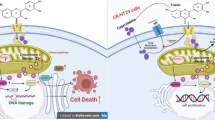
Abstract
Metastases destroy the function of infested organs and are the main reason of cancer-related mortality. Heteronemin, a natural product derived from a marine sponge, was tested in vitro regarding its properties to prevent tumour cell intravasation through the lymph-endothelial barrier. In three-dimensional (3D) cell cultures consisting of MCF-7 breast cancer cell spheroids that were placed on lymph-endothelial cell (LEC) monolayers, tumour cell spheroids induce “circular chemorepellent-induced defects” (CCIDs) in the LEC monolayer; 12(S)-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12(S)-HETE) and NF-κB activity are major factors inducing CCIDs, which are entry gates for tumour emboli intravasating the vasculature. This 3D co-culture is a validated model for the investigation of intravasation mechanisms and of drugs preventing CCID formation and hence lymph node metastasis. Furthermore, Western blot analyses, NF-κB reporter, EROD, SELE, 12(S)-HETE, and adhesion assays were performed to investigate the properties of heteronemin. Five micromolar heteronemin inhibited the directional movement of LECs and, therefore, the formation of CCIDs, which were induced by MCF-7 spheroids. Furthermore, heteronemin reduced the adhesion of MCF-7 cells to LECs and suppressed 12(S)-HETE-induced expression of the EMT marker paxillin, which is a regulator of directional cell migration. The activity of CYP1A1, which contributed to CCID formation, was also inhibited by heteronemin. Hence, heteronemin inhibits important mechanisms contributing to tumour intravasation in vitro and should be tested in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALOX:
-
Lipoxygenase A
- CCIDs:
-
Circular chemorepellent-induced defects
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450
- EMT:
-
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- EROD:
-
Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase
- HUVEC:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cell
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1
- LEC:
-
Lymph-endothelial cell
- MCL2:
-
Myosin light chain 2
- SELE:
-
Selectin E
- 12(S)-HETE 12(S):
-
Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid
References
Carlson RW, Allred DC, Anderson BO, Burstein HJ, Carter WB, Edge SB, Erban JK, Farrar WB, Goldstein LJ, Gradishar WJ, Hayes DF, Hudis CA, Jahanzeb M, Kiel K, Ljung BM, Marcom PK, Mayer IA, McCormick B, Nabell LM, Pierce LJ, Reed EC, Smith ML, Somlo G, Theriault RL, Topham NS, Ward JH, Winer EP, Wolff AC (2009) Breast cancer. Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. NCCN Breast cancer clinical practice guidelines panel. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 7(2):122–192
Cragg GM, Newman DJ, Yang SS (2006) Natural product extracts of plant and marine origin having antileukemia potential. The NCI experience. J Nat Prod 69(3):488–498
Deakin NO, Turner CE (2008) Paxillin comes of age. J Cell Sci 121(15):2435–2444
Digman MA, Brown CM, Horwitz AM, Mantulin WW, Gratton E (2008) Paxillin dynamics measured during adhesion assembly and disassembly by correlation spectroscopy. Biophys J 94(7):2819–2831
Feng J, Masaaki I, Ichikawa K, Isaka N, Nishikawa M, Hartshorne DJ, Nakano T (1999) Inhibitory phosphorylation site for rho-associated kinase on smooth muscle myosin phosphatase. J Cell Biol 274:37385–37390
Folmer F, Jaspars M, Solano G, Cristofanon S, Henry E, Tabudravu J, Black K, Green DH, Küpper FC, Aalbersberg W, Feussner K, Dicato M, Diederich M (2009) The inhibition of TNF-α induced NF-κB activation by marine natural products. Biochem Pharmacol 78:592–606
