Abstract.
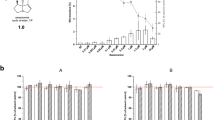
Previous investigations in the rat have shown that the non-provitamin A carotenoid astaxanthin is metabolized into 3-hydroxy-4-oxo-β-ionone and 3-hydroxy-4-oxo-7,8-dihydro-β-ionone and, in addition, is a potent CYP1A gene inducer. Here we investigated the metabolism of this compound as well as its capacity to induce CYP genes in primary cultures of human hepatocytes. Free metabolites of 14C-astaxanthin produced in this cellular model were purified by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) and identified by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyses as 3-hydroxy-4-oxo-β-ionol and 3-hydroxy-4-oxo-β-ionone. In addition, deconjugation of polar compounds by glusulase and further analyses with HPLC and GC-MS revealed four radiolabeled metabolites including: 3-hydroxy-4-oxo-β-ionol, 3-hydroxy-4-oxo-β-ionone, and their reduced forms, 3-hydroxy-4-oxo-7,8-dihydro-β-ionol and 3-hydroxy-4-oxo-7,8-dihydro-β-ionone. The same four metabolites were identified in human plasma from two volunteers who had orally taken 100 mg astaxanthin 24 h before blood collection. In cultured hepatocytes, astaxanthin was a significant inducer of the major cytochrome P450 enzyme, CYP3A4 as well as of CYP2B6, but not of other CYPs, including those from CYP1A and CYP2C families. The lack of autoinduction of astaxanthin metabolism in human hepatocytes suggests that neither CYP3A4 nor CYP2B6 contribute to the formation of metabolites. We conclude that metabolism of astaxanthin and its CYP-inducing capacity are different in humans and in rats. The novel methodology used in our studies could be extended to evaluating the role of metabolites of more important carotenoids such as β-carotene in differentiation and carcinogenicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kistler, A., Liechti, H., Pichard, L. et al. Metabolism and CYP-inducer properties of astaxanthin in man and primary human hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 75, 665–675 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-001-0287-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-001-0287-5