Abstract
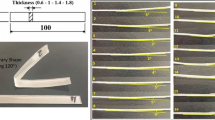
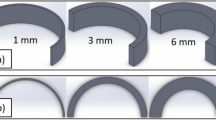
A simple and inactive structure is able to transform into a complex and active one via four-dimensional (4D) printing. Controlling bending deformation, activation time, and temperature is crucial in 4D printing. This study aimed to comprehensively evaluate and analyze the effect of different process parameters on the bending deformation of polylactic acid (PLA) shape-morphing produced by material extrusion additive manufacturing. These parameters included layup, layer thickness, printing speed, nozzle temperature, nozzle diameter, and bed temperature. Since the bending deformation is significantly affected by the specimen wall, this study has focused, for the first time, on the simultaneous influence of process parameters and presence of a wall on the deformation. Furthermore, the study examined the influence of printing parameters on activation time and activation temperature. The results indicated that increasing the pre-strain stored in the parts led to a decrease in activation time and activation temperature. Subsequently, the Taguchi design of experiment method was used to optimize the most influential parameters on the bending deformation. The difference between the optimal predicted and the experimental deformations was less than 2%. Layer thickness, layup, nozzle temperature, and printing speed were recognized as the most effective parameters for controlling deformation, respectively.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings can be shared on request from the authors.
References
Karayel E, Bozkurt Y (2020) Additive manufacturing method and different welding applications. J Mater Res Technol 9:11424–11438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.08.039
Ngo TD, Kashani A, Imbalzano G et al (2018) Additive manufacturing (3D printing): a review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos Part B Eng 143:172–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.02.012
Farazin A, Mohammadimehr M (2022) Effect of different parameters on the tensile properties of printed polylactic acid samples by FDM: experimental design tested with MDs simulation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 118:103–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07330-w
Standard A (2012) ISO/ASTM 52900: 2015 Additive manufacturing general principles-terminology. ASTM F2792–10e1:
Mahshid R, Isfahani MN, Heidari-Rarani M, Mirkhalaf M (2023) Recent advances in development of additively manufactured thermosets and fiber reinforced thermosetting composites: technologies, materials, and mechanical properties. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 171:107584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2023.107584
Heidari-Rarani M (2021) Residual stresses in additive manufacturing of polymers and polymer matrix composites. In: Residual Stresses in Composite Materials. Woodhead Publishing, pp 421–436
Heidari-Rarani M, Ezati N, Sadeghi P, Badrossamay MR (2022) Optimization of FDM process parameters for tensile properties of polylactic acid specimens using Taguchi design of experiment method. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 35:2435–2452. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705720964560
Candal MV, Calafel I, Fernández M et al (2021) Study of the interlayer adhesion and warping during material extrusion-based additive manufacturing of a carbon nanotube/biobased thermoplastic polyurethane nanocomposite. Polymer (Guildf) 224:123734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2021.123734
Rahmati A, Heidari-Rarani M, Lessard L (2021) A novel conservative failure model for the fused deposition modeling of polylactic acid specimens. Addit Manuf 48:102460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2021.102460
Ali MH, Abilgaziyev A, Adair D (2019) 4D printing: a critical review of current developments, and future prospects. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:701–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04258-0
Khalid MY, Arif ZU, Noroozi R et al (2022) 4D printing of shape memory polymer composites: a review on fabrication techniques, applications, and future perspectives. J Manuf Process 81:759–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.07.035
Kuang X, Roach DJ, Wu J et al (2019) Advances in 4D Printing: materials and applications. Adv Funct Mater 29:1805290. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201805290
Ding H, Zhang X, Liu Y, Ramakrishna S (2019) Review of mechanisms and deformation behaviors in 4D printing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:4633–4649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03871-3
Megdich A, Habibi M, Laperrière L (2023) A review on 4D printing: material structures, stimuli and additive manufacturing techniques. Mater Lett 337:133977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2023.133977
Qu H (2020) Additive manufacturing for bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Mater Today Commun 24:101024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101024
Momeni F, Mehdi Hassani NSM, Liu X, Ni J (2017) A review of 4D printing. Mater Des 122:42–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.02.068
Zawaski CE, Wilts EM, Chatham CA et al (2019) Tuning the material properties of a water-soluble ionic polymer using different counterions for material extrusion additive manufacturing. Polymer (Guildf) 176:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.06.005
Zhao W, Zhu J, Liu L et al (2023) A bio-inspired 3D metamaterials with chirality and anti-chirality topology fabricated by 4D printing. Int J Smart Nano Mater 14:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475411.2022.2120110
Pei E, Loh GH (2018) Technological considerations for 4D printing: an overview. Prog Addit Manuf 3:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-018-0047-1
Ansaripour A, Heidari-Rarani M, Mahshid R (2023) A review on 4D printing of polymers and polymer composites. J Sci Technol Compos 10:2147–2165. https://doi.org/10.22068/jstc.2023.1999336.1831
Khalid MY, Arif ZU, Ahmed W et al (2022) 4D printing: technological developments in robotics applications. Sensors Actuators A Phys 343:113670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2022.113670
