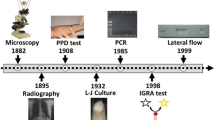
Abstract
Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp), characterized by high virulence and epidemic potential, has become a global public health challenge. Therefore, improving the identification of hvKp and enabling earlier and faster detection in the community to support subsequent effective treatment and prevention of hvKp are an urgent issue. To address these issues, a number of assays have emerged, such as String test, Galleria mellonella infection test, PCR, isothermal exponential amplification, and so on. In this paper, we have collected articles on the detection methods of hvKp and conducted a retrospective review based on two aspects: traditional detection technology and biomarker-based detection technology. We summarize the advantages and limitations of these detection methods and discuss the challenges as well as future directions, hoping to provide new insights and references for the rapid detection of hvKp in the future. The aim of this study is to focus on the research papers related to Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae involving the period from 2012 to 2022. We conducted searches using the keywords “Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae, biomarkers, detection techniques” on ScienceDirect and Google Scholar. Additionally, we also searched on PubMed, using MeSH terms associated with the keywords (such as Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella Infections, Virulence, Biomarkers, diagnosis, etc.).








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support this study are available from the corresponding author or first author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmadi M, Ranjbar R, Behzadi P, Mohammadian T (2022) Virulence factors, antibiotic resistance patterns, and molecular types of clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 20:463–472. https://doi.org/10.1080/14787210.2022.1990040
Algammal A, Hetta HF, Mabrok M, Behzadi P (2023) Editorial: emerging multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens “superbugs”: a rising public health threat. Front Microbiol 14:1135614. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1135614
Anantharajah A, Deltombe M, de Barsy M, Evrard S, Denis O, Bogaerts P, Hallin M, Miendje Deyi VY, Pierard D, Bruynseels P, Boelens J, Glupczynski Y, Huang T-D (2022) Characterization of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in Belgium. Euro J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 41(5):859–865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-022-04438-z
Banakar M, Hamidi M, Khurshid Z, Zafar MS, Sapkota J, Azizian R, Rokaya D (2022) Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection: an updated review. Biosensors 12(11):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110927
Behzadi P, Urbán E, Matuz M et al (2021) The role of gram-negative bacteria in urinary tract infections: current concepts and therapeutic options. Adv Exp Med Biol 1323:35–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/5584_2020_566
Behzadi P, García-Perdomo HA, Autrán Gómez AM et al (2023) Editorial: Uropathogens, urinary tract infections, the host-pathogen interactions and treatment. Front Microbiol 14:1183236. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1183236
Bhaya D, Davison M, Barrangou R (2011) CRISPR-Cas systems in bacteria and archaea: versatile small RNAs for adaptive defense and regulation. Annu Rev Genet 45:273–297. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132430
Biedrzycka M, Izdebski R, Urbanowicz P, Polańska M, Hryniewicz W, Gniadkowski M, Literacka E (2022) MDR carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of the hypervirulence-associated ST23 clone in Poland, 2009–19. J Antimicrob Chemother 77(12):3367–3375. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkac326
Browne N, Heelan M, Kavanagh K (2013) An analysis of the structural and functional similarities of insect hemocytes and mammalian phagocytes. Virulence 4(7):597. https://doi.org/10.4161/viru.25906
Bulger J, MacDonald U, Olson R, Beanan J, Russo TA (2017) Metabolite transporter PEG344 is required for full virulence of hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae strain hvkp1 after pulmonary but not subcutaneous challenge. Infect Immun 85(10):e00093-e117. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00093-17
Cannatelli A, Giani T, D’Andrea MM, Di Pilato V, Arena F, Conte V, Tryfinopoulou K, Vatopoulos A, Rossolini GM (2014) MgrB inactivation is a common mechanism of colistin resistance in KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of clinical origin. Antimicrob Agents Chemoth 58(10):5696–5703. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.03110-14
Cassini A, Högberg LD, Plachouras D et al (2019) Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 19:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4
Catalán-Nájera JC, Garza-Ramos U, Barrios-Camacho H (2017) Hypervirulence and hypermucoviscosity: Two different but complementary Klebsiella spp phenotypes? Virulence. 8(7):1233. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2017.1317412
