Abstract
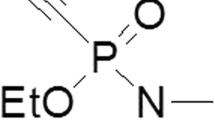
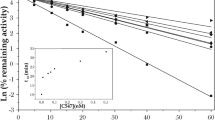
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is the primary target of organophosphorus compounds (OP). The investigation into interactions between AChE, OP and oximes in vitro may be affected by the experimental conditions, e.g. by the buffer system. Hence, it was tempting to investigate the Michaelis–Menten kinetics and the inhibition and reactivation kinetics of paraoxon-ethyl, sarin, soman and VX in the presence of phosphate, MOPS, Tyrode and TRIS buffer with human AChE. Compared to phosphate buffer, the inhibition and reactivation kinetics of human erythrocyte AChE were markedly changed by TRIS and in part by MOPS, whereas Tyrode showed similar results to phosphate buffer. These results indicate an effect of the tested buffers on the properties of AChE, and an interaction between OP and oximes has to be considered for the design of in vitro studies and may impair the comparison of data from different laboratories. In view of the comparability of human in vitro kinetic data determined with phosphate buffer with data from human OP poisoning, it seems to be a suitable buffer for the investigation into interactions between AChE, OP and oximes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Jafari AA, Kamal MA (1996) Optimization and kinetic studies of human erythrocyte membrane- bound acetylcholinesterase. Biochem Mol Biol Int 38:577–586
Aurbek N, Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P, Worek F (2006) Analysis of inhibition, reactivation and aging kinetics of highly toxic organophosphorus compounds with human and pig acetylcholinesterase. Toxicology 224:91–99
Brestkin AP, Vyaz’menskaya MM, Maizel EB (1978) Influence of Triton X-100 on the properties of acetylcholinesterase from human erythrocytes. Biokhimiia 43:94–99
Chow CM, Islam MF (1970) Colorimetric determination of red blood cell acetylcholinesterase activity. Clin Biochem 3:295–306
Davies DR, Green AL (1956) The kinetics of reactivation, by oximes, of cholinesterase inhibited by organophosphorus compounds. Biochem J 63:529–535
Dawson RM, Crone HD (1973) Inorganic ion effects on the kinetic parameters of acetylcholinesterase. J Neurochem 21:247–249
de Jong LPA, Verhagen AAV, Langenberg JP, Hagedorn I, Löffler M (1989) The bispyridinium-dioxime HLö-7: a potent reactivator for acetylcholinesterase inhibited by the stereoisomers of tabun and soman. Biochem Pharmacol 38:633–640
Debord J, Harel M, Verneuil B, Bollinger JC, Dantoine TF (2009) Microcalorimetric study of the inhibition of butyrylcholinesterase by paraoxon. Anal Biochem 389:97–101
Dodge JT, Mitchell C, Hanahan DJ (1963) The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 100:119–130
Eddleston M, Karalliedde L, Buckley N, Fernando R, Hutchinson G, Isbister G, Konradsen F, Murray D, Piola JC, Senanayake N, Sheriff R, Singh S, Siwach SB, Smit L (2002) Pesticide poisoning in the developing world—a minimum pesticides list. Lancet 360:1163–1167
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Anders V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Eyer P (2003) The role of oximes in the management of organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. Toxicol Rev 22:165–190
Eyer P, Worek F, Kiderlen D, Sinko G, Stuglin A, Simeon-Rudolf V, Reiner E (2003) Molar absorption coefficients for the reduced Ellman reagent: reassessment. Anal Biochem 312:224–227
Eyer F, Worek F, Eyer P, Felgenhauer N, Haberkorn M, Zilker T, Thiermann H (2009) Obidoxime in acute organophosphate poisoning: 1—clinical effectiveness. Clin Toxicol 47:798–806
Forsberg A, Puu G (1984) Kinetics for the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase from the electric eel by some organophosphates and carbamates. Eur J Biochem 140:153–156
Grob D (1956) The manifestations and treatment of poisoning due to nerve gas and other organic phosphate anticholinesterase compounds. Arch Intern Med 98:221–239
Hanke DW, Nelson ME, Baskin SI (1991) Cardiotonic drugs inhibit purified mammalian acetylcholinesterase. J Appl Toxicol 11:119–124
Herkert N, Eckert S, Eyer P, Bumm R, Weber G, Thiermann H, Worek F (2008) Identical kinetics of human erythrocyte and muscle acetylcholinesterase with respect to carbamate pre-treatment, residual activity upon soman challenge and spontaneous reactivation after withdrawal of the inhibitors. Toxicology 246:188–192
Kassa J, Cabal J (1999) A comparison of the efficacy of acetylcholinesterase reactivators cyclohexyl methylphosphonofluoridate (GF agent) by in vitro and in vivo methods. Pharmacol Toxicol 84:41–45
