Abstract
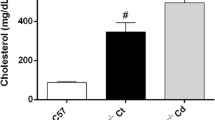
Epidemiological and experimental studies have demonstrated the atherogenic effects of environmental toxicant arsenic and fluoride. Inflammatory mechanism plays an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. The aim of the present study is to determine the effect of chronic exposure to arsenic and fluoride alone or combined on inflammatory response in rabbit aorta. We analyzed the expression of genes involved in leukocyte adhesion [P-selectin (P-sel) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1(VCAM-1)], recruitment and transendothelial migration of leukocyte [interleukin-8 (IL-8) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1)] and those involved in pro-inflammatory cytokines [interleukin-6 (IL-6)]. We found that fluoride and arsenic alone or combined increased the expression of VCAM-1, P-sel, MCP-1, IL-8, and IL-6 at the RNA and protein levels. The gene expressions of inflammatory-related molecules were attenuated when co-exposure to the two toxicants compared with just one of them. We also examined the lipid profile of rabbits exposed to fluoride and (or) arsenic. The results showed that fluoride slightly increased the serum lipids but arsenic decreased serum triglyceride. We showed that inflammatory responses but not lipid metabolic disorder may play a crucial role in the mechanism of the cardiovascular toxicity of arsenic and fluoride.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MF, Ahuja S, Alauddin M, Hug SJ, Lloyd JR, Pfaff A, Pichler T, Saltikov C, Stute M, Van Geen A (2006) Epidemiology. Ensuring safe drinking water in Bangladesh. Science 314:1687–1688
Bhatnagar A (2006) Environmental cardiology: studying mechanistic links between pollution and heart disease. Circ Res 99:692–705
Blankenberg S, Barbaux S, Tiret L (2003) Adhesion molecules and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 170:191–203
Brook RD, Franklin B, Cascio W, Hong Y, Howard G, Lipsett M, Luepker R, Mittleman M, Samet J, Smith SC Jr, Tager I (2004) Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the expert panel on population and prevention science of the American Heart Association. Circulation 109:2655–2671
Chen CJ, Hsueh YM, Lai MS, Shyu MP, Chen SY, Wu MM, Kuo TL, Tai TY (1995) Increased prevalence of hypertension and long-term arsenic exposure. Hypertension 25:53–60
Chen Y, Santella RM, Kibriya MG, Wang Q, Kappil M, Verret WJ, Graziano JH, Ahsan H (2007) Association between arsenic exposure from drinking water and plasma levels of soluble cell adhesion molecules. Environ Health Perspect 115:1415–1420
Cicek E, Aydin G, Akdogan M, Okutan H (2005) Effects of chronic ingestion of sodium fluoride on myocardium in a second generation of rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 24:79–87
Collins RG, Velji R, Guevara NV, Hicks MJ, Chan L, Beaudet AL (2000) P-selectin or intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 deficiency substantially protects against atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Exp Med 191:189–194
Dansky HM, Barlow CB, Lominska C, Sikes JL, Kao C, Weinsaft J, Cybulsky MI, Smith JD (2001) Adhesion of monocytes to arterial endothelium and initiation of atherosclerosis are critically dependent on vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 gene dosage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:1662–1667
Donmez N, Cinar A (2003) Effects of chronic fluorosis on electrocardiogram in sheep. Biol Trace Elem Res 92:115–122
Fan J, Watanabe T (2003) Transgenic rabbits as therapeutic protein bioreactors and human disease models. Pharmacol Ther 99:261–282
Flora SJ, Mittal M, Mishra D (2009) Co-exposure to arsenic and fluoride on oxidative stress, glutathione linked enzymes, biogenic amines and DNA damage in mouse brain. J Neurol Sci 285:198–205
Freni SC (1994) Exposure to high fluoride concentrations in drinking water is associated with decreased birth rates. J Toxicol Environ Health 42:109–121
Hou YC, Hsu CS, Yeh CL, Chiu WC, Pai MH, Yeh SL (2005) Effects of glutamine on adhesion molecule expression and leukocyte transmigration in endothelial cells exposed to arsenic. J Nutr Biochem 16:700–704
Hussain J, Hussain I, Sharma KC (2010) Fluoride and health hazards: community perception in a fluorotic area of central Rajasthan (India): an arid environment. Environ Monit Assess 162:1–14
Kilicalp D, Cinar A, Belge F (2004) Effects of chronic fluorosis on electrocardiogram in dogs. Fluoride 37:96–101
Kim EJ, Park WH, Ahn SG, Yoon JH, Kim SW, Kim SA (2010) 5′-nitro-indirubinoxime inhibits inflammatory response in TNF-alpha stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 211:77–83
Kleemann R, Zadelaar S, Kooistra T (2008) Cytokines and atherosclerosis: a comprehensive review of studies in mice. Cardiovasc Res 79:360–376
Knaapen AM, Curfs DM, Pachen DM, Gottschalk RW, de Winther MP, Daemen MJ, Van Schooten FJ (2007) The environmental carcinogen benzo[a]pyrene induces expression of monocyte-chemoattractant protein-1 in vascular tissue: a possible role in atherogenesis. Mutat Res 621:31–41
Kraugerud M, Zimmer KE, Ropstad E, Verhaegen S (2011) Perfluorinated compounds differentially affect steroidogenesis and viability in the human adrenocortical carcinoma (H295R) in vitro cell assay. Toxicol Lett 205:62–68