Chen YT, Chang HY, Lai YC, Pan CC, Tsai SF, Peng HL (2004) Sequencing and analysis of the large virulence plasmid pLVPK of Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43. Gene. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2004.05.008
Cheng Q, Cheung YC, Chan EWC et al (2022) Unveiling the evolution routes of TEM-type extended-spectrum β-lactamases. Int J Antimicrob Agents 59:106498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106498
Christner M, Rohde H, Wolters M, Sobottka I, Wegscheider K, Aepfelbacher M (2010) Rapid identification of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles by use of matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time of flight mass spectrometry fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol 48(5):1584–1591. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01831-09
Chung DR, Lee H, Park MH, Jung S-I, Chang H-H, Kim Y-S, Son JS, Moon C, Kwon KT, Ryu SY, Shin SY, Ko KS, Kang C-I, Peck KR, Song J-H (2012) Fecal carriage of serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 strains closely related to liver abscess isolates in Koreans living in Korea. Euro J Clin Microb Infect Dis 31(4):481–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-011-1334-7
Cubero M, Grau I, Tubau F et al (2016) Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clones causing bacteraemia in adults in a teaching hospital in Barcelona, Spain (2007–2013). Clin Microbiol Infect 22:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2015.09.025
De Francesco MA, Tiecco G, Scaltriti E, Piccinelli G, Corbellini S, Gurrieri F, Crosato V, Moioli G, Marchese V, Focà E, Bertelli DA, Castelli F, Caruso A (2023) First Italian report of a liver abscess and metastatic endogenous endophthalmitis caused by ST-23 hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in an immunocompetent individual. Infection 51(1):271–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-022-01879-8
DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R et al (2011) A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet 43:491–498. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.806
Fang C-T, Chuang Y-P, Shun C-T, Chang S-C, Wang J-T (2004) A novel virulence gene in klebsiella pneumoniae strains causing primary liver abscess and septic metastatic complications. J Exp Med 199(5):697–705. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20030857
Guerrini V, Louza FA, Rosone G (2020) Metagenomic analysis through the extended Burrows-Wheeler transform. BMC Bioinformatics 21:299. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-020-03628-w
Guk K, Keem JO, Hwang SG, Kim H, Kang T, Lim E-K, Jung J (2017) A facile, rapid and sensitive detection of MRSA using a CRISPR-mediated DNA FISH method, antibody-like dCas9/sgRNA complex. Biosens Bioelectron 95:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.04.016
Harada S, Aoki K, Yamamoto S, Ishii Y, Sekiya N, Kurai H, Furukawa K, Doi A, Tochitani K, Kubo K, Yamaguchi Y, Narita M, Kamiyama S, Suzuki J, Fukuchi T, Gu Y, Okinaka K, Shiiki S, Hayakawa K, Doi Y (2019) Clinical and molecular characteristics of klebsiella pneumoniae isolates causing bloodstream infections in japan: occurrence of hypervirulent infections in health care. J Clin Microbiol 57(11):e01206-e1219. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01206-19
He Z, Xu W, Zhao H, Li W, Dai Y, Lu H, Zhao L, Zhang C, Li Y, Sun B (2022) Epidemiological characteristics an outbreak of ST11 multidrug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in Anhui. Front Microbiol, China. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.996753
Hsu C-R, Lin T-L, Chen Y-C, Chou H-C, Wang J-T (2011) The role of Klebsiella pneumoniae rmpA in capsular polysaccharide synthesis and virulence revisited. Microbiol Reading, England 157(Pt 12):3446–3457. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.050336-0
Huang Y, Li J, Gu D, Fang Y, Chan EW, Chen S, Zhang R (2015) Rapid detection of K1 hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae by MALDI-TOF MS. Front Microbiol 6:1435. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01435
Indrajith S, Mukhopadhyay AK, Chowdhury G, Farraj DAA, Alkufeidy RM, Natesan S, Meghanathan V, Gopal S, Muthupandian S (2021) Molecular insights of Carbapenem resistance Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates with focus on multidrug resistance from clinical samples. J Infect Public Health 14(1):131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2020.09.018
Íñigo M, Coello A, Fernández-Rivas G, Rivaya B, Hidalgo J, Quesada MD, Ausina V (2016) Direct Identification of Urinary Tract Pathogens from Urine Samples, Combining Urine Screening Methods and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol 54(4):988–993. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02832-15
