Abstract
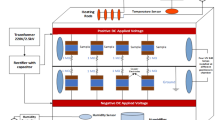
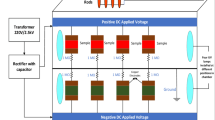
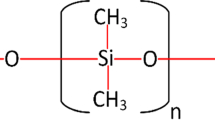
High-voltage polymeric insulators used on transmission lines are likely to degrade due to the multiple environmental stresses as well as electrical surface discharges. In this paper, multi-stress aging performance of high-temperature vulcanized silicone rubber (HTV-SR) filled with different concentrations of silica and alumina trihydrate (ATH) is explored under DC voltage for a period of 5000 h. The degradation of the test specimens has been studied using partial discharge measurement, thermogravimetric analysis, differential scanning calorimetry and mechanical strength analysis. Moreover, partial discharge performance was assessed to see its linkage to aging. When comparing the partial discharge data of the composite with the neat HTV-SR, it is observed that the partial discharge inception voltage of composite samples increases up to 50%. Furthermore, the number of discharge pulses and their magnitude is lower in the composite specimens as compared to the unfilled neat samples. This improvement appears to be caused by nano-particles which reduce oxidation reactions on the surface and the tightness of the bond between polymer matrix and nano-filler particles. The measured mechanical strength and thermal stability data also show the improved performance of hybrid composite samples. This investigation confirms that hybrid composites are quite resistant to aging as compared to neat HTV-SR.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbar M, Ullah R, Alam S (2019) Aging of silicone rubber-based composite insulators under multi-stressed conditions: an overview. Mater Res Exp 6(10):102003
Amin S, Choudry MA, Azam S (2014) Degradation of silicone rubber insulators under the effects of carbon smoke salt and cement deposits. Nucleus 51(4):425–429
Ansorge S, Papailiou K (2015) Mechanical properties of silicone rubber under high loadings of alumina trihydrate filler. J Elastom Plast 48:1–29
Ansorge S, Schmuck F, Papailiou KO (2012) Improved silicone rubbers for the use as housing material in composite insulators. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 19:209–217
Dang B, Hu J, Zhou Y, He J (2017) Remarkably improved electrical insulating performances of lightweight polypropylene nanocomposites with fullerene. J Phys D 50:45530
Farhang F, Ehsani M, Jazayeri SH (2009) Effects of the filler type and quantity on the flashover voltage and hydrophobicity of RTV silicone rubber coatings. Iran Polym J 18:149–157
Fuse N, Ohki Y, Kozako M, Tanaka T (2008) Possible Mechanisms of superior resistance of polyamide nanocomposites to partial discharges and plasma. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 15:161–169
Ghunem RA, Jayaram SH, Cherney EA (2014) Investigation into the eroding dry-band arcing of filled silicone rubber under DC using wavelet-based multiresolution analysis. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 21(2):713–720
Ghunem RA, Jayaram SH, Cherney EA (2015) Suppression of silicone rubber erosion by alumina trihydrate and silica fillers from dry-band arcing under DC. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 22(1):14–20
Imai T, Sawa F, Nakano T, Ozaki T, Shimizu T, Kozako M, Tanaka T (2005) Insulation properties of Nan0- and micro-filler mixture composite. In: IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), pp.171–174.
Kochetov R, Andritsch T, Morshuis PH, Smit JJ (2012) Anomalous behaviour of the dielectric spectroscopy response of nanocomposites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 19(1):107–117
Kozako M, Kido R, Fuse N, Ohki Y, Okamoto T, Tanaka T (2004) Difference in surface degradation due to partial discharges between polyamide nanocomposites and microcomposites. In: Proceedings of IEEE-CEIDP pp: 398–401.
Kozako M, Kuge S, Imai T, Ozaki T, Shimizu T, Tanaka T (2005) Surface erosion due to partial discharges on several kinds of epoxy nanocomposites. In: Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), pp.162–165.
Kozako M, Yamano S, Kido R, Ohki Y, Kohtoh M, Okabe S, Tanaka T (2005) Preparation and preliminary characteristic evaluation of epoxy/alumina nanocomposites. In: Proceedings of 2005 International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials (ISEIM 2005) pp: 231–234.
Kozako M, Kido R, Imai T, Ozaki T, Shimizu T, Tanaka T (2005) Surface roughness change of epoxy/TiO2 nanocomposites due to partial discharges. In: Proceedings of 2005 International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials (ISEIM 2005). pp: 661–664.
