Abstract
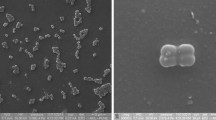
A Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped, spore-forming bacterium, designated NE201T, was isolated from a freshwater pond in Village Nerur, India. Growth was observed in the range of 15–45 °C temperature with optimum at 30 °C, pH range of 5–9 (optimum at 7.0), and at concentrations of NaCl ranging between 0 and 14% (optimum 0%, w/v). The 16S rRNA gene sequence showed the highest similarity with Fictibacillus enclensis NIO-1003T (JF893461) at 99.01% followed by F. rigui WPCB074T (EU939689) at 98.9% and F. solisalsi CGMCC 1.6854T (EU046268) at 98.66%. The digital DNA–DNA hybridization (dDDH) and orthoANI values for strain NE201T against F. enclensis NIO-1003T (GCA_900094955.1) were 33.7% and 87.68%, respectively. The phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene, 92 core genes derived from the genome, and 20 proteins involving over 20,236 amino acid positions revealed the distinct phylogenetic position of strain NE201T and the formation of a clearly defined monophyletic clade with F. enclensis. The strain NE201T showed a unique carbon utilization and assimilation pattern that differentiated it from F. enclensis NIO-1003T. The major fatty acids were anteiso -C15:0 (51.42%) and iso-C15:0 (18.88%). The major polar lipids were phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE, and diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG). The antiSMASH analyzed genome of NE201T highlighted its diverse biosynthetic potential, unveiling regions associated with terpene, non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS), lassopeptides, NI-siderophores, lanthipeptides (LAP), and Type 3 Polyketide Synthases (T3PKS). The overall phenotypic, genotypic, and chemotaxonomic characters strongly suggested that the strain NE201T represents a novel species of genus Fictibacillus for which the name Fictibacillus fluitans sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is NE201T (= MCC 5285 = JCM 36474).


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the reference 16S rRNA gene sequences of the strain NE201T is OR234369 and the draft genome is NZ_JAUHTR000000000.1.
References
Ahmed I, Yokota A, Yamazoe A, Fujiwara T (2007) Proposal of Lysinibacillus boronitolerans gen. nov. sp. nov., and transfer of Bacillus fusiformis to Lysinibacillus fusiformis comb. nov. and Bacillus sphaericus to Lysinibacillus sphaericus comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1117–1125
Auch AF, von Jan M, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2010) Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand Genomic Sci 2:117–134
Baker GC, Smith JJ, Cowan DA (2003) Review and re-analysis of domain-specific 16S primers. J Microbiol Methods 55:541–555
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Blin K, Shaw S, Augustijn HE, Reitz ZL, Biermann F, Alanjary M et al (2023) antiSMASH 7.0: New and improved predictions for detection, regulation, chemical structures and visualisation. Nucleic Acids Res gkad344 51(W1):W46–W50. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad344
Brown J, Pirrung M, McCue LA (2017) FQC Dashboard: integrates FastQC results into a web-based, interactive, and extensible FASTQ quality control tool. Bioinformatics 33:3137–3139
Cantalapiedra CP, Hernández-Plaza A, Letunic I, Bork P, Huerta-Cepas J (2021) eggNOG-mapper v2: functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. bioRxiv 38(12):5825–5829
Card GL (1973) Metabolism of phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, and cardiolipin of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol 114:1125–1137
Chaudhari NM, Gupta VK, Dutta C (2016) BPGA-an ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci Rep 6:1–10
Claus D (1986) Genus Bacillus Cohn 1872, 174^. Bergey’s Man Syst Bacteriol 2:1105–1139
Dastager SG, Mawlankar R, Srinivasan K, Tang S-K, Lee J-C, Ramana VV et al (2014) Fictibacillus enclensis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105:461–469
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemical Bulletin 19:11–15. https://worldveg.tind.io/record/33886/?ln=en
Glaeser SP, Dott W, Busse H-J, Kämpfer P (2013) Fictibacillus phosphorivorans gen. nov., sp. nov. and proposal to reclassify Bacillus arsenicus, Bacillus barbaricus, Bacillus macauensis, Bacillus nanhaiensis, Bacillus rigui, Bacillus solisalsi and Bacillus gelatini in the genus Fictibacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2934–2944