Keijer JH, Wolring GZ, de Jong LPA (1974) Effect of pH, temperature and ionic strength on the aging of phosphonylated cholinesterases. Biochim Biophys Acta 334:146–155
Kitz RJ, Ginsburg S, Wilson IB (1965) Activity-structure relationships in the reactivation of diethylphosphoryl acetylcholinesterase by phenyl-1-methyl pyridinium ketoximes. Biochem Pharmacol 14:1471–1477
Kovarik Z, Calic M, Sinko G, Bosak A, Berend S, Vrdoljak AL, Radic B (2008) Oximes: reactivators of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase and antidotes in therapy against tabun poisoning. Chem Biol Interact 175:173–179
Kuçukkilinç TT, Ozer I (2008) Inhibition of electric eel acetylcholinesterase by triarylmethane dyes. Chem Biol Interact 175:309–311
Luo C, Tong M, Chilukuri N, Brecht K, Maxwell DM, Saxena A (2007) An in vitro comparative study on the reactivation of nerve agent-inhibited guinea pig and human acetylcholinesterases by oximes. Biochemistry 46:11771–11779
Mahler HR (1961) The use of amine buffers in studies with enzymes. Ann NY Acad Sci 92:426–439
Massoulie J, Pezzementi L, Bon S, Krejci E, Vallette FM (1993) Molecular and cellular biology of cholinesterases. Prog Neurobiol 41:31–91
Mendel B, Rudney H (1945) Some effects of salts on true cholinesterase. Science 102:616–617
Pavlic M (1967) The inhibitory effect of TRIS on the activity of cholinesterases. Biochim Biophys Acta 139:133–137
Saxena A, Doctor BP, Maxwell DM, Lenz DE, Radic Z, Taylor P (1993) The role of glutamate-199 in the aging of cholinesterase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197:343–349
Seeger T, Worek F, Szinicz L, Thiermann H (2007) Reevaluation of indirect field stimulation technique to demonstrate oxime effectiveness in OP-poisoning in muscles in vitro. Toxicology 233:209–213
Shih TM (1993) Comparison of several oximes on reactivation of soman-inhibited blood, brain and tissue cholinesterase activity in rats. Arch Toxicol 67:637–646
Sidell FR, Takafuji ET, Franz DR (1997) Medical aspects of chemical and biological warfare. Borden Institute, Washington DC
Taylor P, Radic Z (1994) The cholinesterases: from genes to proteins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 34:281–320
Taylor P, Radic Z, Hosca NA, Camp S, Marchot P, Berman HA (1995) Structural basis for the specificity of cholinesterase catalysis and inhibition. Toxicol Lett 82–83:453–458
Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer F, Worek F, Eyer P, Felgenhauer N, Zilker T (1999) Modern strategies in therapy of organophosphate poisoning. Toxicol Lett 107:233–239
Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P, Zilker T, Worek F (2005) Correlation between red blood cell acetylcholinesterase activity and neuromuscular transmission in organophosphate poisoning. Chem Biol Interact 157–158:345–347
Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P, Felgenhauer N, Zilker T, Worek F (2007) Lessons to be learnt from organophosphorus pesticide poisoning for the treatment of nerve agent poisoning. Toxicology 233:145–154
Thiermann H, Worek F, Eyer P, Eyer F, Felgenhauer N, Zilker T (2009) Obidoxime in acute organophosphate poisoning: 2—PK/PD relationships. Clin Toxicol 47:807–813
Worek F, Diepold C, Eyer P (1999a) Dimethylphosphoryl-inhibited human cholinesterases: inhibition, reactivation, and aging kinetics. Arch Toxicol 73:7–14
Worek F, Mast U, Kiderlen D, Diepold C, Eyer P (1999b) Improved determination of acetylcholinesterase activity in human whole blood. Clin Chim Acta 288:73–90
Worek F, Reiter G, Eyer P, Szinicz L (2002) Reactivation kinetics of acetylcholinesterase from different species inhibited by highly toxic organophosphates. Arch Toxicol 76:523–529
Worek F, Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P (2004) Kinetic analysis of interactions between human acetylcholinesterase, structurally different organophosphorus compounds and oximes. Biochem Pharmacol 68:2237–2248
Worek F, Koller M, Thiermann H, Szinicz L (2005) Diagnostic aspects of organophosphate poisoning. Toxicology 214:182–189
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to T. Hannig and L. Windisch for skillful technical assistance.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wille, T., Thiermann, H. & Worek, F. Effect of different buffers on kinetic properties of human acetylcholinesterase and the interaction with organophosphates and oximes. Arch Toxicol 85, 193–198 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0578-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0578-9