Giessrigl B, Yazici G, Teichmann M, Kopf S, Ghassemi S, Atanasov AG, Dirsch VM, Grusch M, Jäger W, Özmen A, Krupitza G (2012) Effects of scrophularia extracts on tumor cell proliferation, death and intravasation through lymphendothelial cell barriers. Int J Oncol 40(6):2063–2074
Gridling M, Stark N, Madlener S, Lackner A, Popescu R, Benedek B, Diaz R, Tut FM, Vo NTP, Huber D, Gollinger M, Saiko P, Özmen A, Mosgoeller W, de Martin R, Eytner R, Wagner KH, Grusch M, Fritzer-Szekeres M, Szekeres T, Kopp B, Frisch R, Krupitza G (2009) In vitro anti-cancer activity of two ethno-pharmacological healing plants from Guatemala Pluchea odorata and Phlebodium decumanum. Int J Oncol 34(4):1117–1128
Grusch M, Polgar D, Gfatter S, Leuhuber K, Huettenbrenner S, Leisser C, Fuhrmann G, Kassie F, Steinkellner H, Smid K, Peters GJ, Jayaram H, Klepal T, Szekeres T, Knasmüller S, Krupitza G (2002) Maintenance of ATP favours apoptosis over necrosis triggered by benzamide riboside. Cell Death Differ 9:169–178
Honn KV, Tang DG, Grossi I, Duniec ZM, Timar J, Renaud C, Leithauser M, Blair I, Johnson CR, Diglio CA et al (1994) Tumour cell-derived 12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid induces microvascular endothelial cell retraction. Cancer Res 54:565–574
Huang C, Rajfur Z, Borchers C, Schaller MD, Jacobson K (2003) JNK phosphorylates paxillin and regulates cell migration. Nature 424:219–223
Jiang JG, Ning YG, Chen C, Ma D, Liu ZJ, Yang S, Zhou J, Xiao X, Zhang XA, Edin ML, Card JW, Wang J, Zeldin DC, Wang DW (2007) Cytochrome p450 epoxygenase promotes human cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 67(14):6665–6674
Jianxin AY, Deakin NO, Turner CE (2009) Paxillin-kinase-linker tyrosine phosphorylation regulates directional cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 20(22):4706–4719
Kerjaschki D, Bago-Horvath Z, Rudas M, Sexl V, Schneckenleithner C, Wolbank S, Bartel G, Krieger S, Kalt R, Hantusch B, Keller T, Nagy-Bojarszky K, Huttary N, Raab I, Lackner K, Krautgasser K, Schachner H, Kaserer K, Rezar S, Madlener S, Vonach C, Davidovits A, Nosaka H, Hämmerle M, Viola K, Dolznig H, Schreiber M, Nader A, Mikulits W, Gnant M, Hirakawa S, Detmar M, Alitalo K, Nijman S, Offner F, Maier TJ, Steinhilber D, Krupitza G (2011) Lipoxygenase mediates invasion of intrametastatic lymphatic vessels and propagates lymph node metastasis of human mammary carcinoma xenografts in mouse. J Clin Invest 121(5):2000–2012
Kobayashi M, Okamoto T, Hayashi K, Yokoyama N, Sasaki T, Kitagawa I (1994) Marine natural products. XXXII. Absolute configurations of C-4 of the manoalide family, biologically active sesterterpenes from the marine sponge Hyrtios erecta. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 42(2):265–270
Kretschy N, Teichmann M, Kopf S, Atanasov AG, Saiko P, Vonach C, Viola K, Giessrig B, Huttary N, Raab I, Krieger S, Jäger W, Szekeres T, Nijman SM, Mikulits W, Dirsch VM, Dolznig H, Grusch M, Krupitza G (2013) In vitro inhibition of breast cancer spheroid-induced lymphendothelial defects resembling intravasation into the lymphatic vasculature by acetohexamide, isoxsuprine, nifedipine and proadifen. Br J Cancer 108(3):570–578
Leung HWC, Yang WH, Lai MY, Lin CJ, Lee HZ (2007) Inhibition of 12-lipoxygenase during baicalein-induced human lung nonsmall carcinoma H460 cell apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol 45:403–411
