Abstract
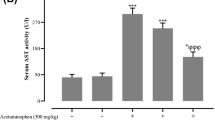
We have addressed in the current study the postulate whether or not carnitine deficiency would represent a risk factor in hepatotoxicity. Carnitine-deficient male Swiss albino rats were obtained following administration of d-carnitine (500 mg/kg, IP) for 10 consecutive days. Serum and liver carnitine levels, both total and free, were assessed to confirm carnitine depletion. Hepatotoxicity was induced by challenging animals with a single dose of paracetamol (1 g/kg, IP). Serum tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) concentration, and serum activities of aspartate amino transferase (AST), alanine amino transferase (ALT) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were undertaken as biomarkers for toxicity. Liver contents of reduced glutathione (GSH), malondialdehyde (MDA), total nitric oxide (NO) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activities were also investigated. Histopathological examination of liver sections was achieved to confirm the biochemical alterations. d-carnitine altered all biochemical markers and also induced mild tissue inflammation with dilatation and congestion of central and portal veins. Paracetamol produced an obvious hepatotoxicity model that was well characterized biochemically and morphologically. Combined administration of d-carnitine and paracetamol synergistically provoked marked toxicity that was more profound than either agent given alone. The present work was further extended to elucidate any hepatoprotective effect of carnitine supplementation in such toxicity paradigm. It was apparent that l-carnitine notably ameliorated all biochemical markers and also mitigated the gross histologic alterations induced by paracetamol. Data obtained so far would suggest that carnitine deficiency could possibly be a sequela as well as a causative clue for paracetamol hepatotoxicity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Salam OM, Baiuomy AR, El-Shenawy SM, Hassan NS (2005) Effect of pentoxifylline on hepatic injury caused in the rat by the administration of carbon tetrachloride or acetaminophen. Pharmacol Rep 57(5):596–603
Abdel-Zaher AO, Abdel-Rahman MM, Hafez MM, Omran FM (2007) Role of nitric oxide and reduced glutathione in the protective effects of aminoguanidine, gadolinium chloride and oleanolic acid against acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal damage. Toxicology 234(1–2):124–134
Al-Majed AA (2007) Carnitine deficiency provokes cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 100(3):145–150
Al-Majed AA, Sayed-Ahmed MM, Al-Yahya AA, Aleisa AM, Al-Rejaie SS, Al-Shabanah OA (2006) Propionyl-l-carnitine prevents the progression of cisplatin-induced cardiomyopathy in a carnitine-depleted rat model. Pharmacol Res 53(3):278–286
Arrigoni-Martelli E, Caso V (2001) Carnitine protects mitochondria and removes toxic acyls from xenobiotics. Drugs Exp Clin Res 27(1):27–49
Bourdi M, Masubuchi Y, Reilly TP, Amouzadeh HR, Martin JL, George JW, Shah AG, Pohl LR (2002) Protection against acetaminophen-induced liver injury and lethality by interleukin 10: role of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Hepatology 35:289–298
Broderick TL (2006) Hypocarnitinaemia induced by sodium pivalate in the rat is associated with left ventricular dysfunction and impaired energy metabolism. Drugs R D 7(3):153–161
Bykov I, Järveläinen H, Lindros K (2003) l-carnitine alleviates alcohol-induced liver damage in rats: role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Alcohol 38(5):400–406
Carter LA, Abney TO, Lapp DF (1995) Biosynthesis and metabolism of carnitine. J Child Neurol 10:(2S)3–7.
