization of developmental toxins from marine and freshwater microalgae. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 145(1):61–72
Calafat AM, Ye X, Wong LY, Reidy JA, Needham LL (2008) Urinary concentrations of triclosan in the US population: 2003–2004. Environ Health Perspect 116(3):303–307
Chambers I, Smith A (2004) Self-renewal of teratocarcinoma and embryonic stem cells. Oncogene 23(43):7150–7160
Chan WK, Chan KM (2012) Disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in zebrafish embryo-larvae following waterborne exposure to BDE-47, TBBPA and BPA. Aquat Toxicol 108:106–111
Chandrasekar G, Arner A, Kitambi SS, Dahlman-Wright K, Lendahl MA (2011) Developmental toxicity of the environmental pollutant 4-nonylphenol in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33(6):752–764
Chen R, Chen J, Cheng S, Qin J, Li W, Zhang L, Jiao H, Yu X, Zhang X, Lahn BT, Xiang AP (2010) Assessment of embryotoxicity of compounds in cosmetics by the embryonic stem cell test. Toxicol Mech Methods 20(3):112–118
Crofton KM, Paul KB, Devito MJ, Hedge JM (2007) Short-term in vivo exposure to the water contaminant triclosan: evidence for disruption of thyroxine. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 24(2):194–197
de Esch C, Slieker R, Wolterbeek A, Woutersen R, de Groot D (2012) Zebrafish as potential model for developmental neurotoxicity testing: a mini review. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34(6):545–553
Halden RU, Paull DH (2005) Co-occurrence of triclocarban and triclosan in U.S. water resources. Environ Sci Technol 39(6):1420–1426
Hermsen SA, van den Brandhof EJ, van der Ven LT, Piersma AH (2011) Relative embryotoxicity of two classes of chemicals in a modified zebrafish embryotoxicity test and comparison with their in vivo potencies. Toxicol In Vitro 25(3):745–753
Ishibashi H, Matsumura N, Hirano M, Matsuoka M, Shiratsuchi H, Ishibashi Y, Takao Y, Arizono K (2004) Effects of triclosan on the early life stages and reproduction of medaka Oryzias latipes and induction of hepatic vitellogenin. Aquat Toxicol 67(2):167–179. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2003.12.005
Ivanova N, Dobrin R, Lu R, Kotenko I, Levorse J, DeCoste C, Schafer X, Lun Y, Lemischka IR (2006) Dissecting self-renewal in stem cells with RNA interference. Nature 442(7102):533–538
Jaenisch R, Young R (2008) Stem cells, the molecular circuitry of pluripotency and nuclear reprogramming. Cell 132(4):567–582
Jung EM, Choi KC, Yu FH, Jeung EB (2010) Effects of 17beta-estradiol and xenoestrogens on mouse embryonic stem cells. Toxicol In Vitro 24(6):1538–1545
Kanellopoulou C, Muljo SA, Kung AL, Ganesan S, Drapkin R, Jenuwein T, Livingston DM, Rajewsky K (2005) Dicer-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells are defective in differentiation and centromeric silencing. Genes Dev 19(4):489–501
Kapinas K, Grandy R, Ghule P, Medina R, Becker K, Pardee A, Zaidi SK, Lian J, Stein J, van Wijnen A, Stein G (2013) The abbreviated pluripotent cell cycle. J Cell Physiol 228(1):9–20
Kim SK, Kim BK, Shim JH, Gil JE, Yoon YD, Kim JH (2006) Nonylphenol and octylphenol-induced apoptosis in human embryonic stem cells is related to Fas–Fas ligand pathway. Toxicol Sci 94(2):310–321
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203(3):253–310
Kleinstreuer NC, Smith AM, West PR, Conard KR, Fontaine BR, Weir-Hauptman AM, Palmer JA, Knudsen TB, Dix DJ, Donley EL, Cezar GG (2011) Identifying developmental toxicity pathways for a subset of ToxCast chemicals using human embryonic stem cells and metabolomics. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 257(1):111–121
Lachnit M, Kur E, Driever W (2008) Alterations of the cytoskeleton in all three embryonic lineages contribute to the epiboly defect of Pou5f1/Oct4 deficient MZspg zebrafish embryos. Dev Biol 315(1):1–17
Marson A, Levine SS, Cole MF, Frampton GM, Brambrink T, Johnstone S, Guenther MG, Johnston WK, Wernig M, Newman J, Calabrese JM, Dennis LM, Volkert TL, Gupta S, Love J, Hannett N, Sharp PA, Bartel DP, Jaenisch R, Young RA (2008) Connecting microRNA genes to the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry of embryonic stem cells. Cell 134(3):521–533
Masui S, Nakatake Y, Toyooka Y, Shimosato D, Yagi R, Takahashi K, Okochi H, Okuda A, Matoba R, Sharov AA, Ko MS, Niwa H (2007) Pluripotency governed by Sox2 via regulation of Oct3/4 expression in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol 9(6):625–635
Mitsui K, Tokuzawa Y, Itoh H, Segawa K, Murakami M, Takahashi K, Maruyama M, Maeda M, Yamanaka S (2003) The homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell 113(5):631–642
Moens CB, Prince VE (2002) Constructing the hindbrain: insights from the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 224(1):1–17
Murchison EP, Partridge JF, Tam OH, Cheloufi S, Hannon GJ (2005) Characterization of Dicer-deficient murine embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(34):12135–12140
Niwa H (2007) How is pluripotency determined and maintained? Development 134(4):635–646