Lu H, Murtagh J, Schwartz EL (2006) The microtubule binding drug laulimalide inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-induced human endothelial cell migration and is synergistic when combined with docetaxel (taxotere). Mol Pharmacol 69(4):1207–1215
Madlener S, Svacinová J, Kitner M, Kopecky J, Eytner R, Lackner A, Vo NTP, Frisch R, Grusch M, de Martin R, Dolezal K, Strnad M, Krupitza G (2009) In vitro anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of extracts of Acalypha alopecuroidea (Euphorbiaceae). Int J Oncol 35(4):881–891
Madlener S, Saiko P, Vonach C, Viola K, Huttary N, Stark N, Popescu R, Gridling M, Vo NT, Herbacek I, Davidovits A, Giessrigl B, Venkateswarlu S, Geleff S, Jäger W, Grusch M, Kerjaschki D, Mikulits W, Golakoti T, Fritzer-Szekeres M, Szekeres T, Krupitza G (2010) Multifactorial anticancer effects of digalloyl-resveratrol encompass apoptosis, cell-cycle arrest, and inhibition of lymphendothelial gap formation in vitro. Br J Cancer 102(9):1361–1370
Nie D, Honn KV (2004) Eicosanoid regulation of angiogenesis in tumors. Semin Thromb Hemost 30:119–125
Nie D, Nemeth J, Qiao Y, Zacharek A, Li L, Hanna K, Tang K, Hillman GG, Cher ML, Grignon DJ, Honn KV (2003) Increased metastatic potential in human prostate carcinoma cells by overexpression of arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase. Clin Exp Metast 20:657–663
Orlowski RZ, Baldwin AS Jr (2002) NF-κB as a therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Mol Med 8(8):385–389
Paulitschke V, Schicher N, Szekeres T, Jäger W, Elbling L, Riemer AB, Scheiner O, Trimurtulu G, Venkateswarlu S, Mikula M, Swoboda A, Fiebiger E, Gerner C, Pehamberger H, Kunstfeld R (2010) 3,3′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexahydroxystilbene impairs melanoma progression in a metastatic mouse model. J Invest Derm 130(6):1668–1679
Rice RL, Tang DG, Hddadi M, Honn KV, Taylor JD (1998) 12(S)-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid increases microfilament content in B16a melanoma cells: a protein kinase-dependent process. Int J Cancer 77:271–278
Schoppmann SF, Soleiman A, Kalt R, Okubo Y, Benisch C, Nagavarapu U, Herron GS, Geleff S (2004) Telomerase-immortalized lymphatic and blood endothelial cells are functionally stable and retain their lineage specificity. Microcirculation 11:261–269
Schumacher M, Cerella C, Eifes S, Chateauvieux S, Morceau F, Jaspars M, Dicato M, and Diederich M (2010) Heteronemin, a spongean sesterterpene, inhibits TNF alpha-induced NF-kappa B activation through proteasome inhibition and induces apoptotic cell death. Biochem Pharmacol 79(4):610–622 Epub. Erratum in: Biochem Pharmacol 2010 79(12):1837
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C (eds) (2009) TNM classification of malignant tumours (Uicc International Union Against Cancer). Wiley-Blackwell, New York
Spector AA, Gordon JA, Moore SA (1988) Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs). Prog Lipid Res 27:271–323
Tang DG, Timar J, Grossi IM, Renaud C, Kimler VA, Diglio CA, Taylor JD, Honn KV (1993) The lipoxygenase metabolite, 12(S)-HETE, induces a protein kinase C-dependent cytoskeletal rearrangement and retraction of microvascular endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 207:361–375
Uchide K, Sakon M, Ariyoshi H, Nakamori S, Tokunaga M, Monden M (2007) Cancer cells cause vascular endothelial cell retraction via 12(S)-HETE secretion; the possible role of cancer cell derived microparticle. Ann Surg Oncol 14:862–868
van Zijl F, Krupitza G, Mikulits W (2011) Initial steps of metastasis: cell invasion and endothelial transmigration. Rev Mutat Res 728(1–2):23–34