Kamau E, Ranson EL, Tsan AT, Bergmann-Leitner ES, Garner OB, Yang S (2022) Clinical and genomic characterization of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp) infections via passive surveillance in Southern California, 2020–2022. Front Microbiol 13:1001169. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1001169
Karampatakis T, Tsergouli K, Behzadi P (2023) Carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae: virulence factors, molecular epidemiology and latest updates in treatment options. Antibiotics 12:234. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020234
Killiny N (2018) Generous hosts: why the larvae of greater wax moth, galleria mellonella is a perfect infectious host model? Virulence 9(1):860–865. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2018.1454172
Kot B, Piechota M, Szweda P et al (2023) Virulence analysis and antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from hospitalised patients in Poland. Sci Rep 13:4448. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-31086-w
Kuypers J, Jerome KR (2017) Applications of digital PCR for clinical microbiology. J Clin Microbiol 55(6):1621–1628. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00211-17
Lai Y-C, Peng H-L, Chang H-Y (2003) RmpA2, an activator of capsule biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43, regulates K2 cps gene expression at the transcriptional level. J Bacteriol 185(3):788–800. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.185.3.788-800.2003
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A et al (2009) The Sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li W, Sun G, Yu Y, Li N, Chen M, Jin R, Jiao Y, Wu H (2014) Increasing occurrence of antimicrobial-resistant hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in China. Clin Infect Dis 58(2):225. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit675
Li Y, Li L, Fan X, Zou Y, Zhang Y, Wang Q, Sun C, Pan S, Wu X, Wang Z (2018) Development of real-time reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) for rapid detection of peste des petits ruminants virus in clinical samples and its comparison with real-time PCR test. Sci Rep 8(1):17760. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35636-5
Li J, Huang Z-Y, Yu T, Tao X-Y, Hu Y-M, Wang H-C, Zou M-X (2019) Isolation and characterization of a sequence type 25 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from the mid-south region of China. BMC Microbiol 19(1):219. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-019-1593-5
Li G, Shi J, Zhao Y, Xie Y, Tang Y, Jiang X, Lu Y (2020) Identification of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates using the string test in combination with Galleria mellonella infectivity. Euro J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39(9):1673–1679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03890-z
Li Y, Hu D, Ma X, Li D, Tian D, Gong Y, Jiang X (2021) Convergence of carbapenem resistance and hypervirulence leads to high mortality in patients with postoperative Klebsiella pneumoniae meningitis. J Glob Ant Resist 27:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2021.02.035
Liao W, Long D, Huang Q, Wei D, Liu X, Wan L, Feng Y, Zhang W, Liu Y (2020) Rapid detection to differentiate hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp) From classical k pneumoniae by identifying peg-344 with loop-mediated isothermal amplication (LAMP). Front Microbiol 11:1189. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01189
Lin Y-T, Siu LK, Lin J-C, Chen T-L, Tseng C-P, Yeh K-M, Chang F-Y, Fung C-P (2012) Seroepidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae colonizing the intestinal tract of healthy Chinese and overseas Chinese adults in Asian countries. BMC Microbiol 12:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-13
Lin B, Hui J, Mao H (2021) Nanopore technology and its applications in gene sequencing. Biosensors (basel) 11:214. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070214
Liu Y-C, Cheng D-L, Lin C-L (1986) Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscess Associated With Septic Endophthalmitis. Arch Intern Med 146(10):1913–1916. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.1986.00360220057011
Liu YM, Li BB, Zhang YY, Zhang W, Shen H, Li H, Cao B (2014) Clinical and molecular characteristics of emerging hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections in mainland China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(9):5379–5385. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02523-14
Liu X, Zhu P, Wang Y, Zhu S, Fu W (2018) Research progress of digital PCR in precise detection of functional nucleic acids [J]. Biotechnol Bulletin. 34:149–162. https://doi.org/10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2018-0568
Liu Y, Long D, Xiang T-X, Du F-L, Wei DD, Wan L-G, Deng Q, Cao X-W, Zhang W (2019) Whole genome assembly and functional portrait of hypervirulent extensively drug-resistant NDM-1 and KPC-2 co-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of capsular serotype K2 and ST86. J Antimicrob Chemother 74(5):1233–1240. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkz023