Kumar N, Sood S, Singh M, Makkar B, Sharma S (2010) Effects of sodium fluoride on the electrocardiogram of male rabbits. Fluoride 43:124–127
Kwok RK (2007) A review and rationale for studying the cardiovascular effects of drinking water arsenic in women of reproductive age. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222:344–350
Lee MY, Bae ON, Chung SM, Kang KT, Lee JY, Chung JH (2002) Enhancement of platelet aggregation and thrombus formation by arsenic in drinking water: a contributing factor to cardiovascular disease. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 179:83–88
Lemaire M, Lemarie CA, Flores MM, Schiffrin EL, Lehoux S, Mann KK (2011) Exposure to moderate arsenic concentrations increases atherosclerosis in apoE−/− mouse model. Toxicol Sci 122:211–221
Libby P (2002) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420:868–874
Liu YJ, Gao Q, Wu CX, Guan ZZ (2010) Alterations of nAChRs and ERK1/2 in the brains of rats with chronic fluorosis and their connections with the decreased capacity of learning and memory. Toxicol Lett 192:324–329
Mittal M, Flora SJ (2006) Effects of individual and combined exposure to sodium arsenite and sodium fluoride on tissue oxidative stress, arsenic and fluoride levels in male mice. Chem Biol Interact 162:128–139
Molenaar TJ, Twisk J, de Haas SA, Peterse N, Vogelaar BJ, Van Leeuwen SH, Michon IN, Van Berkel TJC, Kuiper J, Biessen EA (2003) P-selectin as a candidate target in atherosclerosis. Biochem Pharmacol 66:859–866
O’Brien KD, McDonald TO, Chait A, Allen MD, Alpers CE (1996) Neovascular expression of E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in human atherosclerosis and their relation to intimal leukocyte content. Circulation 93:672–682
Pope CA III, Burnett RT, Thurston GD, Thun MJ, Calle EE, Krewski D, Godleski JJ (2004) Cardiovascular mortality and long-term exposure to particulate air pollution: epidemiological evidence of general pathophysiological pathways of disease. Circulation 109:71–77
Profumo E, Buttari B, Tosti ME, Siracusano A, Ortona E, Margutti P, Capoano R, Salvati B, Rigano R (2008) Association of intracellular pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood with the clinical or ultrasound indications for carotid endarterectomy in patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol 152:120–126
Rocha RA, Gimeno-Alcaniz JV, Martin-Ibanez R, Canals JM, Velez D, Devesa V (2011) Arsenic and fluoride induce neural progenitor cell apoptosis. Toxicol Lett 203:237–244
Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340:115–126
Simeonova PP, Hulderman T, Harki D, Luster MI (2003) Arsenic exposure accelerates atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E (−/−) mice. Environ Health Perspect 111:1744–1748
Song AH, Wang TY, Jiang CY, Zhang ZB, Wang ZS (1990) Observations on fluorotic aorta sclerosis by two dimensional echo cardiography. Endem Dis Bull 5:91–94
Srivastava S, Vladykovskaya EN, Haberzettl P, Sithu SD, D’Souza SE, States JC (2009) Arsenic exacerbates atherosclerotic lesion formation and inflammation in apoE−/− mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 241:90–100
Sun G (2004) Arsenic contamination and arsenicosis in China. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:268–271
Tseng WP (1977) Effects and dose–response relationships of skin cancer and blackfoot disease with arsenic. Environ Health Perspect 19:109–119
Tuncel E (1984) The incidence of moenckeberg calcification in patients with endemic fluorosis. Fluoride 17:4–8
Vestweber D, Blanks JE (1999) Mechanisms that regulate the function of the selectins and their ligands. Physiol Rev 79:181–213
Viswanathan G, Gopalakrishnan S, Siva IS (2010) Assessment of water contribution on total fluoride intake of various age groups of people in fluoride endemic and non-endemic areas of Dindigul district, Tamil Nadu, South India. Water Res 44:6186–6200
Wang SX, Wang ZH, Cheng XT, Li J, Sang ZP, Zhang XD, Han LL, Qiao XY, Wu ZM, Wang ZQ (2007) Arsenic and fluoride exposure in drinking water: children’s IQ and growth in Shanyin county, Shanxi province, China. Environ Health Perspect 115:643–647
Yang J, Li J, Sun T (2003) The characterization of the blood lipid spectrum in subchronic arsenic poisoning rats and it’s mechanism. Chin J Endemiol 22:107–110
Zheng S, Qian Z, Tang F, Sheng L (2005) Suppression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression by crocetin contributes to attenuation of atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Biochem Pharmacol 70:1192–1199
Zheng Y, Wu J, Ng JC, Wang G, Lian W (2002) The absorption and excretion of fluoride and arsenic in humans. Toxicol Lett 133:77–82
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China National Natural Science Foundation (31172376, 31072180 and 31001089).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Niu, R., Sun, Z. et al. Inflammatory responses induced by fluoride and arsenic at toxic concentration in rabbit aorta. Arch Toxicol 86, 849–856 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0803-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0803-9