Niwa H, Miyazaki J, Smith AG (2000) Quantitative expression of Oct-3/4 defines differentiation, dedifferentiation or self-renewal of ES cells. Nat Genet 24(4):372–376
Oliveira R, Domingues I, Koppe Grisolia C, Soares AM (2009) Effects of triclosan on zebrafish early-life stages and adults. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 16(6):679–688
Orvos DR, Versteeg DJ, Inauen J, Capdevielle M, Rothenstein A, Cunningham V (2002) Aquatic toxicity of triclosan. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(7):1338–1349
Peterson RT, Nass R, Boyd WA, Freedman JH, Dong K, Narahashi T (2008) Use of non-mammalian alternative models for neurotoxicological study. Neurotoxicology 29(3):546–555
Queckenberg C, Meins J, Wachall B, Doroshyenko O, Tomalik-Scharte D, Bastian B, Abdel-Tawab M, Fuhr U (2010) Absorption, pharmacokinetics, and safety of triclosan after dermal administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(1):570–572
Robles V, Marti M, Izpisua Belmonte JC (2011) Study of pluripotency markers in zebrafish embryos and transient embryonic stem cell cultures. Zebrafish 8(2):57–63
Rodriguez PE, Sanchez MS (2010) Maternal exposure to triclosan impairs thyroid homeostasis and female pubertal development in Wistar rat offspring. J Toxicol Environ Health A 73(24):1678–1688
Russell LB, Montgomery CS (1980) Use of the mouse spot test to investigate the mutagenic potential of triclosan (Irgasan DP300). Mutat Res 79(1):7–12
Savatier P, Huang S, Szekely L, Wiman KG, Samarut J (1994) Contrasting patterns of retinoblastoma protein expression in mouse embryonic stem cells and embryonic fibroblasts. Oncogene 9(3):809–818
Schuff M, Siegel D, Philipp M, Bundschu K, Heymann N, Donow C, Knochel W (2012) Characterization of Danio rerio Nanog and functional comparison to Xenopus Vents. Stem Cells Dev 21(8):1225–1238
Shi X, Gu A, Ji G, Li Y, Di J, Jin J, Hu F, Long Y, Xia Y, Lu C, Song L, Wang S, Wang X (2011) Developmental toxicity of cypermethrin in embryo-larval stages of zebrafish. Chemosphere 85(6):1010–1016
Stoker TE, Gibson EK, Zorrilla LM (2010) Triclosan exposure modulates estrogen-dependent responses in the female wistar rat. Toxicol Sci 117(1):45–53
Stummann TC, Hareng L, Bremer S (2008) Embryotoxicity hazard assessment of cadmium and arsenic compounds using embryonic stem cells. Toxicology 252(1–3):118–122
Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B, Rigoutsos I (2008a) MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature 455(7216):1124–1128
Tay YM, Tam WL, Ang YS, Gaughwin PM, Yang H, Wang W, Liu R, George J, Ng HH, Perera RJ, Lufkin T, Rigoutsos I, Thomson AM, Lim B (2008b) MicroRNA-134 modulates the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells, where it causes post-transcriptional attenuation of Nanog and LRH1. Stem Cells 26(1):17–29
Usenko CY, Hopkins DC, Trumble SJ, Bruce ED (2012) Hydroxylated PBDEs induce developmental arrest in zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 262(1):43–51
Vallier L, Pedersen RA (2005) Human embryonic stem cells: an in vitro model to study mechanisms controlling pluripotency in early mammalian development. Stem Cell Rev 1(2):119–130
Veldhoen N, Skirrow RC, Osachoff H, Wigmore H, Clapson DJ, Gunderson MP, Van Aggelen G, Helbing CC (2006) The bactericidal agent triclosan modulates thyroid hormone-associated gene expression and disrupts postembryonic anuran development. Aquat Toxicol 80(3):217–227
Wang J, Rao S, Chu J, Shen X, Levasseur DN, Theunissen TW, Orkin SH (2006) A protein interaction network for pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Nature 444(7117):364–368
Wang Y, Medvid R, Melton C, Jaenisch R, Blelloch R (2007) DGCR8 is essential for microRNA biogenesis and silencing of embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Nat Genet 39(3):380–385
Wilson SW, Brand M, Eisen JS (2002) Patterning the zebrafish central nervous system. Results Probl Cell Differ 40:181–215
Xu C, Fan ZP, Muller P, Fogley R, DiBiase A, Trompouki E, Unternaehrer J, Xiong F, Torregroza I, Evans T, Megason SG, Daley GQ, Schier AF, Young RA, Zon LI (2012) Nanog-like regulates endoderm formation through the Mxtx2-Nodal pathway. Dev Cell 22(3):625–638
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National 973 Program(2012CBA01306); National Science Fund for Outstanding Young Scholars(81322039); National Natural Science Foundation(31371524); Distinguished Young Scholars of Jiangsu Province(BK20130041); New Century Excellent Talents of MOE (NCET-13-0870); Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest with the study or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiaojiao Chen, Bo Xu and Xiumei Han have contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Xu, B., Han, X. et al. The effects of triclosan on pluripotency factors and development of mouse embryonic stem cells and zebrafish. Arch Toxicol 89, 635–646 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1270-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1270-2