Liu C, Du P, Yang P, Yi J, Lu M, Shen N (2022) Emergence of extensively drug-resistant and hypervirulent KL2-ST65 Klebsiella pneumoniae harboring blaKPC-3 in Beijing. China. Microbiol Spect. 10(6):e0304422. https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.03044-22
Magill SS, Edwards JR, Bamberg W et al (2014) Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care-associated infections. N Engl J Med 370:1198–1208. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1306801
Maiden MCJ, Jansen van Rensburg MJ, Bray JE, Earle SG, Ford SA, Jolley KA, McCarthy ND (2013) MLST revisited: The gene-by-gene approach to bacterial genomics. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(10):728–736. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3093
Martin RM, Cao J, Wu W, Zhao L, Manthei DM, Pirani A, Snitkin E, Malani PN, Rao K, Bachman MA (2018) Identification of pathogenicity-associated loci in klebsiella pneumoniae from hospitalized patients. Msystems 3(3):e00015-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00015-18
Mmc L, Kl WSD, Rr W, Lm J, Yh G, Ch HSA, Js MSK, Th K (2018) Population genomics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal-group 23 reveals early emergence and rapid global dissemination. Nature Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05114-7
Mukama O, Wu J, Li Z, Liang Q, Yi Z, Lu X, Liu Y, Liu Y, Hussain M, Makafe GG, Liu J, Xu N, Zeng L (2020) An ultrasensitive and specific point-of-care CRISPR/Cas12 based lateral flow biosensor for the rapid detection of nucleic acids. Biosens Bioelect 159:112143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112143
Neoh H, Tan X-E, Sapri HF, Tan TL (2019) Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE): A review of the “gold standard” for bacteria typing and current alternatives. Infection, Genet Evol 74:103935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2019.103935
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, Hase T (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28(12):E63. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.12.e63
Palacios M, Miner TA, Frederick DR, Sepulveda VE, Quinn JD, Walker KA, Miller VL (2018) Identification of two regulators of virulence that are conserved in klebsiella pneumoniae classical and hypervirulent strains. Mbio 9(4):e01443-e1518. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01443-18
Pardee K, Green AA, Takahashi MK, Braff D, Lambert G, Lee JW, Ferrante T, Ma D, Donghia N, Fan M, Daringer NM, Bosch I, Dudley DM, O’Connor DH, Gehrke L, Collins JJ (2016) Rapid, low-cost detection of zika virus using programmable biomolecular components. Cell 165(5):1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.059
Parrott AM, Shi J, Aaron J, Green DA, Whittier S, Wu F (2021) Detection of multiple hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strains in a New York city hospital through screening of virulence genes. Clin Microbiol Infect 27(4):583–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.012
Passet V, Brisse S (2015) Association of tellurite resistance with hypervirulent clonal groups of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol 53(4):1380–1382. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.03053-14
Pereira R, Oliveira J, Sousa M (2020) Bioinformatics and computational tools for next-generation sequencing analysis in clinical genetics. J Clin Med 9:132. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010132
Pu D, Zhao J, Lu B, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Li Z, Zhuo X, Cao B (2023) Within-host resistance evolution of a fatal ST11 hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int J Antimicrob Agents 61(4):106747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106747
Rhoads A, Au KF (2015) PacBio sequencing and its applications. Geno Prot Bioinf 13:278–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2015.08.002
Rohrman BA, Richards-Kortum RR (2012) A paper and plastic device for performing recombinase polymerase amplification of HIV DNA. Lab Chip 12(17):3082–3088. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2lc40423k
Rossolini GM, D’Andrea MM, Mugnaioli C (2008) The spread of CTX-M-type extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Clin Microbiol Infect 14(1):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01867
Russo TA, MacDonald U (2020) The galleria mellonella infection model does not accurately differentiate between hypervirulent and classical klebsiella pneumoniae. Msphere 5(1):e00850-e919. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSphere.00850-19
Russo TA, Marr CM (2019) Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin Microbiol Rev 32(3):e00001-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00001-19
Russo TA, Olson R, Macdonald U, Metzger D, Maltese LM, Drake EJ, Gulick AM (2014) Aerobactin mediates virulence and accounts for increased siderophore production under iron-limiting conditions by hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Imm 82(6):2356. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.01667-13
