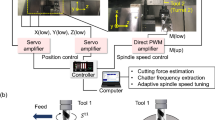
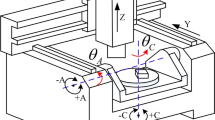
Abstract
Dynamic errors from the robotic machining process can negatively impact the accuracy of manufactured parts. Currently, effectively reducing dynamic errors in robotic machining remains a challenge due to the incomplete understanding of the relationship between machining parameters and dynamic errors, especially for hexapod machining cells. To address this topic, a dynamic error measurement strategy combining a telescoping ballbar, an unscented Kalman filter (UKF), and particle swarm optimization (PSO) was utilized in robotic machining. The machining parameters, including spindle speed, cutting depth, and feeding speed, were defined using the Taguchi method. Simultaneously, vibrations during machining were also systematically measured to fully comprehend the nature of dynamic errors. Experimental results indicate that dynamic errors in a hexapod machining cell (HMC) are significantly amplified in machining setups, ranging from 4 to 20 times greater compared to those of non-machining setups. These errors are particularly influenced by machining parameters, especially for spindle speed. Furthermore, the extracted dynamic errors exhibit comparable frequency distributions, such as spindle frequency and tool passing frequency, to the vibration signals obtained at the chosen sampling rate. This expands the application and enhances the comprehension of dynamic errors for spindle and cutting tool condition recognition.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- UKF:
-
Unscented Kalman filter
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- HMC:
-
Hexapod machining cell
- CD :
-
Circular deviation
- RD :
-
Radial deviation
- DE :
-
Dynamic error
- DTW :
-
Dynamic time warping
References
Kubela T, Pochyly A, Singule V (2016) Assessment of industrial robots accuracy in relation to accuracy improvement in machining processes. In: 2016 IEEE International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (PEMC), 25-28 Sept, pp 720-725. https://doi.org/10.1109/EPEPEMC.2016.7752083
Joshi K, Melkote SN, Anderson M et al (2021) Investigation of cycle time behavior in the robotic grinding process. CIRP Ann-Manuf Sci Technol 35:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2021.06.021
Pham MN, Champliaud H, Liu Z et al (2022) Parameterized finite element modeling and experimental modal testing for vibration analysis of an industrial hexapod for machining. Mech Mach Theory 167:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2021.104502
Schneider U, Drust M, Ansaloni M et al (2016) Improving robotic machining accuracy through experimental error investigation and modular compensation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85(1):3–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6021-2
Schneider U, Ansaloni M, Drust M et al (2013) Experimental Investigation of Sources of Error in Robot Machining. In: Neto P, Moreira AP (eds) Robotics in Smart Manufacturing. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 14–26
Zaghbani I, Songmene V (2009) Estimation of machine-tool dynamic parameters during machining operation through operational modal analysis. Int J Mach Tool Manufact 49(12):947–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2009.06.010
Ni J, Dai R, Yue X et al (2022) Contribution ratio assessment of process parameters on robotic milling performance. Materials 15 (10). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103566
Xu P, Gao Y, Yao X et al (2023) Influence of process parameters and robot postures on surface quality in robotic machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 124(7):2545–2561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10640-2
Guo M, Ye Y, Jiang X et al (2020) Comprehensive effect of multi-parameters on vibration in high-speed precision milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 108(7):2187–2195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05441-4
Hao D, Wang W, Liu Z et al (2019) Experimental study of stability prediction for high-speed robotic milling of aluminum. J Vib Control 26(7–8):387–398. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546319880376
Zhu Z, Tang X, Chen C et al (2022) High precision and efficiency robotic milling of complex parts: challenges, approaches and trends. Chin J Aeronaut 35(2):22–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2020.12.030
Lyu D, Liu Q, Liu H et al (2020) Dynamic error of CNC machine tools: a state-of-the-art review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106(5):1869–1891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04732-9
Qian D, Bi Q (2018) A dynamic machine tool circle test calibration method by R-test. MATEC Web of Conferences 249:02004. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201824902004
Chen D, Zhou S, Dong L et al (2016) An investigation into error source identification of machine tools based on time-frequency feature extraction. Shock Vib 2016:1040942. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1040942
Schmitz T, Ziegert J (2000) Dynamic evaluation of spatial CNC contouring accuracy. Precis Eng 24(2):99–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-6359(99)00034-3
Liu C, Xiang S, Lu C et al (2020) Dynamic and static error identification and separation method for three-axis CNC machine tools based on feature workpiece cutting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107(5):2227–2238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05103-5
Andolfatto L, Lavernhe S, Mayer JRR (2011) Evaluation of servo, geometric and dynamic error sources on five-axis high-speed machine tool. Int J Mach Tool Manufact 51(10):787–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2011.07.002
Elvira-Ortiz DA, Romero-Troncoso RdJ, Jaen-Cuellar AY et al (2016) Vibration suppression for improving the estimation of kinematic parameters on industrial robots. Shock Vib 2016:6954012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6954012
Rahimi MH, Huynh HN, Altintas Y (2021) On-line chatter detection in milling with hybrid machine learning and physics-based model. CIRP Ann-Manuf Sci Technol 35:25–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2021.05.006