Chaturvedi P, Machacha CN (2007) Efficacy of Raphanus sativus in the treatment of paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in albino rats. Br J Biomed Sci 64(3):105–108
DeVivo DC (2002) Effect of l-carnitine treatment for valproate-induced hepatotoxicity. Neurology 58(3):507–508
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 74:214–226
Yen FL, Wu TH, Lt Lin, Lin C (2007) Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Cuscuta chinensis against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 111(1):123–128
Grypioti AD, Theocharis SE, Demopoulos CA, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z, Basayiannis AC, Mykoniatis MG (2006) Effect of platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor antagonist (BN52021) on acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury and regeneration in rats. Liver Int 26(1):97–105
Grypioti AD, Mykoniatis M, Demopoulos CA, Kostopanagiotou G (2007) Recombinant platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase attenuates paracetamol-induced liver oxidative stress, injury, and regeneration. Dig Dis Sci 52(1):192–199
Hartz AL (1947) Simultaneous histologic fixation and gross demonstration of calcification. Am J Clin Pathol 17:750–755
Hinson JA, Reid AB, McCullough SS, James LP (2004) Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: role of metabolic activation, reactive oxygen/nitrogen species, and mitochondrial permeability transition. Drug Metab Rev 36(3–4):805–822
Jaeschke H, Gores GJ, Cederbaum AI, Hinson JA, Pessayre D, Lemasters JJ (2002) Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. ToxIcol Sci 65:166–176
James LP, Mayeux PR, Hinson JA (2003) Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Dispos 31:1499–1506
Kaplowitz N (2004) Acetaminophen hepatoxicity: what do we know, what don’t we know, and what do we do next? Hepatology 40(1):23–26
Karakoç E, Erdem S, Sökmensüer C, Kansu T (2006) Encephalopathy due to carnitine deficiency in an adult patient with gluten enteropathy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108(8):794–797
Kato A, Gabay C, Okaya T, Lentsch AB (2002) Specific role of interleukin-1 in hepatic neutrophil recruitment after ischemia/reperfusion. Am J Pathol 161(5):1797–1803
Klein B, Read PA, Babson AL (1960) Rapid method for the quantitative determination of serum alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chem 6:269–275
Laskin DL, Gardner CR, Price VF, Jollow DJ (1995) Modulation of macrophage functioning abrogates the acute hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen. Hepatology 21:1045–1050
Lee WM (2004) Acetaminophen and the U.S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group: lowering the risks of hepatic failure. Hepatology 40(1):6–9
Longo N, Amat Di San Filippo C, Pasquali M (2006) Disorders of carnitine transport and the carnitine cycle. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 142(2):77–85
LoVecchio F, Shriki J, Samaddar R (2005) L-carnitine was safely administered in the setting of valproate toxicity. Am J Emerg Med 23(3):321–322
Maddrey WC (2005) Drug-induced hepatotoxicity. J Clin Gastroenterol 39:S83–S89
Mahadevan SB, McKiernan PJ, Davies P, Kelly DA (2006) Paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch Dis Child 91(7):598–603
Manktelow A, Meyer A (1986) Lack of correlation between decreases chemotaxis and susceptibility to infection in burned rats. J Trauma 26:143–148
Miranda KM, Espey MG, Wink DA (2001) A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide 5(1):62–71
Moreno FA, Macey H, Schriber B (2005) Carnitine levels in valproic acid-treated psychiatric patients: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Psychiatry 66(5):555–558
Nezu J, Tamai I, Oku A, Ohashi R, Yabuuchi H, Hashimoto N, Nikaido H, Sai Y, Koizumi A, Shoji Y, Takada G, Matsuishi T, Yoshino M, Kato H, Ohura T, Tsujimoto G, Hayakawa J, Shimane M, Tsuji A (1999) Primary systemic carnitine deficiency is caused by mutations in a gene encoding sodium ion-dependent carnitine transporter. Nat Genet 21(1):91–4
Pastorino JG, Snyder JW, Serroni A, Hoek JB, Farber JL (1993) Cyclosporin and carnitine prevent the anoxic death of cultured hepatocytes by inhibiting the mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem 268(19):13791–13798
