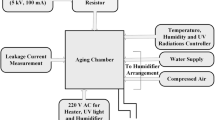
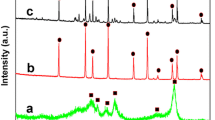
Abstract
The micro-aluminium trihydrate (ATH) and nano-alumina fillers in the silicone rubber (SR) significantly improve the electrical, thermal and mechanical properties. ATH fillers improved the resistance to the corona ageing and water droplet-initiated erosion. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was carried out to understand degradation condition caused due to corona ageing and damage caused due to water droplet-initiated discharges. The inclusion of these fillers significantly altered the surface and bulk charge distribution characteristics of the polymer. A right shift is observed in the trap distribution characteristics. The reduced electric field threshold limit for space charge formation is observed with composites, due to increment in impurities/agglomerations with respect to increment in filler concentration. Performance of composites subjected to polarity reversal is improved on inclusion of nano-filler in addition to micro-filler. The inclusion of fillers enhanced the thermal conductivity and improved significantly thermal stability of the SR composite.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gorur RS, Cherney EA, Burnham JT (1999) Outdoor insulators. In: Ravi S (ed) Gorur Inc., Phoenix
Imai T, Sawa F, Nakano T et al (2006) Effects of nano- and micro-filler mixture on electrical insulation properties of epoxy based composites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 13(2):319–326
Wenying Z, Shuhua Q, Chunchao T et al (2007) Effect of the particle size of Al2O3 on the properties of filled heat-conductive silicone rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 104(2):1312–1318
Nazir MT, Phung BT, Yu S et al (2018) Tracking, erosion and thermal distribution of micro-AIN+nano-SiO2 co-filled silicone rubber for high voltage outdoor insulation. High Volt 3(4):289–294
Kumagai S, Yoshimura N (2001) Tracking and erosion of HTV silicone rubber and suppression mechanism of ATH. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 8(2):203–211
Meyer LH, Cherney EA, Jayaram SH (2004) The role of inorganic fillers in silicone rubber for outdoor insulation alumina tri-hydrate or silica. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 20(4):13–21
Nazir MT, Phung BT, Yu S (2018) Resistance against AC corona discharge of micro-ATH/nano-Al2O3 co-filled silicone rubber composites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 25(2):657–667
Reynders JP, Jandrell IR, Reynders SM(1999) Surface aging mechanisms and their relationship to service performance of silicone rubber insulation. In: Eleventh international symposium on high voltage engineering, vol 4. London, pp 54–58
Venkatesulu B, Thomas MJ (2010) Corona aging studies on silicone rubber nanocomposites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 17(2):625–634
Lopes JS, Jayaram SH, Cherney EA (2001) A study of partial discharges from water droplets on a silicone rubber insulating surface. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 8(2):262–268
Phillips AJ, Childs DJ, Schneider HM (1999) Aging of nonceramic insulators due to corona from water drops. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 14(3):1081–1089
Vas V, Venkatesulu B, Thomas MJ (2012) Tracking and erosion of silicone rubber nanocomposites under DC voltages of both polarities. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 19(1):91–98
Du BX, Yang ZR, Li ZL et al (2017) Surface charge behavior of silicone rubber/SiC composites with field-dependent conductivity. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 24(3):1340–1348
Montanari GC, Morshuis PHF (2005) Space charge phenomenology in polymeric insulating materials. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 12(4):754–767
Meyer L, Omranipour R, Jayaram S et al (2002) The effect of ATH and silica on tracking and erosion resistance of silicone rubber compounds for outdoor insulation. In: IEEE international symposium on electrical insulation, Boston, MA, USA, pp 271–274
Sarathi R, Merin S IP, Subramanian V (2013) Propagation of partial discharge signals and the location of partial discharge occurrences. In: IEEE 8th international conference on industrial and information systems, Peradeniya, pp 92–95
Chen X, Wang X, Wu K et al (2012) Effect of voltage reversal on space charge and transient field in LDPE films under temperature gradient. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 19(1):140–149
Nazemi M, Hinrichsen V (2013) Experimental investigations on water droplet oscillation and partial discharge inception voltage on polymeric insulating surfaces under the influence of AC electric field stress. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 20(2):443–453
Riba JR, Andrea M, Franesca C (2018) Comparative study of AC and positive and negative DC visual corona for sphere-plane gaps in atmospheric air. Energies 11(10):1–18
Ghunem RA, Jayaram SH, Cherney EA (2015) Suppression of silicone rubber erosion by alumina trihydrate and silica fillers from dry-band arcing under DC. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 22(1):14–20
Meyer L, Jayaram S, Cherney EA (2004) Thermal conductivity of filled silicone rubber and its relationship to erosion resistance in the inclined plane test. IEEE Trans Dielec Electric Insul 11(4):620–630
Meyer L, Grishko V, Jayaram S et al (2002) Thermal characteristics of silicone rubber filled with ATH and silica under laser heating. In: Annual report conference on electrical insulation and dielectric phenomena, Cancun, Quintana Roo, Mexico, pp 848–852
Nazir MT, Phung BT, Yu S et al (2018) Effects of thermal properties on tracking and erosion resistance of micro-ATH/AlN/BN filled silicone rubber composites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 25(6):2076–2085
Cheng JP, Liu T, Zhang J et al (2014) Influence of phase and morphology on thermal conductivity of alumina particle/silicone rubber composites. Appl Phys A 117(4):1985–1992
Du BX, Xu H (2014) Effects of thermal conductivity on dc resistance to erosion of silicone rubber/BN nanocomposites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 21(2):511–518
Fabiani D, Montanari GC, Laurent C et al (2007) Polymeric HVDC cable design and space charge accumulation. Part 1: insulation/semicon interface. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 23(6):11–19
Pandey JC, Gupta N (2014) Thermal aging assessment of epoxy-based nanocomposites by space charge and conduction current measurement. In: IEEE electrical insulation conference (EIC). Philadelphia, PA
Ma X, Zhang P, Fan Y et al (2012) Effect of nanoparticles loading on space charge characteristic of Al2O3–silicone rubber nanocomposites. In: 7th International Forum on Strategic Technology (IFOST), Tomsk
Acknowledgements
The Author (R.S) wish to thank Central power research institute, Bangalore for sponsoring the project (NPP/2016/TR/1/27042016) on the study of nanocomposites insulants for power apparatus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinod, P., Desai, B.M.A., Sarathi, R. et al. Investigation on the thermal properties, space charge and charge trap characteristics of silicone rubber nano–micro composites. Electr Eng 103, 1779–1790 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-01195-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-01195-0