Russo TA, Olson R, MacDonald U, Beanan J, Davidson BA (2015) Aerobactin, but not yersiniabactin, salmochelin, or enterobactin, enables the growth/survival of hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae ex vivo and in vivo. Infect Immun 83(8):3325–3333. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00430-15
Russo TA, Olson R, Fang C-T, Stoesser N, Miller M, MacDonald U, Hutson A, Barker JH, La Hoz RM, Johnson JR, Backer M, Bajwa R, Catanzaro AT, Crook D, de Almeda K, Fierer J, Greenberg DE, Klevay M, Patel P, Zola J (2018) Identification of biomarkers for differentiation of hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae from classical k pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol 56(9):e00776-e818. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00776-18
Sanikhani R, Moeinirad M, Solgi H, Hadadi A, Shahcheraghi F, Badmasti F (2021) The face of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from clinical samples of two Iranian teaching hospitals. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 20(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12941-021-00467-2
Segawa S, Sawai S, Murata S, Nishimura M, Beppu M, Sogawa K, Watanabe M, Satoh M, Matsutani T, Kobayashi M, Iwadate Y, Kuwabara S, Saeki N, Nomura F (2014) Direct application of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry to cerebrospinal fluid for rapid pathogen identification in a patient with bacterial meningitis. Clinica Chimica Act Int J Clin Chem 435:59–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2014.04.024
Selvam K, Ahmad Najib M, Khalid MF, Ozsoz M, Aziah I (2022) CRISPR-Cas systems-based bacterial detection: a scoping review. Diagnostics 12(6):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061335
Shi Q, Lan P, Huang D, Hua X, Jiang Y, Zhou J, Yu Y (2018) Diversity of virulence level phenotype of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from different sequence type lineage. BMC Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-018-1236-2
Struve C, Bojer M, Nielsen EM et al (2005) Investigation of the putative virulence gene magA in a worldwide collection of 495 Klebsiella isolates: magA is restricted to the gene cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule serotype K1. J Med Microbiol 54:1111–1113. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.46165-0
Struve C, Roe CC, Stegger M, Stahlhut SG, Hansen DS, Engelthaler DM, Andersen PS, Driebe EM, Keim P, Krogfelt KA (2015) Mapping the evolution of hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae. Mbio 6(4):e00630. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00630-15
Sun X, Wang Y, Zhang L, Liu S, Zhang M, Wang J, Ning B, Peng Y, He J, Hu Y, Gao Z (2020) CRISPR-Cas9 triggered two-step isothermal amplification method for E coli O157:H7 detection based on a metal-organic framework platform. Anal Chem 92(4):3032–3041. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04162
Surgers L, Boyd A, Girard PM, Arlet G, Decré D (2016) ESBL-Producing Strain of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae K2. France. Emerg Infect Dis. 22(9):1687. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2209.160681
Terns MP, Terns RM (2011) CRISPR-based adaptive immune systems. Curr Opin Microbiol 14(3):321–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2011.03.005
Tsai CJ-Y, Loh JMS, Proft T (2016) Galleria mellonella infection models for the study of bacterial diseases and for antimicrobial drug testing. Virulence 7(3):214–229. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2015.1135289
Tsuchida S, Umemura H, Nakayama T (2020) Current status of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) in clinical diagnostic microbiology. Molecules (basel, Switzerland) 25(20):4775. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204775
Valková D, Valkovičová L, Vávrová S, Kováčová E, Mravec J, Turňa J (2007) The contribution of tellurite resistance genes to the fitness of Escherichia coli uropathogenic strains. Open Life Sciences 2(2):182–191. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-007-0019-9
Västermark Å, Almén MS, Simmen MW, Fredriksson R, Schiöth HB (2011) Functional specialization in nucleotide sugar transporters occurred through differentiation of the gene cluster EamA (DUF6) before the radiation of Viridiplantae. BMC Evol Biol 11:123. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-11-123
Wensel CR, Pluznick JL, Salzberg SL, Sears CL (2022) Next-generation sequencing: Insights to advance clinical investigations of the microbiome. J Clin Invest 132(7):e154944. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI154944
Wiedenheft B, Sternberg SH, Doudna JA (2012) RNA-guided genetic silencing systems in bacteria and archaea. Nature 482(7385):331–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10886
Wong Y-P, Othman S, Lau Y-L, Radu S, Chee H-Y (2018) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A versatile technique for detection of micro-organisms. J Appl Microbiol 124(3):626–643. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13647