Brecher C, Brozio M, Klatte M et al (2017) Application of an unscented Kalman filter for modeling multiple types of machine tool errors. Procedia CIRP 63:449–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.344
ISO 230-4:2005 (2005) Test code for machine tools. Circular tests for numerically controlled machine tools. ISO, Geneva
Fesperman RR, Moylan SP, Vogl GW et al (2015) Reconfigurable data driven virtual machine tool: geometric error modeling and evaluation. CIRP Ann-Manuf Sci Technol 10:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2015.03.001
Barnfather J, Goodfellow MJ, Abram T (2018) Achievable tolerances in robotic feature machining operations using a low-cost hexapod. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95(1):1421–1436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1266-1
Slamani M, Nubiola A, Bonev I (2012) Assessment of the positioning performance of an industrial robot. Ind Rob 39(1):57–68. https://doi.org/10.1108/01439911211192501
Urrea C, Agramonte R (2021) Kalman filter: historical overview and review of its use in robotics 60 years after its creation. J Sens 2021:9674015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9674015
Kwon Y, Huang S, Park Y (2011) Enhancing e-quality for manufacture using Kalman filter calibrated visual robotic control. Robot Comput Integrated Manuf 27(5):902–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2011.03.001
Nazarahari M, Rouhani H (2021) A full-state robust extended Kalman filter for orientation tracking during long-duration dynamic tasks using magnetic and inertial measurement units. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 29:1280–1289. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2021.3093006
Merwe Rvd, Wan E (2001) The square-root unscented Kalman filter for state and parameter-estimation. In: 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. Proceedings (Cat. No.01CH37221), 7–11 May 2001, vol 3466, pp 3461–3464. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2001.940586
Julier SJ (2002) The scaled unscented transformation. In: Proceedings of the 2002 American Control Conference 8–10 May 2002, pp 4555–4559. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACC.2002.1025369
Chatzis MN, Chatzi EN (2017) A discontinuous unscented Kalman filter for non-smooth dynamic problems. Front Built Environ 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbuil.2017.00056
Dowson DC, Landau BV (1982) The Fréchet distance between multivariate normal distributions. J Multivar Anal 12(3):450–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/0047-259X(82)90077-X
Kate RJ (2016) Using dynamic time warping distances as features for improved time series classification. Data Min Knowl Discov 30(2):283–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-015-0418-x
Zhang Y, Wang S, Ji G (2015) A comprehensive survey on particle swarm optimization algorithm and its applications. Math Probl Eng 2015:931256. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/931256
Lai X, Qin C, Gao W et al (2018) A state of charge estimator based extended Kalman filter using an electrochemistry-based equivalent circuit model for lithium-ion batteries. Appl Sci 8(9):1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091592
Jatoth RK, Rao DN, Kumar KS (2010) Particle swarm optimization aided unscented Kalman filter for ballistic target tracking. In: 2010 International Conference on Communication Control and Computing Technologies, pp 455–460. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCCT.2010.5670595
Xing K, Bonev IA, Liu Z, Champliaud H (2023) Ballbar applications for machining and non-machining setups in a hexapod-based machining cell. Progress in Canadian Mechanical Engineering 6:315. https://doi.org/10.17118/11143/21054
Grguras D, Kern M, Pusavec F (2019) Cutting performance of solid ceramic and carbide end milling tools in machining of nickel based alloy Inconel 718 and stainless steel 316L. Adv Prod Eng Manag 14(1):27–38. https://doi.org/10.14743/apem2019.1.309
Lv D, Wang Y, Yu X (2020) Effects of cutting edge radius on cutting force, tool wear, and life in milling of SUS-316L steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 111(9):2833–2844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06286-7
Tunc LT, Shaw J (2016) Investigation of the effects of Stewart platform-type industrial robot on stability of robotic milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(1):189–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8420-z
Payet M, Marchetti L, Tabarant M et al (2019) Corrosion mechanisms of 316L stainless steel in supercritical water: the significant effect of work hardening induced by surface finishes. Corros Sci 157:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2019.05.014
Sahoo DK, Nivas Chari A, Sivakrishna Reddy A (2020) Optimization & characterization of friction surfaced coatings of AA6063 aluminium alloy over AISI316 stainless steel substrate. Mater Today: Proceedings 23:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.05.410
Hajiahmadi S (2019) Burr size investigation in micro milling of stainless steel 316L. Int J Lightweight Mater Manuf 2(4):296–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijlmm.2019.07.004
Chai T, Draxler R (2014) Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)? – arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci Model Dev 7(3):1247–1250. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-7-1247-2014
Liao M, Jin R, Ren H et al (2022) Orthogonal experimental design for the optimization of four additives in a model liquid infant formula to improve its thermal stability. LWT 163:113495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113495
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Mr. Mario Corbin, Mr. Joël Grignon, and Dr. Xavier Rimpault for their technical assistance in preparing and manufacturing hardware and fixtures for this study.
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Fonds de recherche du Québec – Nature et technologies (FRQNT) postdoctoral research scholarship and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, K., Bonev, I.A., Liu, Z. et al. Influence of machining parameters on dynamic errors in a hexapod machining cell. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 131, 1317–1334 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-12968-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-12968-3