Li C, Hu J, Lin C, He J (2016) The control mechanism of surface traps on surface charge behavior in alumina-filled epoxy composites. J Phys D 49:445304
Meyer L, Grishko V, Jayaram S, Cherney E, Duley WW (2002) Thermal characteristics of silicone rubber filled with ath and silica under laser heating. In: IEEE-CEIDP, pp. 848–852.
Meyer L, Jayaram SH, Cherney EA (2004a) Thermal conductivity of filled silicone rubber and its relationship to erosion resistance in the inclined plane test. IEEE Trans Dielect Elect Insul 11:620–630
Meyer LH, Cherney EA, Jayaram SH (2004b) The role of inorganic fillers in silicone rubber for outdoor insulation: alumina tri-hydrate or silica. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 20:13–21
Nandi S, Reddy BS, Sharma D (2019) Performance of composite insulators used for electric transmission under extreme climatic conditions. J Mater Eng Perform 28(10):5959–5969
Nazir MT, Phung BT (2018) Accelerated ultraviolet weathering investigation on micro-/nano-SiO2 filled silicone rubber composites. High Voltage 3(4):295–302
Nazir MT, Phung BT, Hoffman M (2016) Performance of silicone rubber composites with SiO2 micro/nano-filler under AC corona discharge. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 23(5):2804–2815
Nazir MT, Phung BT, Yu S, Li S, Xie D, Zhang Y (2018) Thermal distribution analysis and suppression mechanism of carbonized tracking and erosion in silicone rubber/SiO2 nanocomposites. Polym Testing 70:226–233
Nazir MT, Phung BT, Sahoo A, Yu S, Zhang Y, Li S (2019) Surface discharge behaviours, dielectric and mechanical properties of EPDM based nanocomposites containing Nano-BN. Appl Nanosci 9(8):1981–1989
Nelson JK (2007) Overview of Nanodielectrics: Insulating materials of the future. In: Electrical Insulation Conference and Electrical Manufacturing Expo, pp.229–235.
Rajini V, Udayakumar K (2009) Degradation of silicone rubber under AC or DC voltages in radiation environment. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 16(3):834–841
Tanaka T, Kozako M, Ohki Y, Kohtoh Y, Okabe S (2005) Various characteristics of epoxy/ alumina nanocomposite processed in laboratory scale. In: Proceedings of ICEE, pp: 477–480.
Tanaka T, Kozako M, Fuse N, Ohki Y (2005) Proposal of a multi-core model for polymer nanocomposite dielectrics. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 12(4):669–681
Tanaka T, Ohki Y, Shimizu T, Okabe S (2006) Superiority in partial discharge resistance of several polymer nanocomposites. CIGRE Paper 303:8
Tanaka T, Nose A, Ohki Y, Murata Y (2006) PD Resistance evaluation of LDPE/MgO nanocomposite by a rod-to-plane electrode system. Proc ICPADM 2006:319–322
Tanaka T, Yazawa T, Ohki Y, Ochi M, Hara M, Imai T (2007) Frequency accelerated partial discharge resistance of epoxy/clay nanocomposite prepared by newly developed organic modification and solubilization methods. In: IEEE International Conference on Solid Dielectrical (ICSD), pp. 337–340.
Tanaka T, Ohki Y, Ochi M, Hara M, Imai T (2008) Enhanced partial discharge resistance of epoxy/clay nanocomposite prepared by newly developed organic modification and solubilization methods. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 15:81–89
Venkatesulu B, Thomas MJ (2010a) Erosion resistance of alumina filled silicone rubber nanocomposites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 17:615–624
Venkatesulu B, Thomas MJ (2010b) Corona aging studies on silicone rubber nanocomposites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 17:625–634
Wietzke S et al (2011) Terahertz spectroscopy on polymers: A review of morphological studies. J Mol Struct 1006:1–3
Yuan C, Xie C, Li L, Xu X, Gubanski SM, He Z (2016) Dielectric response characterization of in-service aged sheds of (U) HVDC silicone rubber composite insulators. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 23:1418–1426
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullah, R., Akbar, M. & Amin, S. Measuring electrical, thermal and mechanical properties of DC-stressed HTV silicone rubber loaded with nano/micro-fillers exposed to long-term aging. Appl Nanosci 10, 2101–2111 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01381-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01381-3