Wu X, Zhan F, Zhang J, Chen S, Yang B (2022) Identification of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae carrying terW gene by MacConkey-potassium tellurite medium in the general population. Front Public Health 10:946370. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.946370
Yan C, Zhou Y, Du S, Du B, Zhao H, Feng Y, Xue G, Cui J, Gan L, Feng J, Fan Z, Fu T, Xu Z, Zhang Q, Zhang R, Cui X, Tian Z, Chen Y, Zhang T, Yuan J (2023) Recombinase-aided amplification assay for rapid detection of hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae (hvkp) and characterization of the hvkp pathotype. Microbiol Spect. https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.03984-22
Ye M, Tu J, Jiang J, Bi Y, You W, Zhang Y, Ren J, Zhu T, Cao Z, Yu Z, Shao C, Shen Z, Ding B, Yuan J, Zhao X, Guo Q, Xu X, Huang J, Wang M (2016) Clinical and genomic analysis of liver abscess-causing klebsiella pneumoniae identifies new liver abscess-associated virulence genes. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 6:165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2016.00165
Yeh K-M, Chang F-Y, Fung C-P et al (2006) magA is not a specific virulence gene for Klebsiella pneumoniae strains causing liver abscess but is part of the capsular polysaccharide gene cluster of K. pneumoniae serotype K1. J Med Microbiol 55:803–804. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.46368-0
Yh, H., Sh, C., Sw, L., Ce, N., Yt, L., Yw, H., & Tc, Y. (2018). Emergence of an XDR and carbapenemase-producing hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strain in Taiwan. J Antimicrob Chemoth, 73(8). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dky164
Yu WL, Ko WC, Cheng KC, Lee HC, Ke DS, Lee CC, Fung CP, Chuang YC (2006) Association between rmpA and magA genes and clinical syndromes caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Clin Infect Dis 42(10):1351. https://doi.org/10.1086/503420
Yu W-L, Lee M-F, Chen C-C, Tang H-J, Ho C-H, Chuang Y-C (2017) Impacts of hypervirulence determinants on clinical features and outcomes of bacteremia caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing klebsiella pneumoniae. Microb Drug Resist (larchmont, NY) 23(3):376–383. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2016.0018
Zhang R, Lin D, Chan EW, Gu D, Chen GX, Chen S (2015) Emergence of carbapenem-resistant serotype K1 hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae strains in China. Antimicrob Agents Chemoth. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02173-15
Zhang Y, Yao Y, Du W, Wu K, Xu W, Lin M, Tan H, Li J (2017) Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification with Plasmodium falciparum unique genes for molecular diagnosis of human malaria. Path Global Health. 111(5):255. https://doi.org/10.1080/20477724.2017.1347379
Zhang Z, Wen H, Wang H, Zhang P, Li J, Liang Y, Liu Y, Sun L, Xie S (2022) A Case of meningitis in an infant due to hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae transmission within a family. Infect Drug Resis. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S376055
Zhao LM, Li G, Gao Y, Zhu YR, Liu J, Zhu XP (2015) Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detecting tomato chlorosis virus. J Virol Meth. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2014.11.013
Zhao N, Liu JX, Li D, Sun DX (2016) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for visual detection of hepatitis B virus. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi Zhonghua Ganzangbing Zazhi Chinese J Hepatol. 24(6):406–411. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.06.003
Zhao N, Liu J, Sun D (2017) Detection of HCV genotypes 1b and 2a by a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. J Med Virol 89(6):1048–1054. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.24747
Zhou C, Wu Q, He L, Zhang H, Xu M, Yuan B, Jin Z, Shen F (2021) Clinical and molecular characteristics of carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a tertiary hospital in Shanghai, China. Infect Drug Resist 14:2697–2706. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S321704
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the authors for their continued hard work.
Funding
This study was funded by the Zhejiang Provincial Public Welfare Technology Program of China (LGC19H190001, LGF22H190003), Ningbo Clinical Research Center for Digestive System Tumors (Grant No. 2019A21003), and Zhejiang Medicine and Health Science and Technology Project (2021PY021). The authors would like to thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for providing linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Q-bZ and PZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Q-bZ and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Qb., Zhu, P., Zhang, S. et al. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae detection methods: a minireview. Arch Microbiol 205, 326 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03665-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03665-y