Abstract
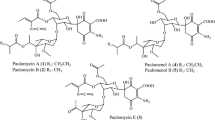
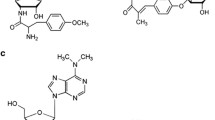
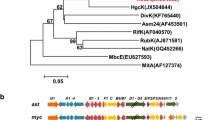
The four overlapping cosmids from the rubradirin producer, Streptomyces achromogenes var rubradiris NRRL 3061, have 58 ORFs within a 105.6 kb fragment. These ORFs harbored essential genes responsible for the formation and attachment of four distinct moieties, along with the genes associated with regulatory, resistance, and transport functions. The PKS (rubA) and glycosyltransferase (rubG2) genes were disrupted in order to demonstrate a complete elimination of rubradirin production. The rubradirin biosynthetic pathway was proposed based on the putative functions of the gene products, the functional identification of sugar genes, and the mutant strains.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHBA:
-
3-Amino-5-hydroxybenzoic acid
- AMC:
-
3-Amino-4-hyrdoxy-7-methoxycoumarin
- DHDP:
-
3,4-Dihydroxydipicolinate
- NRPS:
-
Nonribosomal polypeptide synthetase
- PKS:
-
Polyketide synthase
References
August PR, Tang L, Yoon YJ, Ning S, Muller R, Yu TW, Taylor M, Hoffmann D, Kim CG, Zha-ng X, Hutchinson CR, Floss HC (1998) Biosynthesis of the ansamycin antibiotic rifamycin: deductions from the molecular analysis of the rif biosynthetic gene cluster of Amycolatopsis mediterranei S699. Chem Biol 5:69–79
Bannister B, Zapotocky BA (1992) Protorubradirin, an antibiotic containing a C-nitroso-sugar fr-agment, is the true secondary metabolite produced by Streptomyces achromogenes var. rubradiris. Rubradirin, described earlier, is its photo-oxidation product. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 45:1313–1324
Bhuyan BK, Owen SP, Dietz A (1964) Rubradirin, a new antibiotic. I. Fermentation and biological properties. Antimicrobi Agents Chemother 10:91–96
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Brimacombe JS, Rahman KMM (1983) Synthesis of l-rubranitrose (2,3,6-trideoxy-3-C-methyl-4 -O-methyl-3-nitro-l-xylo-hexopyranose) and naturally occuring d-enantiomer. Carbohydr Res 114:C1–C2
Chen H, Thomas MG, Hubbard BK, Losey HC, Walsh CT, Burkart MD (2000) Deoxysugars in glycopeptide antibiotics: enzymatic synthesis of TDP-l-epivancosamine in chloroeremomycin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11942–11947
Chen H, Walsh CT (2001) Coumarin formation in novobiocin biosynthesis: beta-hydroxylation of the aminoacyl enzyme tyrosyl-S-NovH by a cytochrome P450 NovI. Chem Biol 8:301–312
Daniel RA, Errington J (1993) Cloning, DNA sequence, functional analysis and transcriptional regulation of the genes encoding dipicolinic acid synthetase required for sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol 232:468–483
Eustaquio AS, Luft T, Wang ZX, Gust B, Chater KF, Li SM, Heide L (2003) Novobiocin biosynthesis: inactivation of the putative regulatory gene novE and heterologous expression of genes involved in aminocoumarin ring formation. Arch Microbiol 180:25–32
Guo J, Frost JW (2002) Kanosamine biosynthesis: a likely source of the aminoshikimate pathway’s nitrogen atom. J Am Chem Soc 124:10642–10643
He XM, Liu HW (2002) Formation of unusual sugars: mechanistic studies and biosynthetic applications. Annu Rev Biochem 71:701–754
Kato Y, Bai L, Xue Q, Revill WP, Yu TW, Floss HG (2002) Functional expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of the novel polyketide chain extension unit, methoxymalonyl-acyl carrier protein, and engineered biosynthesis of 2-desmethyl-2-methoxy-6-deoxyerythronolide B. J Am Chem Soc 124:5268–5269
Kessler N, Schuhmann H, Morneweg S, Linne U, Marahiel MA (2004) The linear pentadecapeptide gramicidin is assembled by four multimodular nonribosomal peptide synthetases that comprise 16 modules with 56 catalytic domains. J Biol Chem 279:7413–7419
Kieser T, Mervyn JB, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hoopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Centre, Norwich
Kim C-G, Yu TW, Fryhle CB, Handa S, Floss HG (1998) 3-Amino-5-hydroxybenzoic acid synthase, the terminal enzyme in the formation of the precursor of the mC7N units in rifamycin and related antibiotics. J Biol Chem 13:6030–6040