Green MR, Sambrook J (2017) Preparation of single-stranded bacteriophage M13 DNA by precipitation with polyethylene glycol. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2017:pdb-prot093419
Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G (2013) QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29:1072–1075
Hussey MA, Zayaitz A (2007) Endospore stain protocol. Am Soc Microbiol 8:1–11
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Lane DJ, Pace B, Olsen GJ, Stahl DA, Sogin ML, Pace NR (1985) Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci 82:6955–6959
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2014) Taxonomic use of DNA G+ C content and DNA–DNA hybridization in the genomic age. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:352–356
Minnikin DE, O’donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A et al (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Na S-I, Kim YO, Yoon S-H, Ha S, Baek I, Chun J (2018) UBCG: up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J Microbiol 56:280–285
Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT, Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW (2015) CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res 25:1043–1055
Potter SC, Luciani A, Eddy SR, Park Y, Lopez R, Finn RD (2018) HMMER web server: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res 46:W200–W204
Schumann P (2011) Peptidoglycan structure. In: Methods in microbiology (Elsevier), 101–129
Vaishampayan P, Miyashita M, Ohnishi A, Satomi M, Rooney A, La Duc MT et al (2009) Description of Rummeliibacillus stabekisii gen. nov., sp. nov. and reclassification of Bacillus pycnus Nakamura et al. 2002 as Rummeliibacillus pycnus comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1094–1099
Wainø M, Tindall BJ, Schumann P, Ingvorsen K (1999) Gracilibacillus gen. nov., with description of Gracilibacillus halotolerans gen. nov., sp. nov.; transfer of Bacillus dipsosauri to Gracilibacillus dipsosauri comb. nov., and Bacillus salexigens to the genus Salibacillus gen. nov., as Salibacillus salexig. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 49:821–831
Wick RR, Judd LM, Gorrie CL, Holt KE (2017) Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput Biol 13:e1005595
Wisotzkey JD, Jurtshuk PJR, Fox GE, Deinhard G, Poralla K (1992) Comparative sequence analyses on the 16S rRNA (rDNA) of Bacillus acidocaldarius, Bacillus acidoterrestris, and Bacillus cycloheptanicus and proposal for creation of a new genus, Alicyclobacillus gen. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 42:263–269
Xu L, Dong Z, Fang L, Luo Y, Wei Z, Guo H et al (2019) OrthoVenn2: a web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W52–W58
Yoon J-H, Weiss N, Lee K-C, Lee I-S, Kang KH, Park Y-H (2001) Jeotgalibacillus alimentarius gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from jeotgal with l-lysine in the cell wall, and reclassification of Bacillus marinus Rüger 1983. as Mrinibacillus marinus gen nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2087–2093
Yoon S-H, Ha S-M, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H et al (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613
Zhao Y, Wu J, Yang J, Sun S, Xiao J, Yu J (2012) PGAP: pan-genomes analysis pipeline. Bioinformatics 28:416–418
Funding
The authors acknowledge the funding by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) through the project, grant no. BT/Coord.II/01/03/2016 for in-house facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AM, RT, and YB carried out and compiled the polyphasic characterization; KK performed genome sequencing; AB and KK constructed the phylogenetic trees and did bioinformatic analysis; AM and RT carried out peptidoglycan analysis; ED, VT collected, isolated, and identified the bacterial isolate; AM, RT; compiled the overall data for the manuscript; KK analyzed the data; SD and KK curated the manuscript; AY conceptualized, coordinated the overall work, edited, analyzed the data, and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
No human or animal subjects were recruited for this study.
Additional information
Communicated by Wen-Jun Li.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, A., Maurya, A., Bhavsar, Y. et al. Fictibacillus fluitans sp. nov., isolated from freshwater pond. Arch Microbiol 206, 70 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03794-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03794-4