Raina A, Haq MIU, Javaid M et al (2021) 4D printing for automotive industry applications. J Inst Eng Ser D 102:521–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-021-00284-z
Subeshan B, Baddam Y, Asmatulu E (2021) Current progress of 4D-printing technology. Prog Addit Manuf 6:495–516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-021-00182-6
Champeau M, Heinze DA, Viana TN et al (2020) 4D printing of hydrogels: a review. Adv Funct Mater 30:1910606. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201910606
Farid MI, Wu W, Liu X, Wang P (2021) Additive manufacturing landscape and materials perspective in 4D printing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 115:2973–2988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07233-w
Zeng C, Liu L, Du Y et al (2023) A shape-memory deployable subsystem with a large folding ratio in China’s Tianwen-1 Mars exploration mission. Engineering 28:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.01.005
Mehrpouya M, Vahabi H, Janbaz S et al (2021) 4D printing of shape memory polylactic acid (PLA). Polymer (Guildf) 230:124080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2021.124080
Alikarami N, Abrisham M, Huang X et al (2022) Compatibilization of PLA grafted maleic anhydrate through blending of thermoplastic starch (TPS) and nanoclay nanocomposites for the reduction of gas permeability. Int J Smart Nano Mater 13:130–151. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475411.2022.2051639
DeStefano V, Khan S, Tabada A (2020) Applications of PLA in modern medicine. Eng Regen 1:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engreg.2020.08.002
Shao L-H, Zhao B, Zhang Q et al (2020) 4D printing composite with electrically controlled local deformation. Extrem Mech Lett 39:100793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eml.2020.100793
Wu J, Zhao Z, Kuang X et al (2018) Reversible shape change structures by grayscale pattern 4D printing. Multifunct Mater 1:15002. https://doi.org/10.1088/2399-7532/aac322
Akbari S, Sakhaei AH, Kowsari K et al (2018) Enhanced multimaterial 4D printing with active hinges. Smart Mater Struct 27:65027. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/aabe63
Alshahrani HA (2021) Review of 4D printing materials and reinforced composites: behaviors, applications and challenges. J Sci Adv Mater Devices 6:167–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2021.03.006
Xin X, Liu L, Liu Y, Leng J (2020) 4D printing auxetic metamaterials with tunable, programmable, and reconfigurable mechanical properties. Adv Funct Mater 30:2004226. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202004226
Hu GF, Damanpack AR, Bodaghi M, Liao WH (2017) Increasing dimension of structures by 4D printing shape memory polymers via fused deposition modeling. Smart Mater Struct 26:125023. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/aa95ec
Bodaghi M, Noroozi R, Zolfagharian A et al (2019) 4D printing self-morphing structures. Materials (Basel) 12:1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081353
Van Manen T, Janbaz S, Zadpoor AA (2017) Programming 2D/3D shape-shifting with hobbyist 3D printers. Mater Horizons 4:1064–1069. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7mh00269f
Bodaghi M, Damanpack AR, Liao WH (2017) Adaptive metamaterials by functionally graded 4D printing. Mater Des 135:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.08.069
Kačergis L, Mitkus R, Sinapius M (2019) Influence of fused deposition modeling process parameters on the transformation of 4D printed morphing structures. Smart Mater Struct 28:105042. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/ab3d18
Yu Y, Liu H, Qian K et al (2020) Material characterization and precise finite element analysis of fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites for 4D printing. CAD Comput Aided Des 122:102817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2020.102817
Goo B, Hong CH, Park K (2020) 4D printing using anisotropic thermal deformation of 3D-printed thermoplastic parts. Mater Des 188:108485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108485
Tezerjani SMD, Yazdi MS, Hosseinzadeh MH (2022) The effect of 3D printing parameters on the shape memory properties of 4D printed polylactic acid circular disks: an experimental investigation and parameters optimization. Mater Today Commun 33:104262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104262
Alshebly YS, Nafea M, Mustapha KB, et al (2022) Variable stiffness 4D printing. Smart Mater Addit Manuf Vol 2 4D Print Mech Model Adv Eng Appl 407–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-95430-3.00015-4
Jamshidi M, Salimi Nezhad I, Golzar M, Behravesh AH (2021) Investigation of the effect of 3D printing parameters on shape-shifting of flat sturctures to three-dimensional shapes. J Sci Technol Compos 7:1271–1278. https://doi.org/10.22068/jstc.2021.141438.1693
Sun X, Mazur M, Cheng CT (2023) A review of void reduction strategies in material extrusion-based additive manufacturing. Addit Manuf 67:103463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2023.103463
Garzon-Hernandez S, Garcia-Gonzalez D, Jérusalem A, Arias A (2020) Design of FDM 3D printed polymers: an experimental-modelling methodology for the prediction of mechanical properties. Mater Des 188:108414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108414
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aref Ansaripour: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, software, and writing the original draft. Mohammad Heidari-Rarani: supervision, project administration, conceptualization, and writing—reviewing and editing. Rasoul Mahshid: writing—reviewing and editing, supervision, and methodology. Mahdi Bodaghi: writing—reviewing and editing and methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 18861 KB)
Supplementary file2 (MP4 20738 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ansaripour, A., Heidari-Rarani, M., Mahshid, R. et al. Influence of extrusion 4D printing parameters on the thermal shape-morphing behaviors of polylactic acid (PLA). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 132, 1827–1842 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13470-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13470-6