Abstract
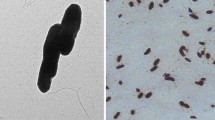
This study describes a bacterium strain RBPA9 isolated from a municipality waste dumping area capable of degrading phenol, proposed as a novel species of Pseudomonas. Cells are Gram-negative, rod shaped, aerobic and motile. The genome is 3.92 Mb, and the G + C content is 64.64%. The overall genome relatedness indices such as in silico DNA–DNA hybridization (isDDH), average nucleotide identity (ANI), and average amino acid identity (AAI) values were below 70% and 95–96%, respectively. Phylogenetic analysis based on genome-wide core genes and 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that strain RBPA9 clustered with Pseudomonas stutzeri ATCC 17588 T in both the phylogenetic trees. Maximum growth was recorded at 200 mg /L concentration of phenol which was consumed within 24 h. A gene cluster of phenol degradation pathway was detected. The quantitative real-time PCR (RT-PCR) demonstrated the expression of all the genes required in the meta-cleavage pathway of phenol in RBPA9. Our results reveal that strain RBPA9 represents a novel species for which Pseudomonas phenolilytica sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is RBPA9T (= TBRC 15231 T = NBRC 115284 T).





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for the genome and 16S rRNA gene sequences of Pseudomonas strain RBPA9 are CP058908 and MW241387, respectively.
References
Alcalde M, Ferrer M, Plou FJ, Ballesteros A (2006) Environmental biocatalysis: from remediation with enzymes to novel green processes. Trends Biotechnol 24:281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.04.002
Arai H, Ohishi T, Chang ME, Kudo T (2000) Arrangement and regulation of the genes for meta-pathway enzymes required for degradation of phenol in Comamonas testosteroni TA441. Microbiology 146:1707–1715. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-146-7-1707
Arora PK, Bae H (2014) Bacterial degradation of chlorophenols and their derivatives. Microb Cell Fact 13:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-13-31
Arutchelvan V, Kanakasabai V, Elangovan R, Nagarajan S, Muralikrishnan V (2006) Kinetics of high strength phenol degradation using Bacillus brevis. J Hazard Mater 129:216–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.040
Babich H, Davis DL (1981) Phenol: a review of environmental and health risks. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 1:90–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-2300(81)90071-4
Bernardet JF, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B, Subcommittee on the taxonomy of Flavobacterium and Cytophaga-like bacteria of the International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes (2002) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1049–1070. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-52-3-1049
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917. https://doi.org/10.1139/o59-099
Coyle CG, Parkin GF, Gibson DT (1993) Aerobic, phenol-induced TCE degradation in completely mixed, continuous-culture reactors. Biodegradation 4:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00701455
Das L, Deb S, Das SK (2021) Description of Acinetobacter kanungonis sp. nov., based on phylogenomic analysis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 71: 004833 https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004833
Folsom BR, Chapman PJ, Pritchard PH (1990) Phenol and trichloroethylene degradation by Pseudomonas cepacia G4: kinetics and interactions between substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1279–1285
Frasson D, Opoku M, Picozzi T, Torossi T, Balada S, Smits THM, Hilber U (2017) Pseudomonas wadenswilerensis sp. nov. and Pseudomonas reidholzensis sp. nov., two novel species within the Pseudomonas putida group isolated from forest soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2853–2861. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002035
Gomila M, Peña A, Mulet M, Lalucat J, García-Valdés E (2015) Phylogenomics and systematics in Pseudomonas. Front Microbiol 6:214. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00214
Götz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Williams TD, Nagaraj SH, Nueda MJ, Robles M, Talon M, Dopazo J, Conesa A (2008) High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res 36:3420–3435. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn176
Grant JR, Stothard P (2008) The CGView Server: a comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W181–W184. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn179
Konstantinidis KT, Tiedje JM (2005a) Genomic insights that advance the species definition for prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2567–2572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409727102
Konstantinidis KT, Tiedje JM (2005b) Towards a genome-based taxonomy for prokaryotes. J Bacteriol 87:6258–6264. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.18.6258-6264.2005
Kumari P, Poddar A, Das SK (2014) Marinomonas fungiae sp. nov., isolated from the coral Fungia echinata from the Andaman Sea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:487–494. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.054809-0
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Stærfeldt H-H, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNammer: consistent annotation of rRNA genes in genomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm160