Pons R, De Vivo DC (1995) Primary and secondary carnitine deficiency syndromes. J Child Neurol 10(Suppl. 2):S8–S24
Potter WZ, Davis DC, Mitchell JR, Jollow DJ, Gillette JR, Brodie BB (1973) Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. 3. Cytochrome P-450-mediated covalent binding in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 187(1):203–210
Prieto JA, Andrade F, Aldámiz-Echevarría L, Sanjurjo P (2006) Determination of free and total carnitine in plasma by an enzymatic reaction and spectrophotometric quantitation spectrophotometric determination of carnitine. Clin Biochem 39(10):1022–1027
Raghavendran HB, Sathivel A, Devaki T (2006) Defensive nature of Sargassum polycystum (Brown alga) against acetaminophen-induced toxic hepatitis in rats: role of drug metabolizing microsomal enzyme system, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and fate of liver cell structural integrity. World J Gastroenterol 12(24):3829–3834
Reitman A, Frankel S (1957) The determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol 28:56–63
Rinaldo P, Matern D (2002) Fatty acid oxidation disorders. Annu Rev Physiol 64:477–502
Roberts RA, Ganey PE, Ju C, Kamendulis LM, Rusyn I, Klaunig JE (2007) Role of the Kupffer Cell in Mediating Hepatic Toxicity and Carcinogenesis. Tox Sci 96(1):2–15
Rubio-Gozalbo ME, Bakker JA, Waterham HR, Wanders RJ (2004) Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency, clinical, biochemical and genetic aspects. Mol Aspects Med 25(5–6):521–532
Rumack BH (2004) Acetaminophen misconceptions. Hepatology. 40(1):10–15
Sayed-Ahmed MM, Eissa MA, Kenawy SA, Mostafa N, Calvani M, Osman AM (2004) Progression of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in a carnitine-depleted rat model. Chemotherapy 50(4):162–170
Sener G, Ekşioğlu-Demiralp E, Cetiner M, Ercan F, Sirvanci S, Gedik N, Yeğen BC (2006) L-Carnitine ameliorates methotrexate-induced oxidative organ injury and inhibits leukocyte death. Cell Biol Toxicol 22(1):47–60
Spasov AA, Iezhitsa IN (2005) Stereopharmacology of carnitine. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova 91(12):1469–1480
Spasov AA, Iezhitsa IN, Pisarev VB, Snigur GL, Kravchenko MS (2006) Changes in myocardium, skeletal muscle and liver of rats fed carnitine-deficient diet and treated with carnitine optical isomers. Morfologiia 129(3):48–52
Stanley CA (2004) Carnitine deficiency disorders in children, Ann NY Acad Sci 1033:42–51
Toklu HZ, Sehirli AO, Velioğlu-Oğünç A, Cetinel S, Sener G (2006) Acetaminophen-induced toxicity is prevented by beta-D-glucan treatment in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 543(1–3):133–140
Túnez I, Muñoz MC, Medina FJ, Salcedo M, Feijóo M, Montilla P (2007) Comparison of melatonin, vitamin E and l-carnitine in the treatment of neuro- and hepatotoxicity induced by thioacetamide. Cell Biochem Funct 25(2):119–127
Uchiyama M, Mihara K (1978) Determination of malondialdehyde precursor in tissue by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278
Winterbourn CC, Brennan SO (1997) Characterization of the oxidation products of the reaction between reduced glutathione and hypochlorous acid. Biochem J 326:87–92
Woldseth B, Rootwelt T (2006) Mitochondrial beta-oxidation defects. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 126(6):756–759
Wolters G, Kuijpers LP, Kacaki J, Shuurs AH (1977) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for hepatitis B surface antigen. J Infect Dis 136:S311–S317
Yapar K, Kart A, Karapehlivan M, Atakisi O, Tunca R, Erginsoy S, Citil M (2007) Hepatoprotective effect of l-carnitine against acute acetaminophen toxicity in mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol 59(2):121–128
Yemitan OK, Izegbu MC (2006) Protective effects of Zingiber officinale (Zingiberaceae) against carbon tetrachloride and acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Phytother Res 20(11):997–1002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arafa, H.M.M. Carnitine deficiency: a possible risk factor in paracetamol hepatotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 83, 139–150 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0330-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0330-x