Lamichhane J, Liou K, Lee HC, Kim CG, Sohng JK (2006) Functional characterization of ketoreductase (rubN6) and aminotransferase (rubN4) genes in the gene cluster of Streptomyces achromogenes var. rubradiris. Biotechnol Lett 28:545–553
Maharjan J, Liou K, Lee HC, Kim CG, Lee JJ, Yoo JC, Sohng JK (2003) Functional identificati-on of rub52 gene involved in the biosynthesis of rubradirin. Biotechnol Lett 25:909–915
Marshall VP, McWethy SJ, Sirotti JM, Cialdella JI (1990) The effect of neutral resins on the fermentation production of rubradirin. J Ind Microbiol 5:283–287
Payton M, Mushtaq A, Yu TW, Wu LJ, Sinclair J, Sim E (2001) Eubacterial arylamine N-acetylt-ransferases— identification and comparison of 18 members of the protein family with conserved active site cysteine, histidine and aspartate residues. Microbiology 147:1137–1147
Rascher A, Hu Z, Viswanathan N, Schirmer A, Reid R, Nierman WC, Lewis M, Hutchinson CR (2003) Cloning and characterization of a gene cluster for geldanamycin production in Streptomyces hygroscopicus NRRL 3602. FEMS Microbiol Lett 218:223–230
Reusser F (1973) Rubradirin, an inhibitor of ribosomal polypeptide biosynthesis. Biochemistry 12:1136–1142
Reusser F (1979) Inhibition of ribosomal and RNA polymerase functions by rubradirin and its aglycone. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 32:1186–1192
Russer F, Bannister B, Tarpley WG, Althaus IW, Zapotocky BA (1988) Rubradirin derivatives for treatment of HIV infection. Patent Cooperation Treaty W08808707
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sohng JK, Oh TJ, Lee JJ, Kim CG (1997) Identification of a gene cluster of biosynthetic genes of rubradirin substructures in S. achromogenes var. rubradiris NRRL3061. Mol Cells 7:674–681
Staffa A, Zazopoulos E, Mercure S, Nowacki P (2001) Genetic locus for everninomicin biosynth-esis. Patent WO 0155180-A49
Sun Y, Zhou X, Dong H, Tu G, Wang M, Wang B, Deng Z (2003) A complete gene cluster from Streptomyces nanchangensis NS3226 encoding biosynthesis of the polyether ionophore nanchangmycin. Chem Biol 10:431–441
Tang L, Yoon YJ, Choi CY, Hutchinson CR (1998) Characterization of the enzymatic domains in the modular polyketide synthase involved in rifamycin B biosynthesis by Amycolatopsis mediterranei. Gene 216:255–265
Volchegursky Y, Hu Z, Katz L, McDaniel R (2000) Biosynthesis of the anti-parasitic agent megalomicin: transformation of erythromycin to megalomicin in Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Mol Microbiol 37:752–762
Wherli W (1977) Topics in current chemistry. Ansamycins. chemistry, biosynthesis and biological activity, vol 72. Berlin Heidelberg, pp 21–49
Yoo JC, Choi JY, Yun SC, Kim CG, Lee JJ, Kim SB, Sohng JK (2000) Sequence analysis and expression of rubN2 as dTDP-Glucose 4,6-dehydratase gene cloned from Streptomyces achromogenes var. rubradiris NRRL 3061, rubradirin producer. J Biochem Mol Biol Biophys 4:313–321
Yu TW, Bai L, Clade D, Hoffmann D, Toelzer S, Trinh KQ, Xu J, Moss SJ, Leistner E, Floss HG (2002) The biosynthetic gene cluster of the maytansinoid antitumor agent ansamitocin from Actinosynnema pretiosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7968–7973
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the 21C Frontier Microbial Genomics and Application Center Program, Ministry of Science & Technology (Grant MG02-0301-004-2-3-1), Republic of Korea. The standard rubradirin sample was supplemented by Pfizer Global Research and Development Strategic Alliances, Eastern Point Road, Gorton, Connecticut.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jean-Luc Pernodet.
The GeneBank accession number for the sequence reported in this paper is AJ871581.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, CG., Lamichhane, J., Song, KI. et al. Biosynthesis of rubradirin as an ansamycin antibiotic from Streptomyces achromogenes var. rubradiris NRRL3061. Arch Microbiol 189, 463–473 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0337-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0337-3