Viola K, Kopf S, Huttary N, Vonach C, Kretschy N, Teichmann M, Giessrigl B, Raab I, Stary S, Krieger S, Keller T, Bauer S, Hantusch B, Szekeres T, de Martin R, Jäger W, Mikulits W, Dolznig H, Krupitza G, Grusch M (2013a) Bay11-7082 inhibits the disintegration of the lymphendothelial barrier triggered by MCF-7 breast cancer spheroids; the role of ICAM-1 and adhesion. Br J Cancer 108(3):564–569
Viola K, Kopf S, Rarova L, Jarukamjorn K, Kretschy N, Teichmann M, Vonach C, Atanasov AG, Giessrigl B, Huttary N, Raab I, Krieger S, Strnad M, de Martin R, Saiko P, Szekeres T, Knasmüller S, Dirsch VM, Jäger W, Grusch M, Dolznig H, Mikulits W, Krupitza G (2013b) Xanthohumol attenuates tumor cell-mediated breaching of the lymphoendothelial barrier and prevents intravasation and metastasis. Arch Toxicol [Epub ahead of print]
Vonach C, Viola K, Giessrigl B, Huttary N, Raab I, Kalt R, Krieger S, Vo NTP, Madlener S, Bauer S, Marian B, Hämmerle M, Kretschy N, Teichmann M, Hantusch B, Stary S, Unger C, Seelinger M, Eger A, Mader R, Jäger W, Schmidt W, Grusch M, Dolznig H, Mikulits W, Krupitza G (2011) NF-κB mediates the12(S)-HETE-induced endothelial to mesenchymal transition of lymphendothelial cells during the intravasation of breast carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 105(2):263–271
West KA, Zhang H, Brown MC, Nikolopoulos SN, Riedy MC, Horwitz AF, Turner CE (2001) The LD4 motif of paxillin regulates cell spreading and motility through an interaction with paxillin kinase linker (PKL). J Cell Biol 154(1):161–176
Wonganuchitmeta SN, Yuenyongsawad S, Keawpradub N, Plubrukarn A (2004) Antitubercular sesterterpenes from the Thai sponge Brachiaster sp. J Nat Prod 7(10):1767–1770
Yoshimura R, Matsuyama M, Mitsuhashi M, Takemoto Y, Tsuchida K, Kawahito Y, Sano H, Nakatani T (2004) Relationship between lipoxygenase and human testicular cancer. Int J Mol Med 13:389–393
Zhang JS, Nelson M, Wang L, Liu W, Qian CP, Shridhar V, Urrutia R, Smith DI (1998) Identification and chromosomal localization of CTNNAL1, a novel protein homologous to alpha-catenin. Genomics 54:149–154
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Toni Jäger for preparing the figures and to Prof Ulrichova for kindly providing HUVEC cells. Heteronemin was a kind gift of Professor Marcel Jaspars (University of Aberdeen) and was originally obtained from the NCI open repository. This work was supported by the Austrian Science Fund, FWF, grant number P20905-B13 (to W.M.), and grant numbers S10704-B03 and S10704-B13 (to V.M.D.), by the European Union, FP7 Health Research, project number HEALTH-F4-2008-202047 (to W.M.), further by a grant of the Fellinger foundation (to G.K.), grants of the Herzfelder family foundation (to T.S., H.D., P.S. and M.G.), a grant of the “Hochschuljubilaeumsstiftung der Stadt Wien” grant number H-2498/2011 (to P.S.), a scholarship from the Austrian exchange service OeAD (to K.J.). Grant Agency of the Czech Republic GACR (P505/11/1163) and ED0007/01/01 (to L.R. and M.S) from the Centre of the Region Haná for Biotechnological and Agricultural Research is also gratefully acknowledged.
Conflict of interests
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopf, S., Viola, K., Atanasov, A.G. et al. In vitro characterisation of the anti-intravasative properties of the marine product heteronemin. Arch Toxicol 87, 1851–1861 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1045-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1045-1