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Loh KC, Tan CP (2000) Effect of additional carbon sources on biodegradation of phenol. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 64:756–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s0012800068
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.5.0955
Mateo-Estrada V, Graña-Miraglia L, López-Leal G, Castillo-Ramírez S (2019) Phylogenomics reveals clear cases of misclassification and genus-wide phylogenetic markers for Acinetobacter. Genome Biol Evol 11:2531–2541. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evz178
Medema MH, Takano E, Breitling R (2013) Detecting sequence homology at the gene cluster level with MultiGeneBlast. Mol Biol Evol 30:1218–1223. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst025
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/14/60
Moss CW, Samuels SB, Weaver RE (1972) Cellular fatty acid composition of selected Pseudomonas species. Applied Microbiol 24:596–598. https://doi.org/10.1128/am.24.4.596-598.1972
Na S-I, Kim YO, Yoon S-H, Ha S-M, Baek I, Chun J (2018) UBCG: up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J Microbiol 56:280–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-8014-6
Nešvera J, Rucká L, Miroslav Pátek M (2015) Catabolism of phenol and its derivatives in bacteria: genes, their regulation, and use in the biodegradation of toxic pollutants. Adv Appl Microbiol 93:107–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aambs.2015.06.002
Orata FD, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Sauvageau D, Stein LY (2018) Phylogenomic analysis of the gammaproteobacterial methanotrophs (order Methylococcales) calls for the reclassification of members at the genus and species levels. Front Microbiol 9:3162. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.03162
Pandey J, Heipieper HJ, Chauhan A, Arora PK, Prakash D, Takeo M, Jain RK (2011) Reductive dehalogenation mediated initiation of aerobic degradation of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol (2C4NP) by Burkholderia sp. strain SJ98. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:597–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3254-y
Peix A, Ramírez-Bahena MH, Velázquez E (2018) The current status on the taxonomy of Pseudomonas revisited: An update. Infect Genet Evol 57:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2017.10.026
Palleroni NJ. Pseudomonas. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (editors) (2005) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, 2, 2nd ed. Boston: Springer; pp. 323–379
Rucká L, Nešvera J, Pátek M (2017) Biodegradation of phenol and its derivatives by engineered bacteria: current knowledge and perspectives. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2339-x
Sawada H, Fujikawa T, Tsuji M, Satou M. 2021. Pseudomonas allii sp. nov., a pathogen causing soft rot of onion in Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 71: 004582. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004582
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In methods for general and molecular bacteriology, pp. 607–655. Edited by Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
Tian M, Du D, Zhou W, Zeng X, Cheng G (2017) Phenol degradation and genotypic analysis of dioxygenase genes in bacteria isolated from sediments. Braz J Microbiol 48:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2016.12.002
Tomei MC, Angelucci DM, Clagnan E, Brusetti L (2021) Anaerobic biodegradation of phenol in wastewater treatment: achievements and limits. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:2195–2224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11182-5
Wilderman PJ, Vasil AI, Wesley E, Martin WE, Murphy RC, Vasil ML (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa Synthesizes phosphatidylcholine by use of the phosphatidylcholine synthase pathway. J Bacteriol 184:4792–4799. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.184.17.4792-4799.2002
Acknowledgements
The author R.R.A.K. acknowledge the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, Government of India for providing the research fellowship. We acknowledge the Distributed Information Sub-Center (DISC) at the Institute of Life Sciences, Bhubaneswar, for the computational facility. This work was supported by the funding received from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (D.O.No. BT/BI/04/058/2002 VOL-II) to SKD. We are thankful to Professor B. Schink (Universitaet Konstanz, Germany) for etymological advice.
Funding
This work was supported by the funding received from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (D.O.No. BT/BI/04/058/2002 VOL-II) to SKD under the Distributed Information Sub-Center (DISC) project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.K.D. developed the concept, R.R.A.K. conducted the experiment. R.R.A.K. and S.K.D. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All of us read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kujur, R.R.A., Das, S.K. Pseudomonas phenolilytica sp. nov., a novel phenol-degrading bacterium. Arch Microbiol 204, 320 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02912-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02912-y